Docker Hub is a repository service and it is a cloud-based service where people push their Docker Container Images and also pull the Docker Container Images from the Docker Hub anytime or anywhere via the internet. It provides features such as you can push your images as private or public.
Mainly DevOps team uses the Docker Hub. It is an open-source tool and freely available for all operating systems. It is like storage where we store the images and pull the images when it is required. When a person wants to push/pull images from the Docker Hub they must have a basic knowledge of Docker. Let us discuss the requirements of the Docker tool.
Docker is a tool nowadays enterprises adopting rapidly day by day. When a Developer team wants to share the project with all dependencies for testing then the developer can push their code on Docker Hub with all dependencies. Firstly create the Images and push the Image on Docker Hub. After that, the testing team will pull the same image from the Docker Hub eliminating the need for any type of file, software, or plugins for running the Image because the Developer team shares the image with all dependencies.

Main Uses of Docker Hub
- Efficient Image Management: Docker Hub simplifies the storage, management, and sharing of Docker images, making it easy to organize and access container images from anywhere.
- Enhanced Security: It runs security checks on images and provides detailed reports on potential vulnerabilities, ensuring safer deployments.
- Automation Capabilities: With features like webhooks, Docker Hub can automate continuous deployment and testing processes, streamlining your CI/CD pipeline.
- Integration and Collaboration: Docker Hub integrates seamlessly with popular tools like GitHub and Jenkins, and allows managing permissions for users and teams, facilitating efficient collaboration.
Creating Repository in Docker Hub
The following steps guide you in creating a first repository in Dockerhub using GUI:
Step 1: Firstly navigate to the Dockerhub and sign in with your credentials and then select Create Repository.
-(1).webp)
Step 2: After that, we will be taken to a screen for configuring the repository, where we must choose the namespace, repository name, and optional description.
- In the visibility area, as indicated in the picture, there are two options: Public and Private. We can choose any of them depending on the type of organization you are in.
- If you chose Public, everyone will be able to push-pull and use the image because it will be accessible to everyone. If you select the private option, only those with access to that image can view and utilize it. it.
.webp)
Step 3: At finally repository is created with the help of the Docker Commands we can push or pull the image. The following command is used for pushing the docker image that exists in local to the Dockerhub.
docker push <your-username>/my-testprivate-repo>.
.webp)
Push Docker Images to Docker Hub
The push command as the name suggests itself is used to pushing a docker image onto the docker hub.Try to Follow this example to get an idea of the push command:
Step 1: Open Docker in your system. Locate the Images that you want to push using the below command:
docker images

The above command will list all the images on your system.
Step 2: Go to the browser and search hub.docker.com.
Step 3: Sign up on the docker hub if you do not have a docker hub account, after login on to docker hub.
Step 4: Back to the docker terminal and execute the below command:
docker login
Step 5: Then give your credential and type in your docker hub username or password.
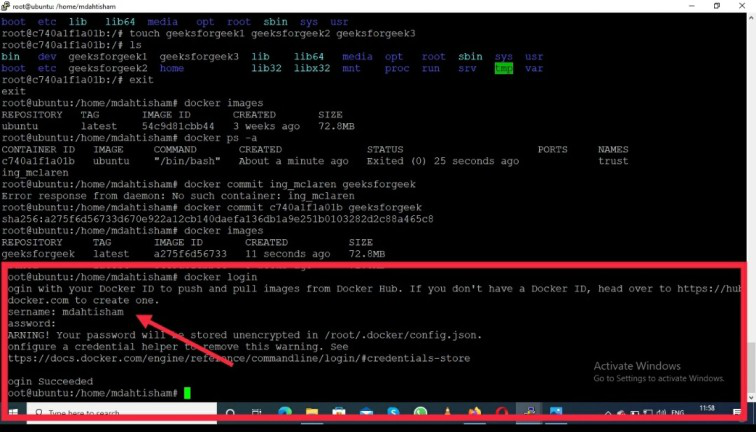
Step 6: After that hit the Enter key you will see login success on your screen.

Step 7: Then type the tag images name, docker hub username, and give the name it appears on the docker hub using the below command:
# docker tag geeksforgeek mdahtisham/geeksimage
geeksforgeek - Image name
mdahtisham - Docker hub username
geeksimage - With this name Image will appear on the docker hub
Step 8: Now push your image using the below command:
# docker push mdahtisham/geeksimage

Note: Below you can see the Docker Image successfully pushed on the docker hub: mdahtisham/geeksimage

Pull Docker Images From Docker Hub
The pull command is used to get an image from the Docker Hub to the local docker environment.Follow this example to get an overview of the pull command in Docker:
Step 1: Now you can search the image using the below command in docker as follows:
# docker search imagename
One can see all images on your screen if available images with this name.One can also pull the images if one knows the exact name
Step 2: Now pull the image see the below command.
# docker pull mdahtisham/geeksimage
mdahtisham - Docker Hub username
geeksimage - With this name Image will appear on the docker hub

Step 3: Now check for the pulled image in the local docker environment using the below command:
# docker images

Docker Hub Web Services
Docker Hub offers a variety of web services designed to help developers manage, collaborate, and deploy container images effectively. These features make Docker Hub a useful platform for developers to store, manage, and collaborate on containerized applications throughout the development and deployment process. Here’s a look at what it provides:
- Image Repositories: Docker Hub primarily serves as a registry where you can store and access container images. You have the option to create both public and private repositories, browse official images, and upload your custom images.
- Automated Builds: Docker Hub can link directly to code repositories like GitHub or Bitbucket to build images automatically. When you update your code, Docker Hub can build new images to keep everything in sync, making continuous deployment easier.
- Webhooks:Webhook integrations on Docker Hub allow you to trigger specific actions, such as deploying an image or sending notifications, whenever an image is updated. This can be useful for automating steps in CI/CD pipelines.
- Image Scanning: Docker Hub offers security scanning (for Pro and Team accounts), which checks images for known vulnerabilities. This provides insights into any security risks within your images.
- Team Collaboration: Docker Hub includes tools for managing users, teams, and permissions within an organization, making it easier for teams to share and control access to Docker images.
- Official and Verified Publisher Images: Docker Hub hosts trusted images from software vendors and the community. These verified and official images are reliable starting points for building applications.
- Activity Monitoring: Each repository on Docker Hub includes an activity log. It records when images are pushed, pulled, or updated, helping you keep track of who accessed or modified your images.
Difference Between Github and Docker Hub
The following are the difference between github and dockerhub:
| Feature | GitHub | Docker Hub |
|---|
| Primary Purpose | Code Repository and Version Control | Docker Image Repository and Management |
| Content | Source Code, Documentation | Docker Container Images |
| Integration | Works with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Travis CI | Integrates with CI/CD tools and Docker itself |
| Visibility | Public and Private Repositories | Public and Private Repositories |
| Security | Code scanning and vulnerability alerts | Image security scans and vulnerability reports |
Docker Hub Usage and Rate Limits
1. Understanding Docker Hub Usage
On Docker Hub, "usage" refers to both the data you store on the platform and the amount of data you transfer by pulling images. Regularly monitoring this usage can help you manage resources more effectively and avoid extra charges. Keeping an eye on usage is also a great way to ensure your CI/CD processes and development workflows run smoothly without interruptions.
2. Fair Use Policy
Docker Hub enforces a fair use policy to keep the platform running smoothly for everyone. This means if your account starts to use an unusually high amount of data, with excessive pull requests or storage, Docker Hub may temporarily slow down (throttle) your activity or impose restrictions. This is meant to prevent any single user from impacting the performance for others.
3. How to View and Track Usage?
Docker Hub makes it easy to keep tabs on your data usage:
- Get Usage Reports: Sign in to Docker Hub and head to the Usage page, where you can download a report of your usage in CSV format. You’ll need to select the date range, and Docker Hub will send the report to your email.
- Insights from Reports: Reviewing these reports regularly is a helpful way to see which repositories or accounts are using the most data, so you can make adjustments if necessary.
4. Tips for Optimizing Usage
To make the most of your Docker Hub account and manage data effectively:
- Monitor usage regularly: Check frequently to see which images or accounts are consuming the most data.
- Use local caching: To save bandwidth, consider caching images locally instead of repeatedly pulling the same image.
- Set up automation in CI/CD: Configure your CI/CD pipelines to pull images only when necessary, which helps you stay within rate limits.
- Perform regular clean-ups: Deleting outdated or unused images can free up storage and make your account easier to manage.
5. Pull Attribution
- Private Repositories: Any pulls from private repositories are counted toward the owner’s account.
- Public Repositories: Pulls for public repositories are attributed based on the user’s domain or organizational membership.
6. Docker Hub Rate Limits for Pulls
Depending on your account type, Docker Hub applies different pull limits:
Account Type | Pull Limit (Every 6 Hours) | Daily Pull Limit | Additional Options |
|---|
Anonymous Users | 100 pulls per IP | N/A | None |
|---|
Authenticated Users | 200 pulls per IP | N/A | None |
|---|
Paid Subscribers | Customizable | Up to 5,000 pulls | Add-ons available |
|---|
7. Checking Your Docker Hub Rate Limits
If you exceed your rate limits, Docker Hub will respond with a '429' status code, meaning you’ve hit the cap. You can also use API response headers to check where you stand with your current pull limit in real time, which helps you adjust if you’re nearing the threshold.
Authenticate Docker Hub Pull Requests
To authenticate pull requests on Docker Hub, follow the instructions specific to your platform:
1. Docker Desktop
- Launch Docker Desktop.
- Click on Sign in / Create Docker ID in the menu.
- Follow the prompts to log in.
2. Docker Engine
- Open your terminal.
- Enter the command 'docker login' to authenticate with Docker Hub. For details on using this command, check the Docker documentation.
3. Docker Swarm
If you're using Docker Swarm, add the '--with-registry-auth' flag to your command for authentication with Docker Hub.
- For additional guidance, refer to the section on creating a service in Docker's documentation.
- If deploying an application with a Docker Compose file, look up the instructions for 'docker stack deploy'.
4. GitHub Actions
- When using GitHub Actions to build and push images, refer to the documentation for the "login action".
- For other actions, make sure to include your username and access token to authenticate.
5. Kubernetes
- If you're in a Kubernetes setup, follow the guidelines on pulling images from a private registry for authentication steps.
For third-party services, check the specific instructions from your provider on how to authenticate with the Docker registry. Some examples include:
- Artifactory
- AWS CodeBuild
- AWS ECS/Fargate
- Azure Pipelines
- Chipper CI
- CircleCI
- Codefresh
- Drone.io
- GitLab
- LayerCI
- TeamCity
Difference Between Dockerhub and Docker Registry
The following are the differences between Dockerhub and Docker Registry:
| Feature | Docker Hub | Docker Registry |
|---|
| Service Type | Cloud-based repository service | Self-hosted registry service |
| Accessibility | Public and private image repositories | Primarily private, customizable |
| Integration | Integrates with GitHub, Jenkins, and more | Can be integrated with various CI/CD tools |
| Security | Built-in security scans and vulnerability reports | Security depends on implementation |
| Automation | Supports webhooks for CI/CD automation | Requires manual setup for automation |
Best Practices For Docker Hub Security
To enhance security and mitigate risks associated with container images on Docker Hub, consider implementing the following best practices:
1. Select the appropriate base image
- Source Trustworthiness: Opt for images from trusted sources. Docker Hub categorizes images by trust levels, with official images curated by Docker providing the highest assurance. Alternatively, use Docker Certified images, which have been validated against Docker’s standards, or Verified Publisher images.
- Minimize Size: Choose the smallest base image that fulfills your project requirements. Smaller images offer advantages such as faster downloads, reduced storage, and a minimized attack surface by limiting dependencies that could introduce vulnerabilities.
2. Utilize multi-stage builds
- Multi-stage builds enable you to create a streamlined and manageable Dockerfile. Each stage can utilize a different base image tailored for specific development tasks.
- By employing multiple 'FROM' statements, you can copy necessary artifacts, like compiled binaries, from one stage to another. This approach helps reduce complexity and keeps development tools out of production images, thus minimizing potential vulnerabilities.
3. Scan images during development
- Regularly scanning your Docker images throughout the development lifecycle is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities early. As you create or rebuild images, new vulnerabilities may be introduced, so it’s important to incorporate scanning into your workflow.
- Set up automated scans during the build process before images are pushed to Docker Hub or other registries. This ensures vulnerabilities are addressed proactively before deployment.
4. Scan images in production
- Continuously monitor your container images to identify newly discovered vulnerabilities. Relying solely on past scans can leave your production environment at risk, as vulnerabilities may emerge after your last review.
- Maintain a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) for each image to track dependencies. Be vigilant about alerts regarding new vulnerabilities affecting previously scanned images and take prompt action to remediate any issues before redeploying.
Advantages of Docker Hub
The following are the advantages of Docker hub:
- Docker Container Images are light in weight.
- We can push the images within a minute and with help of a command.
- It is a secure method and also provides a feature like pushing the private image or public image.
- Docker hub plays a very important role in industries as it becomes more popular day by day and it acts as a bridge between the developer team and the testing team.
- If a person wants to share their code, software any type of file for public use, you can just make the images public on the docker hub.
Features of Docker Hub
The following are the features of dockerhub:
- Storage, management, and sharing of images with others are made simple via Docker Hub.
- Docker Hub runs the necessary security checks on our images and generates a full report on any security flaws.
- Docker Hub can automate the processes like Continuous deployment and Continuous testing by triggering the Webhooks when the new image is pushed into Docker Hub.
- With the help of Docker Hub, we can manage the permission for the users, teams, and organizations.
- We can integrate Docker Hub into our tools like GitHub, Jenkins which makes workflows easy.
Similar Reads
What is Docker? Have you ever wondered about the reason for creating Docker Containers in the market? Before Docker, there was a big issue faced by most developers whenever they created any code that code was working on that developer computer, but when they try to run that particular code on the server, that code
12 min read
Introduction to Docker
Docker Installation
Docker - Installation on WindowsIn this article, we are going to see how to install Docker on Windows. On windows if you are not using operating system Windows 10 Pro then you will have to install our docker toolbox and here docker will be running inside a virtual machine and then we will interact with docker with a docker client
2 min read
How to Install Docker using Chocolatey on Windows?Installing Docker in Windows with just the CLI is quite easier than you would expect. It just requires a few commands. This article assumes you have chocolatey installed on your respective windows machine. If not, you can install chocolatey from here. Chocolatey is a package manager for the Windows
4 min read
How to Install and Configure Docker in Ubuntu?Docker is a platform and service-based product that uses OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages known as containers. Containers are separated from one another and bundle their software, libraries, and configuration files. Docker is written in the Go language. Docker can be installed
6 min read
How to Install Docker on MacOS?Pre-requisites: Docker-Desktop Docker Desktop is a native desktop application for Windows and Mac's users created by Docker. It is the most convenient way to launch, build, debug, and test containerized apps. Docker Desktop includes significant and helpful features such as quick edit-test cycles, fi
2 min read
How to install and configure Docker on Arch-based Linux Distributions(Manjaro) ?In this article, we are going to see how to install and configure Docker on Arch-based Linux Distributions. Docker is an open-source containerization platform used for building, running, and managing applications in an isolated environment. A container is isolated from another and bundles its softwa
2 min read
How to Install Docker-CE in Redhat 8?Docker is a tool designed to make it easier to create, deploy, and run applications by using containers. Containers allow a developer to package up an application with all the parts it needs, such as libraries and other dependencies, and deploy it as one package. Installing Docker-CE in Redhat 8: St
2 min read
Docker Commands
Docker Images
What is Docker Image?Docker Image is an executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an application. This image informs how a container should instantiate, determining which software components will run and how. Docker Container is a virtual environment that bundles application code with all the
10 min read
Working with Docker ImagesIf you are a Docker developer, you might have noticed that working with multiple Docker Images at the same time might be quite overwhelming sometimes. Managing numerous Docker Images all through a single command line is a very hefty task and consumes a lot of time. In this article, we are going to d
2 min read
Docker - Publishing Images to Docker HubDocker is a container platform that facilitates creating and managing containers. In this article, we will see how docker stores the docker images in some popular registries like Dockerhub and how to publish the Docker images to Docker Hub. By publishing the images to the docker hub and making it pu
8 min read
Docker CommitDocker is an open-source container management service and one of the most popular tools of DevOps which is being popular among the deployment team. Docker is mostly used in Agile-based projects which require continuous delivery of the software. The founder, Chief Technical Officer, and Chief Archite
10 min read
Docker - Using Image TagsImage tags are used to describe an image using simple labels and aliases. Tags can be the version of the project, features of the Image, or simply your name, pretty much anything that can describe the Image. It helps you manage the project's version and lets you keep track of the overall development
7 min read
Next.js Docker ImagesUsing Next.js Docker images allows your app to deploy to multiple environments, and is more portable, isolated and scalable in dev and prod. Docker’s containerization makes app management super easy, you can move from one stage to another with performance.Before we get started, let’s cover the basic
14 min read
How to Use Local Docker Images With Minikube?Minikube is a software that helps in the quick setup of a single-node Kubernetes cluster. It supports a Virtual Machine (VM) that runs over a docker container and creates a Kubernetes environment. Now minikube itself acts as an isolated container environment apart from the local docker environment,
7 min read
Docker Containers
Containerization using DockerDocker is the containerization platform that is used to package your application and all its dependencies together in the form of containers to make sure that your application works seamlessly in any environment which can be developed or tested or in production. Docker is a tool designed to make it
9 min read
Virtualisation with Docker ContainersIn a software-driven world where omnipresence and ease of deployment with minimum overheads are the major requirements, the cloud promptly takes its place in every picture. Containers are creating their mark in this vast expanse of cloud space with the world’s top technology and IT establishments re
8 min read
Docker - Docker Container for Node.jsNode.js is an open-source, asynchronous event-driven JavaScript runtime that is used to run JavaScript applications. It is widely used for traditional websites and as API servers. At the same time, a Docker container is an isolated, deployable unit that packages an application along with its depende
12 min read
Docker - Remove All Containers and ImagesIn Docker, if we have exited a container without stopping it, we need to manually stop it as it has not stopped on exit. Similarly, for images, we need to delete them from top to bottom as some containers or images might be dependent on the base images. We can download the base image at any time. So
10 min read
How to Push a Container Image to a Docker Repository?In this article we will look into how you can push a container image to a Docker Repository. We're going to use Docker Hub as a container registry, that we're going to push our Docker image to. Follow the below steps to push container Image to Docker repository:Step 1: Create a Docker Account The f
3 min read
Docker - Container LinkingDocker is a set of platforms as a service (PaaS) products that use the Operating system level visualization to deliver software in packages called containers.There are times during the development of our application when we need two containers to be able to communicate with each other. It might be p
4 min read
How to Manage Docker Containers?Before virtualization, the management of web servers and web applications was tedious and much less effective. Thanks to virtualization, this task has been made much easier. This was followed by containerization which took it a notch higher. For network engineers, learning the basics of virtualizati
13 min read
Mounting a Volume Inside Docker ContainerWhen you are working on a micro-service architecture using Docker containers, you create multiple Docker containers to create and test different components of your application. Now, some of those components might require sharing files and directories. If you copy the same files in all the containers
10 min read
Difference between Docker Image and ContainerPre-requisite: Docker Docker builds images and runs containers by using the docker engine on the host machine. Docker containers consist of all the dependencies and software needed to run an application in different environments. What is Docker Image?The concept of Image and Container is like class
5 min read
Difference between Virtual Machines and ContainersVirtual machines and Containers are two ways of deploying multiple, isolated services on a single platform. Virtual Machine:It runs on top of an emulating software called the hypervisor which sits between the hardware and the virtual machine. The hypervisor is the key to enabling virtualization. It
2 min read
How to Install Linux Packages Inside a Docker Container?Once you understand how to pull base Docker Images from the Docker registry, you can now simply pull OS distributions such as Ubuntu, CentOS, etc directly from the Docker hub. However, the OS Image that you have pulled simply contains a raw file system without any packages installed inside it. When
2 min read
Copying Files to and from Docker ContainersWhile working on a Docker project, you might require copying files to and from Docker Containers and your Local Machine. Once you have built the Docker Image with a particular Docker build context, building it again and again just to add small files or folders inside the Container might be expensive
9 min read
How to Run MongoDB as a Docker Container?MongoDB is an open-source document-oriented database designed to store a large scale of data and allows you to work with that data very efficiently. It is categorized under the NoSQL (Not only SQL) database because the storage and retrieval of data in MongoDB are not in the form of tables. In this
4 min read
Docker - Docker Container for Node.jsNode.js is an open-source, asynchronous event-driven JavaScript runtime that is used to run JavaScript applications. It is widely used for traditional websites and as API servers. At the same time, a Docker container is an isolated, deployable unit that packages an application along with its depende
12 min read
Docker - Container for NGINXDocker is an open-source platform that enables developers to easily develop, ship, and run applications. It packages an application along with its dependencies in an isolated virtual container which usually runs on a Linux system and is quite light compared to a virtual machine. The reason is that a
11 min read
How to Provide the Static IP to a Docker Container?Docker is an open-source project that makes it easier to create, deploy and run applications. It provides a lightweight environment to run your applications.It is a tool that makes an isolated environment inside your computer. Think of Docker as your private room in your house. Living with your fami
2 min read
Docker Compose
Docker Swarm
Docker Networking
Docker NetworkingPre-requisite: Docker Docker Networking allows you to create a Network of Docker Containers managed by a master node called the manager. Containers inside the Docker Network can talk to each other by sharing packets of information. In this article, we will discuss some basic commands that would help
5 min read
Docker - Managing PortsPre-requisites: Docker Docker is a set of platform-as-a-service products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. These containers may need to talk to each other or to services outside docker, for this we not only need to run the image but also expose the c
4 min read
Creating a Network in Docker and Connecting a Container to That NetworkNetworks are created so that the devices which are inside that network can connect to each other and transfer of files can take place. In docker also we can create a network and can create a container and connect to the respective network and two containers that are connected to the same network can
2 min read
Connecting Two Docker Containers Over the Same NetworkWhenever we expose a container's port in docker, it creates a network path from the outside of that machine, through the networking layer, and enters that container. In this way, other containers can connect to it by going out to the host, turning around, and coming back in along that path.Docker of
3 min read
How to use Docker Default Bridge Networking?Docker allows you to create dedicated channels between multiple Docker Containers to create a network of Containers that can share files and other resources. This is called Docker Networking. You can create Docker Networks with various kinds of Network Drivers which include Bridge drivers, McVLAN dr
7 min read
Create your own secure Home Network using Pi-hole and DockerPi-hole is a Linux based web application, which is used as a shield from the unwanted advertisement in your network and also block the internet tracking system. This is very simple to use and best for home and small office networks. This is totally free and open-source. It also allows you to manage
3 min read
Docker Registry