Data Structure Types, Classifications and Applications
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
A data structure is a storage that is used to store and organize data. It is a way of arranging data on a computer so that it can be accessed and updated efficiently.
A data structure organizes, processes, retrieves, and stores data, making it essential for nearly every program or software system. To help you master them, we've compiled a comprehensive guide covering types, classifications, and applications of data structures. This article simplifies everything, helping you choose the right one in minutes.
Classification of Data Structure
Data structure has many different uses in our daily life. There are many different data structures that are used to solve different mathematical and logical problems. By using data structure, one can organize and process a very large amount of data in a relatively short period. Let's look at different data structures that are used in different situations.
 Classification of Data Structure
Classification of Data Structure- Linear data structure: Data structure in which data elements are arranged sequentially or linearly, where each element is attached to its previous and next adjacent elements, is called a linear data structure.
Examples: array, stack, queue, linked list, etc.- Static data structure: Static data structure has a fixed memory size. It is easier to access the elements in a static data structure.
Example: array data structure. - Dynamic data structure: In the dynamic data structure, the size is not fixed. It can be randomly updated during the runtime which may be considered efficient concerning the memory (space) complexity of the code.
Examples: stack and queue data structures.
- Non-linear data structure: Data structures where data elements are not placed sequentially or linearly are called non-linear data structures. In a non-linear data structure, we can't traverse all the elements in a single run.
Examples: tree and graph data structures.
Arrays Data Structure
An array is a linear data structure and it is a collection of element of same data type stored at contiguous memory locations.
It offers mainly the following advantages.
- Random Access: i-th elements can be accessed in O(1) Time as we have the base address and every element is of same size.
- Cache Friendliness: Since elements are stored at contiguous locations, we get the advantage of locality of reference.
 Array
Array Different applications of an array are as follows:
Arrays efficiently manage and store database records.
- It helps in implementing sorting algorithm.
- It is also used to implement other data structures like Stacks, Queues, Heaps, Hash tables, etc.
- An array can be used for CPU scheduling.
Want to get started with arrays? You can try out our curated articles and lists for the best practice:
Linked list Data Structure
A linked list is a linear data structure in which elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image.
 Linked List
Linked ListApplications of the Linked list
- Linked lists are used to implement other data structures like stacks, queues, etc.
- It is used for the representation of sparse matrices.
- It is used in the linked allocation of files.
- Linked lists are used to display image containers. Users can visit past, current, and next images.
- They are used to perform undo operations.
Want to get started with a linked list? You can try out our curated articles and lists for the best practice:
Stack Data Structure
Stack is a linear data structure that follows LIFO(Last in first out) principle i.e., entering and retrieving data is possible from only one end. The entering and retrieving of data is also called push and pop operation in a stack.
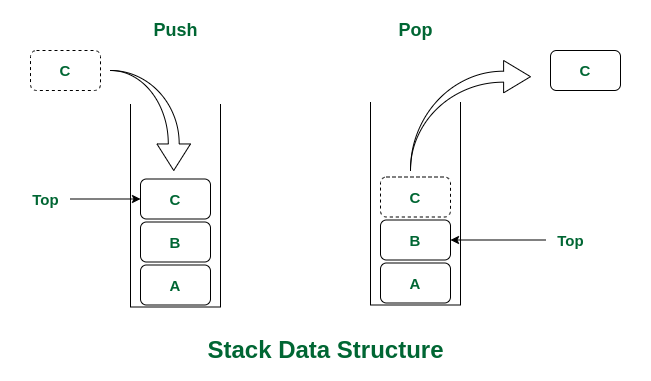 Stack
StackApplications of Stack
Different applications of Stack are as follows:
Want to get started with Stack? You can try out our curated articles and lists for the best practice:
Queue Data Structure
Queue is a linear data structure that follows First In First Out(FIFO) principle i.e. the data item stored first will be accessed first. In this, entering is done from one end and retrieving data is done from other end. An example of a queue is any queue of consumers for a resource where the consumer that came first is served first.
 Queue
QueueApplications of Queue:
Different applications of Queue are as follows:
- Queue is used for handling website traffic.
- It helps to maintain the playlist in media players.
- It helps in serving requests on a single shared resource, like a printer, CPU task scheduling, etc.
- Queues are used for job scheduling in the operating system.
Want to get started with Queue? You can try out our curated articles and lists for the best practice:
Tree Data Structure
A tree is a non-linear and hierarchical data structure where the elements are arranged in a tree-like structure. In a tree, the topmost node is called the root node. Each node contains some data, and data can be of any type. It consists of a central node, structural nodes, and sub-nodes which are connected via edges. Different tree data structures allow quicker and easier access to the data as it is a non-linear data structure.
 Tree
TreeApplications of Tree:
- Heap is a tree data structure that is implemented using arrays and used to implement priority queues.
- B-Tree and B+ Tree are used to implement indexing in databases.
- Syntax Tree helps in scanning, parsing, generation of code, and evaluation of arithmetic expressions in Compiler design.
- Spanning trees are used in routers in computer networks.
- Domain Name Server also uses a tree data structure.
Want to get started with Tree? You can try out our curated articles and lists for the best practice:
Binary Search Tree Data Structure
A Binary Search Tree (or BST) is a data structure used for organizing and storing data in a sorted manner. Each node in a Binary Search Tree has at most two children, a left child and a right child, with the left child containing values less than the parent node and the right child containing values greater than the parent node. This hierarchical structure allows for efficient searching, insertion, and deletion operations on the data stored in the tree.

Applications of Binary Search Tree:
- A Self-Balancing BST maintains a sorted stream of data in RAM, useful for tracking online orders by price and querying item counts above or below a given cost.
- It enables a doubly-ended priority queue, supporting both extractMin() and extractMax() in O(log n) time, unlike a Binary Heap.
- Many algorithmic problems, like counting smaller elements on the right or finding the smallest greater element, benefit from a Self-Balancing BST.
- TreeMap and TreeSet in Java, and set and map in C++, are implemented using Red-Black Trees, a type of Self-Balancing BST.
Want to get started with BST? You can try out our curated articles and lists for the best practice:
Graph Data Structure
A graph is a non-linear data structure that consists of vertices (or nodes) and edges. It consists of a finite set of vertices and set of edges that connect a pair of nodes. The graph is used to solve the most challenging and complex programming problems. It has different terminologies which are Path, Degree, Adjacent vertices, Connected components, etc.
 Graph
GraphApplications of Graph:
- The operating system uses Resource Allocation Graph.
- Also used in the World Wide Web where the web pages represent the nodes.
- One of the most common real-world examples of a graph is Google Maps where cities are located as vertices and paths connecting those vertices are located as edges of the graph.
- A social network is also one real-world example of a graph where every person on the network is a node, and all of their friendships on the network are the edges of the graph.
Want to get started with Graph? You can try out our curated articles and lists for the best practice:
Please refer Advanced Data Structure for more advanced data structures.
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem