Solidity is a programming language that is used to write smart contracts for the Ethereum blockchain. One important concept in Solidity is conversions, which allow you to change the type of a variable or expression. The article focuses on discussing three types of conversions in Solidity.
The following conversions will be discussed here:
- Implicit Conversions.
- Explicit Conversions.
- Conversions between Literals and Elementary Types.
Let's start discussing each of these conversions in detail.
Implicit Conversions
These occur automatically when a variable or expression of one type is assigned to a variable of a different type. For example, an integer can be implicitly converted to a fixed point number or a string. These are performed using built-in functions such as 'uint()', and 'int()'.
Here is the syntax for some of the common conversion functions in Solidity:
1. uint()
Converts an expression to an unsigned integer (uint).
Example:
bytes memory b = "Hello World";
uint a = uint(b); // a is now 7210465
2. int()
Converts an expression to a signed integer (int).
Example:
bytes memory b = "Hello World";
int a = int(b); // a is now 7210465
3. bytes()
Converts an expression to a byte array (bytes).
Example:
uint a = 10;
bytes b = bytes(a); // b is now [0x0a]
4. address()
Converts an expression to an address type.
Example:
bytes memory b = "0x742d35Cc6634C0532925a3b844Bc454e4438f44e";
address a = address(b); // a is now 0x742d35Cc6634C0532925a3b844Bc454e4438f44e
5. bool()
Converts an expression to a boolean type.
Example:
bytes memory b = "Hello World";
bool a = bool(b); // a is now true
The below code demonstrates an implicit conversion from a 'uint' to an 'int':
Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// an implicit conversion from a
// 'uint' to an 'int'
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract ImplicitConversion {
function add() public pure returns (uint) {
uint a = 10;
uint b = 20;
return a + b;
}
}
Explanation:
In this example, the function add() declares two variables a and b of type uint and assigns them the values 10 and 20 respectively. Then it returns the sum of both variables. The sum of these variables is implicitly converted to uint as both variables are of uint type.
Output:

Explicit Conversions
These are performed using built-in functions such as 'bytes()'. These functions allow you to convert a variable or expression to a specific type. Explicit conversions are performed using type casts.
1. Integer Converted to Smaller Type
If an integer is converted to a smaller type then the higher-order bits are cut-off.
uint32 a = 0x432178;
uint16 b = uint16(a); // b will be 0x2178 now
2. Integer Converted to Larger Type
If an integer is explicitly converted to a larger type, it is padded on the left.
uint16 a = 0x4356;
uint32 b = uint32(a); // b will be 0x00004356 now
3. Fixed-size Bytes Converted to Smaller Types
Fixed-size bytes when converted to smaller types will cut off the sequence.
bytes2 a = 0x4326;
bytes1 b = bytes1(a); // b will be 0x43
4. Fixed-size Bytes Converted to Larger Types
Explicitly converting fixed-size bytes to a larger type, it is padded on the right.
bytes2 a = 0x4235;
bytes4 b = bytes4(a); // b will be 0x42350000
5. Explicit Conversion Between Integers and Fixed-size Byte Arrays
Explicit conversions between integers and fixed-size byte arrays are allowed only if both have the same size. Intermediate conversions are required to convert between integers and fixed-size byte arrays of different sizes.
bytes2 a = 0x3423;
uint32 b = uint16(a); // b will be 0x00003423
uint32 c = uint32(bytes4(a)); // c will be 0x34230000
uint8 d = uint8(uint16(a)); // d will be 0x23
uint8 e = uint8(bytes1(a)); // e will be 0x34
The below code demonstrates explicit conversion from a string literal to a bytes variable:
Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// explicit conversion
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract ExplicitConversion
{
function convert() public pure returns (bytes memory) {
string memory str = "Hello World";
bytes memory b = bytes(str);
return b;
}
}
Explanation:
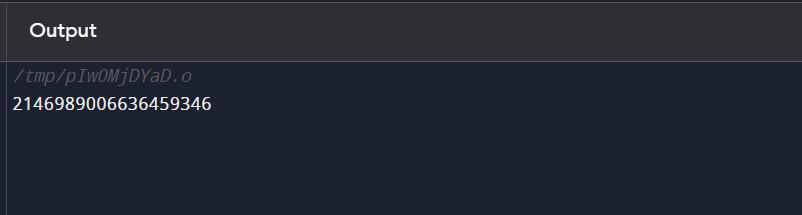
In this example, the function convert() declares a variable b of type bytes memory and assigns it the value "Hello World". Then it uses the bytes() function to explicitly convert the value of b to a byte type, and it returns the converted value. The output of the above code will be a single number, the result of converting the bytes of the string "Hello World" to an unsigned integer.
Output:
Conversions between Literals and Elementary Types
1. Integer Types
Decimal and hexadecimal literals can be implicitly converted to any integer type that is large enough to represent the literal without any truncation.
Valid:
unit8 a = 23;
uint32 b = 2134;
Invalid:
uint16 c = 0x123456;
Error: Literal is too large to fit in unit16.
2. Fixed-Size Byte Arrays
Decimal number literals cannot be implicitly converted to fixed-size byte arrays but hexadecimal number literals can be converted to fixed-size byte arrays but only if the number of hex digits exactly fits the size of the byte type. Decimal and hexadecimal number literals that have a value of zero can be converted to any fixed-size bytes type.
Valid:
bytes2 a = 0x1234;
bytes2 b = 0;
Invalid:
bytes2 a = 54321;
bytes2 b = 0x123;
String literals and hex string literals can be implicitly converted to fixed-size byte arrays only if the number of characters matches the size of the byte type.
Valid:
bytes2 a = hex"1234";
bytes2 b = "xy";
Invalid:
bytes2 a = hex"12";
bytes2 b = "xyz";
3. Addresses
Explicit conversions to address are allowed only from bytes20 and uint160. Hex literals of the correct size that pass the checksum test are of address type. No other literals cannot be implicitly converted to the address type.
Conversions between literals and elementary types are an essential aspect of Solidity programming. They enable developers to manipulate data stored in variables and make it easier to perform operations on that data. Understanding the different types of conversions available in Solidity and how they can be used is important for writing efficient and effective smart contracts.
Similar Reads
Solidity Tutorial Solidity tutorial is designed for those who want to learn Solidity programming language and for experienced Solidity developers looking to gain a deeper understanding of the language. The following Solidity tutorial explains the basic and advanced concepts of Solidity programming language and provid
6 min read
Solidity Basics
Introduction to SoliditySolidity is a brand-new programming language created by Ethereum which is the second-largest market of cryptocurrency by capitalization, released in the year 2015 and led by Christian Reitwiessner. Some key features of solidity are listed below: Solidity is a high-level programming language designed
5 min read
Setting Up Smart Contract Development EnvironmentA development environment is an environment in which all the resources and tools are available which are used to develop a program or software product. Here, an attempt to create a development environment that is a collection of the processes and tools that are used to develop smart contracts.There
5 min read
Solidity - Basic SyntaxSolidity is a programming language specifically designed for developing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It is a high-level, statically-typed language with syntax and features similar to those of JavaScript, C++, and Python. Solidity is used to write self-executing smart contracts that ca
5 min read
"Hello World" Smart Contract in Remix-IDEWhat do you mean by Smart Contract? Smart contracts are self-executing contracts. The term was coined by Nick in 1994. Smart contracts are very different from traditional software programs. They are immutable once deployed on the blockchain. It was because of Ethereum the term smart contract became
4 min read
Solidity - CommentsComments are an important aspect of programming as they help in providing clarity and understanding to the code. They allow developers to document the code and explain its purpose, making it easier for others to read and maintain the code. Solidity, being a programming language, also supports the us
4 min read
Solidity - TypesSolidity is a statically typed language, which implies that the type of each of the variables should be specified. Data types allow the compiler to check the correct usage of the variables. The declared types have some default values called Zero-State, for example for bool the default value is False
4 min read
Variable and Operators
Control Flow in Solidity
Reference & Mapping Types in Solidity
Solidity - StringsSolidity is syntactically similar to JavaScript, C++, and Python. So it uses similar language structures to those languages. Strings in Solidity is a data type used to represent/store a set of characters. Examples: "Hii" // Valid string "Hello World" // Valid string "2022" // Valid string In Solidi
3 min read
Solidity - ArraysArrays are data structures that store the fixed collection of elements of the same data types in which each and every element has a specific location called index. Instead of creating numerous individual variables of the same type, we just declare one array of the required size and store the element
6 min read
Solidity - Enums and StructsEnums are the way of creating user-defined data types, it is usually used to provide names for integral constants which makes the contract better for maintenance and reading. Enums restrict the variable with one of a few predefined values, these values of the enumerated list are called enums. Option
3 min read
Solidity - MappingsMapping in Solidity acts like a hash table or dictionary in any other language. These are used to store the data in the form of key-value pairs, a key can be any of the built-in data types but reference types are not allowed while the value can be of any type. Mappings are mostly used to associate t
4 min read
Solidity - ConversionsSolidity is a programming language that is used to write smart contracts for the Ethereum blockchain. One important concept in Solidity is conversions, which allow you to change the type of a variable or expression. The article focuses on discussing three types of conversions in Solidity. The follow
6 min read
Solidity - Ether UnitsIn the world of Ethereum smart contracts, understanding how Ether (ETH) and its subunits work is crucial. Solidity is the programming language used to write these smart contracts, and it interacts directly with Ether, the cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. This article focuses on discussing Eth
7 min read
Solidity - Special VariablesThere exist special variables and functions in solidity which exist in the global namespace and are mainly used to provide information about the blockchain or utility functions. They are of two types: 1) Block and Transaction Properties: Block Transaction Properties block.coinbase (address payable)C
3 min read
Solidity - Style GuideSolidity is a computer programming language used to create Ethereum smart contracts. These contracts self-execute. The code and the agreements contained therein are enforced by the blockchain network. Solidity is a high-level language, meaning that it is designed to be human-readable and easy to wri
13 min read
Solidity Functions
Solidity - FunctionsA function is basically a group of code that can be reused anywhere in the program, which generally saves the excessive use of memory and decreases the runtime of the program. Creating a function reduces the need of writing the same code over and over again. With the help of functions, a program can
4 min read
Solidity - Function ModifiersFunction behavior can be changed using function modifiers. Function modifier can be used to automatically check the condition prior to executing the function. These can be created for many different use cases. Function modifier can be executed before or after the function executes its code. The modi
8 min read
Solidity - View and Pure FunctionsThe view functions are read-only function, which ensures that state variables cannot be modified after calling them. If the statements which modify state variables, emitting events, creating other contracts, using selfdestruct method, transferring ethers via calls, Calling a function which is not 'v
2 min read
Solidity - Fall Back FunctionThe solidity fallback function is executed if none of the other functions match the function identifier or no data was provided with the function call. Only one unnamed function can be assigned to a contract and it is executed whenever the contract receives plain Ether without any data. To receive E
3 min read
Solidity Function OverloadingFunction overloading in Solidity lets you specify numerous functions with the same name but varying argument types and numbers.Solidity searches for a function with the same name and parameter types when you call a function with certain parameters. Calls the matching function. Compilation errors occ
1 min read
Mathematical Operations in SoliditySolidity is a brand-new programming language created by the Ethereum which is the second-largest market of cryptocurrency by capitalization, released in the year 2015 led by Christian Reitwiessner. Ethereum is a decentralized open-source platform based on blockchain domain, used to run smart contrac
6 min read
Solidity Advanced
Solidity - Basics of ContractsSolidity Contracts are like a class in any other object-oriented programming language. They firmly contain data as state variables and functions which can modify these variables. When a function is called on a different instance (contract), the EVM function call happens and the context is switched i
4 min read
Solidity - InheritanceInheritance is one of the most important features of the object-oriented programming language. It is a way of extending the functionality of a program, used to separate the code, reduces the dependency, and increases the re-usability of the existing code. Solidity supports inheritance between smart
6 min read
Solidity - ConstructorsA constructor is a special method in any object-oriented programming language which gets called whenever an object of a class is initialized. It is totally different in case of Solidity, Solidity provides a constructor declaration inside the smart contract and it invokes only once when the contract
4 min read
Solidity - Abstract ContractAbstract contracts are contracts that have at least one function without its implementation or in the case when you don't provide arguments for all of the base contract constructors. Also in the case when we don't intend to create a contract directly we can consider the contract to be abstract. An i
3 min read
Solidity - Basics of InterfaceInterfaces are the same as abstract contracts created by using an interface keyword, also known as a pure abstract contract. Interfaces do not have any definition or any state variables, constructors, or any function with implementation, they only contain function declarations i.e. functions in inte
2 min read
Solidity - LibrariesLibraries in solidity are similar to contracts that contain reusable codes. A library has functions that can be called by other contracts. Deploying a common code by creating a library reduces the gas cost. Functions of the library can be called directly when they do not modify the state variables i
4 min read
Solidity - AssemblyAssembly or Assembler language indicates a low-level programming language that can be converted to machine code by using assembler. Assembly language is tied to either physical or a virtual machine as their implementation is an instruction set, and these instructions tell the CPU to do that fundamen
4 min read
What are Events in Solidity?Solidity Events are the same as events in any other programming language. An event is an inheritable member of the contract, which stores the arguments passed in the transaction logs when emitted. Generally, events are used to inform the calling application about the current state of the contract, w
2 min read
Solidity - Error HandlingSolidity has many functions for error handling. Errors can occur at compile time or runtime. Solidity is compiled to byte code and there a syntax error check happens at compile-time, while runtime errors are difficult to catch and occurs mainly while executing the contracts. Some of the runtime erro
6 min read
Top 50 Solidity Interview Questions and Answers Solidity is an object-oriented programming language used to implement smart contracts on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, which generates transaction records in the system. To excel in your journey toward top companies as a Solidity developer, you need to master some important Solidity Interview
15+ min read