A trigger is a special stored procedure in a database that automatically executes when specific events (like INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE) occur on a table. Triggers help automate tasks, maintain data consistency, and record database activities. Each trigger is tied to a particular table and runs without manual execution.
Example: Automatically Track When a User Record Is Updated
Step 1: Create Main Table
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100),
updated_at TIMESTAMP
);
Step 2: Create Trigger
This trigger automatically updates the updated_at field whenever the user record is modified.
CREATE TRIGGER update_timestamp
BEFORE UPDATE ON users
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
SET NEW.updated_at = CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
END;
Step 3: Insert Sample Data
INSERT INTO users (id, name, email) VALUES (1, 'Amit', '[email protected]');
Output
Step 4: Update a Record
UPDATE users SET email = '[email protected]' WHERE id = 1;
| id | name | email | updated_at |
|---|
| 1 | Amit | [email protected] | 2025-10-27 12:45:23 (current timestamp auto-updated) |
Syntax:
create trigger [trigger_name]
[before | after]
{insert | update | delete}
on [table_name]
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
END;
In this explanation:
- trigger_name: The name of the trigger to be created
- BEFORE | AFTER: Specifies whether the trigger is fired before or after the triggering event (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
- {INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE}: Specifies the operation that will activate the trigger.
- table_name: The name of the table the trigger is associated with.
- FOR EACH ROW: Indicates that the trigger is row-level, meaning it executes once for each affected row.
- trigger_body: The SQL statements to be executed when the trigger is fired.
Types of SQL Triggers
Triggers can be categorized into different types based on the action they are associated with:

1. DDL Triggers
The Data Definition Language (DDL) command events such as Create_table, Create_view, drop_table, Drop_view, and Alter_table cause the DDL triggers to be activated. They allow us to track changes in the structure of the database. The trigger will prevent any table creation, alteration, or deletion in the database.
Example: Prevent Table Deletions
CREATE TRIGGER prevent_table_creation
ON DATABASE
FOR CREATE_TABLE, ALTER_TABLE, DROP_TABLE
AS
BEGIN
PRINT 'you can not create, drop and alter table in this database';
ROLLBACK;
END;
Output:

2. DML Triggers
DML triggers fire when we manipulate data with commands like INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. These triggers are perfect for scenarios where we need to validate data before it is inserted, log changes to a table, or cascade updates across related tables.
Example: Prevent Unauthorized Updates Let’s say you want to prevent users from updating the data in a sensitive students table. We can set up a trigger to handle that:
CREATE TRIGGER prevent_update
ON students
FOR UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE
AS
BEGIN
RAISERROR ('You can not insert, update and delete rows in this table.', 16, 1);
END;
Output:
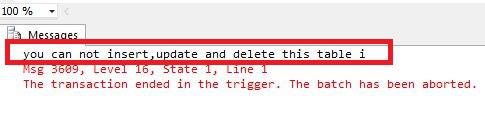 DML Trigger
DML TriggerNote: ROLLBACK TRANSACTION can included for safety, but in most cases RAISERROR itself will prevent the DML from completing.
3. Logon Triggers
Logon triggers fire in response to user logon events. They are used to monitor login activity, restrict access, or limit active sessions for a login. Messages and errors from these triggers appear in the SQL Server error log. However, they cannot handle authentication errors.
Example: Track User Logins
CREATE TRIGGER track_logon
ON LOGON
AS
BEGIN
PRINT 'A new user has logged in.';
END;
Real-World Use Cases of SQL Triggers
Triggers can automatically perform tasks, like updating related tables when data changes. Imagine we have a database for students, where the student_gradestable holds individual subject grades. If the grade of a student is updated, we may also need to update the total_scorestable.
CREATE TRIGGER update_student_score
AFTER UPDATE ON student_grades
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
UPDATE total_scores
SET score = score + :new.grade
WHERE student_id = :new.student_id;
END;
This ensures that every time a student's grade is updated, the total score in the total_scores table is automatically recalculated.
2. Data Validation (Before Insert Trigger Example)
Triggers can be used to validate data before it is inserted into a table, ensuring that the data follows specific business rules. For instance, we may want to ensure that the grades being inserted are within a valid range (say 0 to 100).
CREATE TRIGGER validate_grade
BEFORE INSERT ON student_grades
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF :new.grade < 0 OR :new.grade > 100 THEN
RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20001, 'Invalid grade value.');
END IF;
END;
The trigger checks if the inserted grade is valid. If not, it throws an error and prevents the insertion.
Viewing and Managing Triggers in SQL
If we are working with many tables across multiple databases, we can use a simple query to list all available triggers in our SQL Server instance. This is helpful for tracking and managing triggers, especially when dealing with tables that have similar names across databases.
SELECT name, is_instead_of_trigger
FROM sys.triggers
WHERE type = 'TR';
Key Terms
- name: The name of the trigger.
- is_instead_of_trigger: Whether the trigger is an INSTEAD OF trigger.
- type = 'TR': This filters the results to show only triggers.
The SQL Server Management Studio makes it very simple to display or list all triggers that are available for any given table. The following steps will help us accomplish this: Go to the Databases menu, select the desired database, and then expand it.
- Select the Tables menu and expand it.
- Select any specific table and expand it.
- We will get various options here. When we choose the Triggers option, it displays all the triggers available in this table.
BEFORE and AFTER Triggers
SQL triggers can be specified to run BEFORE or AFTER the triggering event.
- BEFORE Triggers: These run before the action (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) is executed. They’re great for data validation or modifying values before they are committed to the database.
- AFTER Triggers: Execute after the SQL statement completes. Useful for logging or cascading updates to other tables.
Example: Using BEFORE Trigger for Calculations
Given Student Report Database, in which student marks assessment is recorded. In such a schema, create a trigger so that the total and percentage of specified marks are automatically inserted whenever a record is inserted. Here, a trigger will invoke before the record is inserted so BEFORE Tag can be used.
Query
mysql>>desc Student;
Output:
 Student Datatype
Student DatatypeBelow SQL statement will create a trigger in the student database in which whenever subjects marks are entered, before inserting this data into the database, the trigger will compute those two values and insert them with the entered values. In this way, triggers can be created and executed in the databases.
 Stud_marks
Stud_marksOutput:
 Output
Output
Explore
SQL Tutorial
6 min read
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security