Secrets Store CSI driver for Kubernetes secrets - Integrates secrets stores with Kubernetes via a Container Storage Interface (CSI) volume.
The Secrets Store CSI driver secrets-store.csi.k8s.com allows Kubernetes to mount multiple secrets, keys, and certs stored in enterprise-grade external secrets stores into their pods as a volume. Once the Volume is attached, the data in it is mounted into the container's file system.
- Mounts secrets/keys/certs to pod using a CSI volume
- Supports CSI Inline volume (Kubernetes version v1.15+)
- Supports mounting multiple secrets store objects as a single volume
- Supports pod identity to restrict access with specific identities (WIP)
- Supports multiple secrets stores as providers
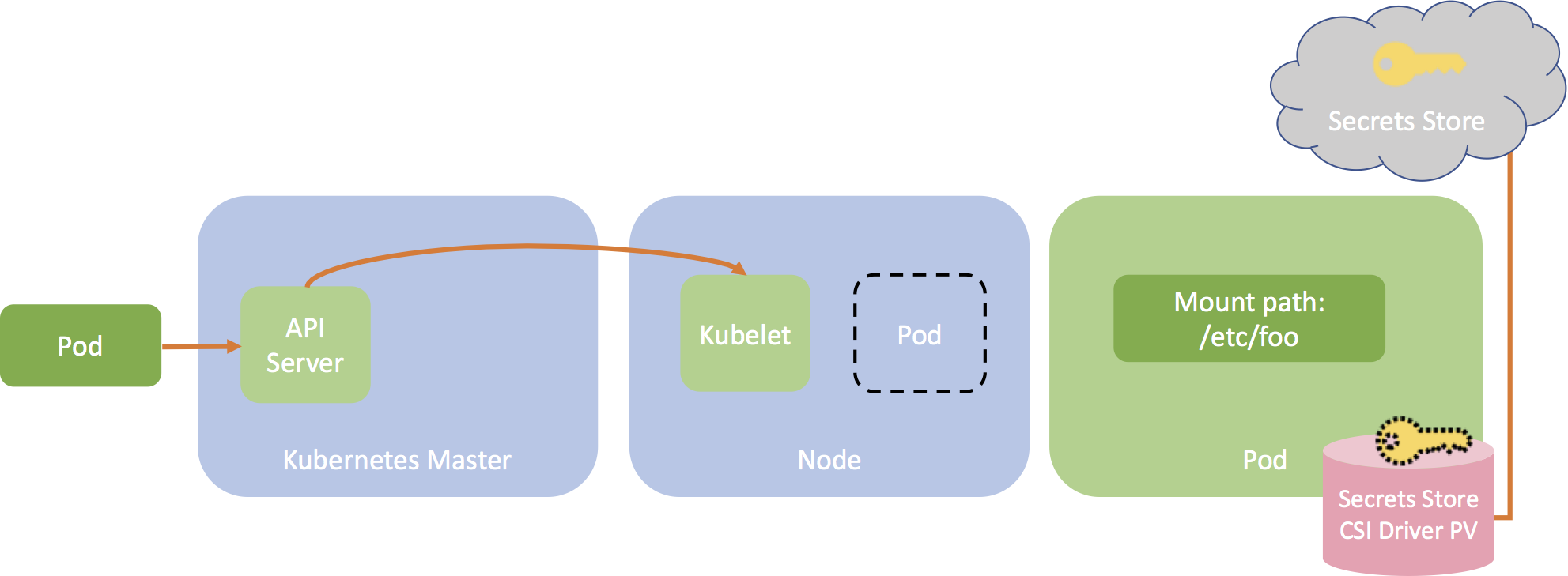
The diagram below illustrates how Secrets Store CSI Volume works.
- Deploy a Kubernetes cluster v1.15.0-alpha.2+ and make sure it's reachable. The CSI Inline Volume feature was introduced in v1.15.0.
- Update the API Server manifest to append the following feature gate:
--feature-gates=CSIInlineVolume=true- Update Kubelet manifest on each node to append the
CSIInlineVolumefeature gate:
--feature-gates=CSIInlineVolume=true[Optional] Mount Secret Data to Resource through PVC, not Inline
- If CSI Inline volume is not a requirement and creating PVs and PVCs is acceptable, then the minimum supported Kubernetes Version is v1.13.0.
Make sure you already have helm CLI installed.
$ cd charts/secrets-store-csi-driver
$ helm install . -n csi-secrets-store --namespace devExpected output:
NAME: csi-secrets-store
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Jan 7 18:39:41 2019
NAMESPACE: dev
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/RoleBinding
NAME AGE
csi-attacher-role-cfg 1s
==> v1/DaemonSet
csi-secrets-store-secrets-store-csi-driver 1s
==> v1/StatefulSet
csi-secrets-store-attacher 1s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
csi-secrets-store-attacher-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s
csi-secrets-store-secrets-store-csi-driver-9crwj 0/2 ContainerCreating 0 1s
csi-secrets-store-secrets-store-csi-driver-pcbtg 0/2 ContainerCreating 0 1s
==> v1beta1/CustomResourceDefinition
NAME AGE
csidrivers.csi.storage.k8s.io 1s
==> v1/ClusterRole
driver-registrar-runner 1s
external-attacher-runner 1s
==> v1/ClusterRoleBinding
csi-driver-registrar-role 1s
csi-attacher-role 1s
==> v1/Role
external-attacher-cfg 1s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
csi-driver-registrar 1s
csi-attacher 1s
==> v1/Service
csi-secrets-store-attacher 1s
NOTES:
The Secrets Store CSI Driver is getting deployed to your cluster.
To verify that Secrets Store CSI Driver has started, run:
kubectl --namespace=dev get pods -l "app=secrets-store-csi-driver"
Now you can follow these steps https://github.com/deislabs/secrets-store-csi-driver#use-the-secrets-store-csi-driver
to create a PersistentVolume, a static PVC, and a deployment using the PVC.
$ kubectl --namespace=dev get pods -l "app=secrets-store-csi-driver"
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
csi-secrets-store-attacher-0 1/1 Running 0 43s
csi-secrets-store-secrets-store-csi-driver-9crwj 2/2 Running 0 43s
csi-secrets-store-secrets-store-csi-driver-pcbtg 2/2 Running 0 43s
[ALTERNATIVE DEPLOYMENT OPTION] Using Deployment Yamls
kubectl apply -f deploy/crd-csi-driver-registry.yaml
kubectl apply -f deploy/rbac-csi-driver-registrar.yaml
kubectl apply -f deploy/rbac-csi-attacher.yaml
kubectl apply -f deploy/csi-secrets-store-attacher.yaml
kubectl apply -f deploy/secrets-store-csi-driver.yaml
kubectl apply -f deploy/csidriver.yamlTo validate the installer is running as expected, run the following commands:
kubectl get poYou should see the Secrets Store CSI driver pods running on each agent node:
csi-secrets-store-2c5ln 2/2 Running 0 4m
csi-secrets-store-attacher-0 1/1 Running 0 6m
csi-secrets-store-qp9r8 2/2 Running 0 4m
csi-secrets-store-zrjt2 2/2 Running 0 4m-
Select a provider from the list of supported providers
-
Update deployment of resource to add inline volume using the Secrets Store CSI driver, follow specific deployment steps for the selected provider to update all the required fields in this deployment yaml.
volumes:
- name: secrets-store-inline
csi:
driver: secrets-store.csi.k8s.com
readOnly: true
volumeAttributes:
providerName: "azure"
usePodIdentity: "false" # [OPTIONAL] if not provided, will default to "false"
keyvaultName: "" # the name of the KeyVault
objects: |
array:
- |
objectName: secret1
objectType: secret # object types: secret, key or cert
objectVersion: "" # [OPTIONAL] object versions, default to latest if empty
- |
objectName: key1
objectType: key
objectVersion: ""
resourceGroup: "" # the resource group of the KeyVault
subscriptionId: "" # the subscription ID of the KeyVault
tenantId: "" # the tenant ID of the KeyVault
nodePublishSecretRef:
name: secrets-store-creds
- Deploy your resource with the inline CSI volume
kubectl apply -f deploy/example/nginx-pod-secrets-store-inline-volume.yamlValidate the pod has access to the secret from your secrets store instance:
kubectl exec -it nginx-secrets-store-inline ls /mnt/secrets-store/
testsecret[Optional] Mount Secret Data to Resource through PVC, not Inline
- To create a Secrets Store CSI PersistentVolume, follow specific deployment steps for the selected provider to update all the required fields in this deployment yaml.
csi:
driver: secrets-store.csi.k8s.com
readOnly: true
volumeHandle: kv
volumeAttributes:
providerName: "azure"
...- Deploy your PersistentVolume (CSI Volume)
kubectl apply -f deploy/example/pv-secrets-store-csi.yaml- Deploy a static pvc pointing to your persistentvolume
kubectl apply -f deploy/example/pvc-secrets-store-csi-static.yaml- Fill in the missing pieces in this pod deployment yaml to create your own pod pointing to your PVC. Make sure to specify the mount point.
volumeMounts:
- name: secrets-store01
mountPath: "/mnt/secrets-store"Example of an nginx pod accessing a secret from a PV created by the Secrets Store CSI Driver:
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-secrets-store
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx-secrets-store
volumeMounts:
- name: secrets-store01
mountPath: "/mnt/secrets-store"
volumes:
- name: secrets-store01
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-secrets-store- Deploy your resource with PVC
kubectl apply -f deploy/example/nginx-pod-secrets-store.yamlValidate the pod has access to the secret from your secrets store instance:
kubectl exec -it nginx-secrets-store ls /mnt/secrets-store/
testsecretThis project features a pluggable provider interface developers can implement that defines the actions of the Secrets Store CSI driver.
This enables on-demand retrieval of sensitive objects storied an enterprise-grade external secrets store into Kubernetes while continue to manage these objects outside of Kubernetes.
Each provider may have its own required properties.
Providers must provide the following functionality to be considered a supported integration.
- Provides the backend plumbing necessary to access objects from the external secrets store.
- Conforms to the current API provided by the Secrets Store CSI Driver.
- Does not have access to the Kubernetes APIs and has a well-defined callback mechanism to mount objects to a target path.
- Supported Providers:
Create a new directory for your provider under providers and implement the following interface.
Then add your provider in providers/register/provider_<provider_name>.go. Make sure to add a build tag so that
your provider can be excluded from being built. The format for this build tag
should be no_<provider_name>_provider.
// Provider contains the methods required to implement a Secrets Store CSI Driver provider.
type Provider interface {
// MountSecretsStoreObjectContent mounts content of the secrets store object to target path
MountSecretsStoreObjectContent(ctx context.Context, attrib map[string]string, secrets map[string]string, targetPath string, permission os.FileMode) error
}Run unit tests locally with make test.
WIP
WIP