Traversal of Binary Search Tree in downward direction from a specific node
Last Updated :
18 Apr, 2023
Given a Binary Search Tree with unique node values and a target value. Find the node whose data is equal to the target and return all the descendant (of the target) node's data which are vertically below the target node. Initially, you are at the root node.
Note: If the target node is not present in bst then return -1. And, if No descendant node is present return -1.
Examples:
Input: Target Node = 65
 Binary Search Tree (1.1)
Binary Search Tree (1.1)
Output: 40, 48, 46
Explanation:
 Binary Search Tree (1.2)
Binary Search Tree (1.2)
Input: Target Node: 98
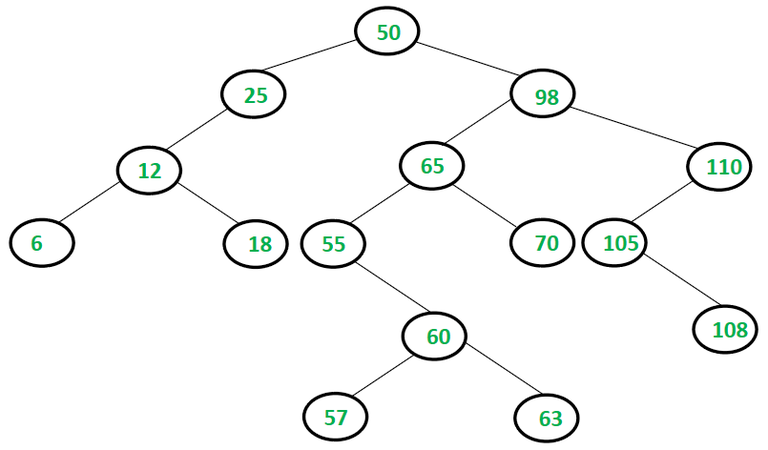 Binary Search Tree (2.1)
Binary Search Tree (2.1)
Output: 70 63 105
Explanation:
 Binary Search Tree (2.2)
Binary Search Tree (2.2)
Approach: This can be solved with the following idea:
The main idea of the code is to traverse a Binary Search Tree in a manner such that, when we encounter a node when level value becomes zero then we print that node as output. To achieve this, the code uses a recursive function called "downTraverse" which takes a target node and a level as input. When the function encounters a node when level value is zero then, it prints the node's value as output. We keeps track of how many nodes have been printed as output using a variable called "node".
Steps involved in the implementation of code:
- Firstly, Traverse the Binary Search Tree normally and Find the target node.
- If the target node is found, the program calls the downTraverse function and recursively traverses the left subtree and right subtree. If the target node is not found, the program prints an error message.
- downTraverse function recursively traverses the tree down from the target node, printing out the values of any nodes that are on the same vertical line as the target node.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to Traverse vertically
// downward in Binary Search Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Variable for keep track of the nodes
// that are exactly below
// to the target node
int node = 0;
// Binary Search Tree has info, pointer to
// left child and a pointer to right child
struct Tree {
struct Tree *left, *right;
int info;
};
typedef struct Tree Tree;
// Function to Insert a node in BST
Tree* INSERT(Tree* T, int x)
{
Tree* temp;
if (T == NULL) {
T = (Tree*)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
T->left = T->right = NULL;
T->info = x;
return T;
}
else if ((T->info) > x) {
(T->left) = INSERT((T->left), x);
}
else if ((T->info) <= x) {
(T->right) = INSERT((T->right), x);
}
return T;
}
// Function to find the address
// of the target node
Tree* FindNode(Tree* root, int target)
{
if (root == NULL || (root->info) == target)
return root;
else if (target > (root->info))
return (FindNode(root->right, target));
else
return (FindNode(root->left, target));
}
// Function to Traverse Vertically
// Downward in BST
void downTraverse(Tree* target, int level)
{
if (target == NULL) {
return;
}
else if (level == 0) {
if (node != 0)
cout << (target->info) << "\n";
node++;
}
downTraverse(target->left, level - 1);
downTraverse(target->right, level + 1);
if (node == 0)
cout << "No nodes have been found that are "
"vertically downward from the target "
"node.\n";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int x, target;
Tree *root = NULL, *targetNode = NULL;
root = INSERT(root, 65);
INSERT(root, 23);
INSERT(root, 17);
INSERT(root, 40);
INSERT(root, 20);
INSERT(root, 50);
INSERT(root, 48);
INSERT(root, 43);
INSERT(root, 46);
INSERT(root, 45);
INSERT(root, 47);
INSERT(root, 85);
INSERT(root, 93);
// Finding the target node
// with value 65
targetNode = FindNode(root, 65);
// Confirming that BST contains
// the target node or not
if (targetNode == NULL) {
cout << "-1";
}
else {
downTraverse(targetNode, 0);
}
return 0;
}
// Java program to Traverse vertically downward in Binary
// Search Tree
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Binary Search Tree has info, pointer to left child and a
// pointer to right child
class Tree {
Tree left, right;
int info;
}
class GFG {
// Variable for keep track of the nodes that are exactly
// below to the target node
static int node = 0;
// Function to Insert a node in BST
static Tree INSERT(Tree T, int x)
{
if (T == null) {
T = new Tree();
T.left = null;
T.right = null;
T.info = x;
return T;
}
else if (T.info > x) {
T.left = INSERT(T.left, x);
}
else if (T.info <= x) {
T.right = INSERT(T.right, x);
}
return T;
}
// Function to find the address of the target node
static Tree FindNode(Tree root, int target)
{
if (root == null || root.info == target)
return root;
else if (target > root.info)
return FindNode(root.right, target);
else
return FindNode(root.left, target);
}
// Function to Traverse Vertically Downward in BST
static void downTraverse(Tree target, int level)
{
if (target == null) {
return;
}
else if (level == 0) {
if (node != 0)
System.out.println(target.info);
node++;
}
downTraverse(target.left, level - 1);
downTraverse(target.right, level + 1);
if (node == 0)
System.out.println(
"No nodes have been found that are "
+ "vertically downward from the target "
+ "node.");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x, target;
Tree root = null, targetNode = null;
root = INSERT(root, 65);
INSERT(root, 23);
INSERT(root, 17);
INSERT(root, 40);
INSERT(root, 20);
INSERT(root, 50);
INSERT(root, 48);
INSERT(root, 43);
INSERT(root, 46);
INSERT(root, 45);
INSERT(root, 47);
INSERT(root, 85);
INSERT(root, 93);
// Finding the target node with value 65
targetNode = FindNode(root, 65);
// Confirming that BST contains the target node or
// not
if (targetNode == null) {
System.out.println("-1");
}
else {
downTraverse(targetNode, 0);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by karthik.
# Python program to Traverse vertically
# downward in Binary Search Tree
# Variable for keep track of the nodes
# that are exactly below
# to the target node
node = 0
# Binary Search Tree has info, pointer to
# left child and a pointer to right child
class Tree:
def __init__(self):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.info = None
# Function to Insert a node in BST
def INSERT(T, x):
if T == None:
T = Tree()
T.left = T.right = None
T.info = x
return T
elif (T.info) > x:
T.left = INSERT(T.left, x)
elif (T.info) <= x:
T.right = INSERT(T.right, x)
return T
# Function to find the address
# of the target node
def FindNode(root, target):
if root == None or (root.info) == target:
return root
elif target > (root.info):
return FindNode(root.right, target)
else:
return FindNode(root.left, target)
# Function to Traverse Vertically
# Downward in BST
def downTraverse(target, level):
global node
if target == None:
return
elif level == 0:
if node != 0:
print(target.info)
node += 1
downTraverse(target.left, level - 1)
downTraverse(target.right, level + 1)
if node == 0:
print("No nodes have been found that are vertically downward from the target node.")
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
x, target = 0, 0
root, targetNode = None, None
root = INSERT(root, 65)
INSERT(root, 23)
INSERT(root, 17)
INSERT(root, 40)
INSERT(root, 20)
INSERT(root, 50)
INSERT(root, 48)
INSERT(root, 43)
INSERT(root, 46)
INSERT(root, 45)
INSERT(root, 47)
INSERT(root, 85)
INSERT(root, 93)
# Finding the target node
# with value 65
targetNode = FindNode(root, 65)
# Confirming that BST contains
# the target node or not
if targetNode == None:
print("-1")
else:
downTraverse(targetNode, 0)
// C# program to Traverse vertically downward in Binary
// Search Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Binary Search Tree has info, pointer to left child and a
// pointer to right child
class Tree {
public Tree left, right;
public int info;
}
public class GFG {
// Variable for keep track of the nodes that are exactly
// below to the target node
static int node = 0;
// Function to Insert a node in BST
static Tree INSERT(Tree T, int x)
{
if (T == null) {
T = new Tree();
T.left = null;
T.right = null;
T.info = x;
return T;
}
else if (T.info > x) {
T.left = INSERT(T.left, x);
}
else if (T.info <= x) {
T.right = INSERT(T.right, x);
}
return T;
}
// Function to find the address of the target node
static Tree FindNode(Tree root, int target)
{
if (root == null || root.info == target)
return root;
else if (target > root.info)
return FindNode(root.right, target);
else
return FindNode(root.left, target);
}
// Function to Traverse Vertically Downward in BST
static void downTraverse(Tree target, int level)
{
if (target == null) {
return;
}
else if (level == 0) {
if (node != 0)
Console.WriteLine(target.info);
node++;
}
downTraverse(target.left, level - 1);
downTraverse(target.right, level + 1);
if (node == 0)
Console.WriteLine(
"No nodes have been found that are "
+ "vertically downward from the target "
+ "node.");
}
static public void Main()
{
// Code
int x, target;
Tree root = null, targetNode = null;
root = INSERT(root, 65);
INSERT(root, 23);
INSERT(root, 17);
INSERT(root, 40);
INSERT(root, 20);
INSERT(root, 50);
INSERT(root, 48);
INSERT(root, 43);
INSERT(root, 46);
INSERT(root, 45);
INSERT(root, 47);
INSERT(root, 85);
INSERT(root, 93);
// Finding the target node with value 65
targetNode = FindNode(root, 65);
// Confirming that BST contains the target node or
// not
if (targetNode == null) {
Console.WriteLine("-1");
}
else {
downTraverse(targetNode, 0);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by lokesh.
// JavaScript program to Traverse vertically downward in Binary
// Search Tree
// Binary Search Tree has info, pointer to left child and a
// pointer to right child
class Tree {
constructor() {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.info = 0;
}
}
// Variable for keep track of the nodes that are exactly
// below to the target node
let node = 0;
// Function to Insert a node in BST
function INSERT(T, x) {
if (T === null) {
T = new Tree();
T.left = null;
T.right = null;
T.info = x;
return T;
} else if (T.info > x) {
T.left = INSERT(T.left, x);
} else if (T.info <= x) {
T.right = INSERT(T.right, x);
}
return T;
}
// Function to find the address of the target node
function FindNode(root, target) {
if (root === null || root.info === target) return root;
else if (target > root.info) return FindNode(root.right, target);
else return FindNode(root.left, target);
}
// Function to Traverse Vertically Downward in BST
function downTraverse(target, level) {
if (target === null) {
return;
} else if (level === 0) {
if (node !== 0) console.log(target.info);
node++;
}
downTraverse(target.left, level - 1);
downTraverse(target.right, level + 1);
if (node === 0)
console.log(
"No nodes have been found that are " +
"vertically downward from the target " +
"node."
);
}
// Code
let x, target;
let root = null,
targetNode = null;
root = INSERT(root, 65);
INSERT(root, 23);
INSERT(root, 17);
INSERT(root, 40);
INSERT(root, 20);
INSERT(root, 50);
INSERT(root, 48);
INSERT(root, 43);
INSERT(root, 46);
INSERT(root, 45);
INSERT(root, 47);
INSERT(root, 85);
INSERT(root, 93);
// Finding the target node with value 65
targetNode = FindNode(root, 65);
// Confirming that BST contains the target node or not
if (targetNode === null) {
console.log("-1");
} else {
downTraverse(targetNode, 0);
}
Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of nodes
Auxiliary Space: O(H)
Similar Reads
Sum of Descendant Nodes Below Target in Binary Search Tree Given a Binary Search Tree with unique node values and a target value. You have to find the node whose data is equal to the target and return the sum of all descendant (of target) node's data which are vertically below the target node. Initially, you are at the root node. Note: If the target node is
12 min read
Middle To Up-Down Order traversal of a Binary Tree Given a binary tree, the task is to traverse this binary tree from the middle to the up-down order. In Middle to up-down order traversal, the following steps are performed: First, print the middle level of the tree.Then, print the elements at one level above the middle level of the tree.Then, print
15+ min read
Find parent of given node in a Binary Tree with given postorder traversal Given two integers N and K where N denotes the height of a binary tree, the task is to find the parent of the node with value K in a binary tree whose postorder traversal is first 2^{N}-1 natural numbers (1, 2, ... 2^{N}-1) For N = 3, the Tree will be - 7 / \ 3 6 / \ / \ 1 2 4 5 Examples: Input: N =
9 min read
Find the kth node in vertical order traversal of a Binary Tree Given a binary tree and an integer k, the task is to return the kth node in the vertical order traversal of a binary tree. If no such node exists then return -1.The vertical order traversal of a binary tree means to print it vertically.Examples: Input: k = 3Output: 1Explanation: The below image show
9 min read
Binary Search Tree (BST) Traversals – Inorder, Preorder, Post Order Given a Binary Search Tree, The task is to print the elements in inorder, preorder, and postorder traversal of the Binary Search Tree. Input: A Binary Search TreeOutput: Inorder Traversal: 10 20 30 100 150 200 300Preorder Traversal: 100 20 10 30 200 150 300Postorder Traversal: 10 30 20 150 300 200 1
10 min read