Waterfall Model - Software Engineering
Last Updated :
26 Apr, 2025
The Waterfall Model is a Traditional Software Development Methodology. It was first introduced by Winston W. Royce in 1970. It is a linear and sequential approach to software development that consists of several phases.
This classical waterfall model is simple and idealistic. It is important because most other Types of Software Development Life Cycle Models are a derivative of this. In this article, we will see the Waterfall Model in detail.
What is the SDLC Waterfall Model?
The waterfall model is a Software Development Model used in the context of large, complex projects, typically in the field of information technology. It is characterized by a structured, sequential approach to Project Management and Software Development.
The Waterfall Model is useful in situations where the project requirements are well-defined and the project goals are clear. It is often used for large-scale projects with long timelines, where there is little room for error and the project stakeholders need to have a high level of confidence in the outcome.
Read more: Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Models
Phases of Waterfall Model
Classical Waterfall Model divides the life cycle into a set of phases. The development process can be considered as a sequential flow in the waterfall. The different sequential phases of the classical waterfall model are follow:
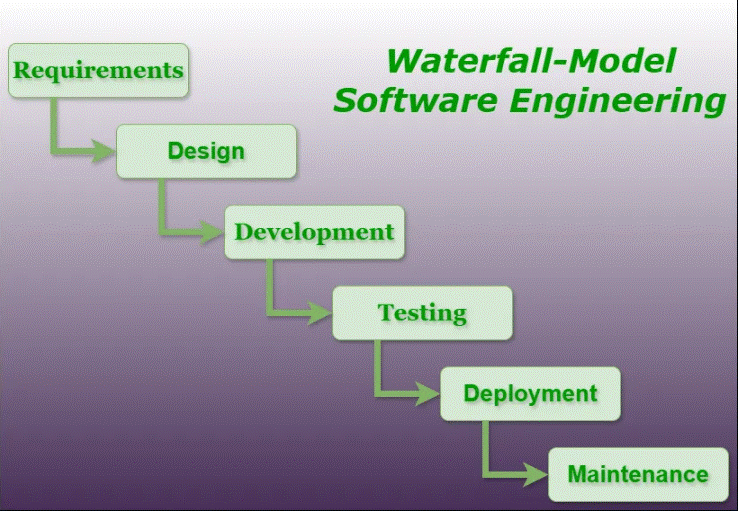 Waterfall Model-Software Engineering
Waterfall Model-Software EngineeringLet us now learn about each of these phases in detail which include further phases.
1. Requirements Analysis and Specification
Requirement Analysis and specification phase aims to understand the exact requirements of the customer and document them properly. This phase consists of two different activities.
1. Requirement Gathering and Analysis: Firstly all the requirements regarding the software are gathered from the customer and then the gathered requirements are analyzed.
The goal of the analysis part is to remove incompleteness (an incomplete requirement is one in which some parts of the actual requirements have been omitted) and inconsistencies (an inconsistent requirement is one in which some part of the requirement contradicts some other part).
2. Requirement Specification: These analyzed requirements are documented in a software requirement specification (SRS) document. SRS document serves as a contract between the development team and customers. Any future dispute between the customers and the developers can be settled by examining the SRS document.
2. Design
The goal of this Software Design Phase is to convert the requirements acquired in the SRS into a format that can be coded in a programming language. It includes high-level and detailed design as well as the overall software architecture. A Software Design Document is used to document all of this effort (SDD).
- High-Level Design (HLD): This phase focuses on outlining the broad structure of the system. It highlights the key components and how they interact with each other, giving a clear overview of the system’s architecture.
- Low-Level Design (LLD): Once the high-level design is in place, this phase zooms into the details. It breaks down each component into smaller parts and provides specifics about how each part will function, guiding the actual coding process.
3. Development
In the Development Phase software design is translated into source code using any suitable programming language. Thus each designed module is coded. The unit testing phase aims to check whether each module is working properly or not.
- In this phase, developers begin writing the actual source code based on the designs created earlier.
- The goal is to transform the design into working code using the most suitable programming languages.
- Unit tests are often performed during this phase to make sure that each component functions correctly on its own.
4. Testing and Deployment
1. Testing: Integration of different modules is undertaken soon after they have been coded and unit tested. Integration of various modules is carried out incrementally over several steps. During each integration step, previously planned modules are added to the partially integrated system and the resultant system is tested. Finally, after all the modules have been successfully integrated and tested, the full working system is obtained and system testing is carried out on this. System testing consists of three different kinds of testing activities as described below.
- Alpha testing: Alpha testing is the system testing performed by the development team.
- Beta testing: Beta testing is the system testing performed by a friendly set of customers.
- Acceptance testing: After the software has been delivered, the customer performs acceptance testing to determine whether to accept the delivered software or reject it.
2. Deployment: Once the software has been thoroughly tested, it's time to deploy it to the customer or end-users. This means making the software ready and available for use, often by moving it to a live or staging environment.
During this phase, we also focus on helping users get comfortable with the software by providing training, setting up necessary environments, and ensuring everything is running smoothly. The goal is to make sure the system works as expected in real-world conditions and that users can start using it without any hitches.
5. Maintenance
In Maintenance Phase is the most important phase of a software life cycle. The effort spent on maintenance is 60% of the total effort spent to develop a full software. There are three types of maintenance.
- Corrective Maintenance: This type of maintenance is carried out to correct errors that were not discovered during the product development phase.
- Perfective Maintenance: This type of maintenance is carried out to enhance the functionalities of the system based on the customer’s request.
- Adaptive Maintenance: Adaptive maintenance is usually required for porting the software to work in a new environment such as working on a new computer platform or with a new operating system.
Features of Waterfall Model
Following are the features of the waterfall model:
- Sequential Approach: The waterfall model involves a sequential approach to software development, where each phase of the project is completed before moving on to the next one.
- Document-Driven: The waterfall model depended on documentation to ensure that the project is well-defined and the project team is working towards a clear set of goals.
- Quality Control: The waterfall model places a high emphasis on quality control and testing at each phase of the project, to ensure that the final product meets the requirements and expectations of the stakeholders.
- Rigorous Planning: The waterfall model involves a careful planning process, where the project scope, timelines, and deliverables are carefully defined and monitored throughout the project lifecycle.
Overall, the waterfall model is used in situations where there is a need for a highly structured and systematic approach to software development. It can be effective in ensuring that large, complex projects are completed on time and within budget, with a high level of quality and customer satisfaction.
Importance of Waterfall Model
Following are the importance of waterfall model:
- Clarity and Simplicity: The linear form of the Waterfall Model offers a simple and unambiguous foundation for project development.
- Clearly Defined Phases: The Waterfall Model phases each have unique inputs and outputs, guaranteeing a planned development with obvious checkpoints.
- Documentation: A focus on thorough documentation helps with software comprehension, maintenance, and future growth.
- Stability in Requirements: Suitable for projects when the requirements are clear and stable, reducing modifications as the project progresses.
- Resource Optimization: It encourages effective task-focused work without continuously changing contexts by allocating resources according to project phases.
- Relevance for Small Projects: Economical for modest projects with simple specifications and minimal complexity.
Example of Waterfall Model
Here we can take a Real world example of the Waterfall Model.
Real-Life Example of Waterfall Model: Developing an Online Banking System
1. Analysis
This phase will be tasked with gathering all the information available on customer banking requirements, transactions, security protocols, and devising the different parameters that’ll be used for determining the core functionalities of the online banking system, such as account management, fund transfers, bill payments, and loan applications.
2. Design
In this example of the Waterfall Model, the design phase is all about fine-tuning the parameters established in the analysis phase. The system’s architecture will be designed to manage sensitive data securely, avoid transactional errors, and ensure high performance. This includes database structure, user interface design, encryption protocols, and multi-factor authentication to protect user accounts.
3. Implementation
This all-important phase involves doing dummy runs of the online banking system with a provisional set of banking transactions and customer data to see the accuracy with which the system can handle transactions, balance inquiries, fund transfers, and bill payments. These results should be matched with results from banking experts and auditors who ensure compliance with banking regulations and accuracy in transactions.
4. Testing
As with any example of the Waterfall Model, the testing phase is about ensuring that all features of the online banking system function smoothly. This includes testing for security vulnerabilities, transaction accuracy, performance under heavy load, and user interface responsiveness. Special attention is given to testing secure logins, data encryption, and ensuring that sensitive data is handled correctly throughout the system.
5. Maintenance
In the final phase, the online banking system should be checked for any necessary updates or alterations that may be required, besides the expected inclusion of new features or changes in banking regulations. Regular updates will also be needed for security patches, performance improvements, and the addition of new services like mobile banking, instant loans, or personalized financial advice.
Advantages of Waterfall Model
The classical waterfall model is an idealistic model for software development. It is very simple, so it can be considered the basis for other software development life cycle models. Below are some of the major advantages of this SDLC model.
- Easy to Understand: The Classical Waterfall Model is very simple and easy to understand.
- Individual Processing: Phases in the Classical Waterfall model are processed one at a time.
- Properly Defined: In the classical waterfall model, each stage in the model is clearly defined.
- Clear Milestones: The classical Waterfall model has very clear and well-understood milestones.
- Properly Documented: Processes, actions, and results are very well documented.
- Reinforces Good Habits: The Classical Waterfall Model reinforces good habits like define-before-design and design-before-code.
- Working: Classical Waterfall Model works well for smaller projects and projects where requirements are well understood.
Disadvantages of Waterfall Model
The Classical Waterfall Model suffers from various shortcomings we can’t use it in real projects, but we use other software development lifecycle models which are based on the classical waterfall model. Below are some major drawbacks of this model.
- No Feedback Path: In the classical waterfall model evolution of software from one phase to another phase is like a waterfall. It assumes that no error is ever committed by developers during any phase. Therefore, it does not incorporate any mechanism for error correction.
- Difficult to accommodate Change Requests: This model assumes that all the customer requirements can be completely and correctly defined at the beginning of the project, but the customer's requirements keep on changing with time. It is difficult to accommodate any change requests after the requirements specification phase is complete.
- No Overlapping of Phases: This model recommends that a new phase can start only after the completion of the previous phase. But in real projects, this can't be maintained. To increase efficiency and reduce cost, phases may overlap.
- Limited Flexibility: The Waterfall Model is a rigid and linear approach to software development, which means that it is not well-suited for projects with changing or uncertain requirements. Once a phase has been completed, it is difficult to make changes or go back to a previous phase.
- Limited Stakeholder Involvement: The Waterfall Model is a structured and sequential approach, which means that stakeholders are typically involved in the early phases of the project (requirements gathering and analysis) but may not be involved in the later phases (implementation, testing, and deployment).
- Late Defect Detection: In the Waterfall Model, testing is typically done toward the end of the development process. This means that defects may not be discovered until late in the development process, which can be expensive and time-consuming to fix.
- Lengthy Development Cycle: The Waterfall Model can result in a lengthy development cycle, as each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. This can result in delays and increased costs if requirements change or new issues arise.
When to Use Waterfall Model?
Here are some cases where the use of the Waterfall Model is best suited:
- Well-understood Requirements: Before beginning development, there are precise, reliable, and thoroughly documented requirements available.
- Very Little Changes Expected: During development, very little adjustments or expansions to the project's scope are anticipated.
- Small to Medium-Sized Projects: Ideal for more manageable projects with a clear development path and little complexity.
- Predictable: Projects that are predictable, low-risk, and able to be addressed early in the development life cycle are those that have known, controllable risks.
- Regulatory Compliance is Critical: Circumstances in which paperwork is of utmost importance and stringent regulatory compliance is required.
- Client Prefers a Linear and Sequential Approach: This situation describes the client's preference for a linear and sequential approach to project development.
- Limited Resources: Projects with limited resources can benefit from a set-up strategy, which enables targeted resource allocation.
The Waterfall approach involves less user interaction in the product development process. The product can only be shown to end user when it is ready.
Applications of Waterfall Model
Here are some application of SDLC waterfall model:
- Large-scale Software Development Projects: The Waterfall Model is often used for large-scale software development projects, where a structured and sequential approach is necessary to ensure that the project is completed on time and within budget.
- Safety-Critical Systems: The Waterfall Model is often used in the development of safety-critical systems, such as aerospace or medical systems, where the consequences of errors or defects can be severe.
- Government and Defense Projects: The Waterfall Model is also commonly used in government and defense projects, where a rigorous and structured approach is necessary to ensure that the project meets all requirements and is delivered on time.
- Projects with well-defined Requirements: The Waterfall Model is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements, as the sequential nature of the model requires a clear understanding of the project objectives and scope.
- Projects with Stable Requirements: The Waterfall Model is also well-suited for projects with stable requirements, as the linear nature of the model does not allow for changes to be made once a phase has been completed.
For more, you can refer to the Uses of Waterfall Model.
Conclusion
The Waterfall Model has good conventional Software Development Processes. This model is sequential technique provides an easily understood and applied structured framework. Here we learned the Waterfall model in detail.
Similar Reads
Software Engineering Tutorial Software Engineering is a subdomain of Engineering in which you learn to develop, design, test, and maintain software using a systematic and structured approach. Software is a collection of programs. And that programs are developed by software engineers In this Software Engineering Tutorial, you wil
7 min read
Software Engineering Basics
Introduction to Software EngineeringSoftware is a program or set of programs containing instructions that provide the desired functionality. Engineering is the process of designing and building something that serves a particular purpose and finds a cost-effective solution to problems. Table of ContentWhat is Software Engineering?Key P
11 min read
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Software development life cycle (SDLC) is a structured process that is used to design, develop, and test good-quality software. SDLC, or software development life cycle, is a methodology that defines the entire procedure of software development step-by-step. The goal of the SDLC life cycle model is
11 min read
Software Quality - Software EngineeringTraditionally, a high-quality product is outlined in terms of its fitness of purpose. That is, a high-quality product will specifically be what the users need to try. For code products, the fitness of purpose is typically taken in terms of satisfaction of the wants arranged down within the SRS docum
5 min read
ISO/IEC 9126 in Software EngineeringThe International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established a series of ISO and ISO/IEC standards for software quality. Starting with the ISO 9000-3 instructions for implementing the ISO 9001 standard, which is concerned with quality assurance processes, to the creation, supply, install
4 min read
Boehm's Software Quality ModelIn 1978, B.W. Boehm introduced his software quality model, which defines software quality through a hierarchical structure of attributes and metrics. This model is similar to the McCall Quality Model but encompasses a wider range of characteristics, including hardware performance-related ones. Boehm
4 min read
Software Crisis - Software EngineeringThe term "software crisis" refers to the numerous challenges and difficulties faced by the software industry during the 1960s and 1970s. It became clear that old methods of developing software couldn't keep up with the growing complexity and demands of new projects. This led to high costs, delays, a
3 min read
Software Measurement & Metrices
Software Measurement and MetricsSoftware Measurement: A measurement is a manifestation of the size, quantity, amount, or dimension of a particular attribute of a product or process. Software measurement is a titrate impute of a characteristic of a software product or the software process. Table of Content Software Measurement Prin
4 min read
People Metrics and Process Metrics in Software EngineeringPeople Metrics and Process Metrics, both play important roles in software development. People Metrics helps in quantifying the useful attributes whereas Process Metrics creates the body of the software. People metrics focus on how well team members work together and their overall satisfaction, while
8 min read
Halstead’s Software Metrics - Software EngineeringHalstead's Software metrics are a set of measures proposed by Maurice Halstead to evaluate the complexity of a software program. These metrics are based on the number of distinct operators and operands in the program and are used to estimate the effort required to develop and maintain the program. T
11 min read
Cyclomatic ComplexityCyclomatic complexity, developed by Thomas McCabe, is a metric that measures the complexity of a program by counting its decision points. It measures the number of unique paths through the code, indicating how complex the logic is. Lower complexity suggests simpler, more manageable code, reducing th
6 min read
Functional Point (FP) Analysis - Software EngineeringFunctional Point Analysis (FPA) is a software measurement technique used to assess the size and complexity of a software system based on its functionality. It involves categorizing the functions of the software, such as input screens, output reports, inquiries, files, and interfaces, and assigning w
8 min read
Lines of Code (LOC) in Software EngineeringA line of code (LOC) is any line of text in a code that is not a comment or blank line, and also header lines, in any case of the number of statements or fragments of statements on the line. LOC consists of all lines containing the declaration of any variable, and executable and non-executable state
4 min read
Software Development Models & Agile Methods
Waterfall Model - Software EngineeringThe Waterfall Model is a Traditional Software Development Methodology. It was first introduced by Winston W. Royce in 1970. It is a linear and sequential approach to software development that consists of several phases. This classical waterfall model is simple and idealistic. It is important because
13 min read
What is Spiral Model in Software Engineering?The Spiral Model is one of the most important SDLC model. The Spiral Model is a combination of the waterfall model and the iterative model. It provides support for Risk Handling. The Spiral Model was first proposed by Barry Boehm. This article focuses on discussing the Spiral Model in detail.Table o
9 min read
Prototyping Model - Software EngineeringPrototyping Model is a way of developing software where an early version, or prototype, of the product is created and shared with users for feedback. The Prototyping Model concept is described below: Table of ContentWhat is Prototyping Model?Phases of Prototyping ModelTypes of Prototyping ModelsAdva
7 min read
Incremental Process Model - Software EngineeringThe Incremental model is a software Development approach which is used to breakdown the project into smaller and easily manageable parts. In these, each part passes through Requirement, Design, Testing phases and Implementation phase. The overall process continue until we got the complete System.Inc
6 min read
Rapid Application Development Model (RAD) - Software EngineeringThe RAD model or Rapid Application Development model is a type of software development methodology that emphasizes quick and iterative release cycles, primarily focusing on delivering working software in shorter timelines. Unlike traditional models such as the Waterfall model, RAD is designed to be
9 min read
Coupling and Cohesion - Software EngineeringThe purpose of the Design phase in the Software Development Life Cycle is to produce a solution to a problem given in the SRS(Software Requirement Specification) document. The output of the design phase is a Software Design Document (SDD). Coupling and Cohesion are two key concepts in software engin
10 min read
Agile Software Development - Software EngineeringAgile Software Development is a Software Development Methodology that values flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction. It is based on the Agile Manifesto, a set of principles for software development that prioritize individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration,
15+ min read
SRS & SPM
Software Requirement Specification (SRS) FormatIn order to form a good SRS, here you will see some points that can be used and should be considered to form a structure of good Software Requirements Specification (SRS). These are below mentioned in the table of contents and are well explained below. Table of ContentIntroductionGeneral description
5 min read
Software Engineering | Quality Characteristics of a good SRSRelated Article: Writing a good SRS for your project Quality characteristics of a good Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document include:Complete: The SRS should include all the requirements for the software system, including both functional and non-functional requirements.Consistent: The S
7 min read
Software Project Management (SPM) - Software EngineeringSoftware Project Management (SPM) is a proper way of planning and leading software projects. It is a part of project management in which software projects are planned, implemented, monitored, and controlled. In this article, we are discussing Software Project Management (SPM) topics that are useful
8 min read
COCOMO Model - Software EngineeringThe Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) It was proposed by Barry Boehm in 1981 and is based on the study of 63 projects, which makes it one of the best-documented models. It is a Software Cost Estimation Model that helps predict the effort, cost, and schedule required for a software development project
15+ min read
Capability Maturity Model (CMM) - Software EngineeringThe Capability Maturity Model (CMM) is a tool used to improve and refine software development processes. It provides a structured way for organizations to assess their current practices and identify areas for improvement. CMM consists of five maturity levels: initial, repeatable, defined, managed, a
11 min read
Integrating Risk Management in SDLC | Set 1The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a conceptual model for defining the tasks performed at each step of the software development process. This model gives you a brief about the life cycle of Software in the development phase. In this particular article, we are going to discuss risk managem
8 min read
Software Maintenance - Software EngineeringSoftware Maintenance refers to the process of modifying and updating a software system after it has been delivered to the customer. This involves fixing bugs, adding new features, and adapting to new hardware or software environments. Effective maintenance is crucial for extending the software's lif
14 min read
Testing & Debugging
What is Software Testing?Software testing is an important process in the Software Development Lifecycle(SDLC). It involves verifying and validating that a Software Application is free of bugs, meets the technical requirements set by its Design and Development, and satisfies user requirements efficiently and effectively.Here
11 min read
Types of Software TestingSoftware testing is a important of software development life-cycle that ensures a product works correctly, meets user expectations, and is free of bugs. There are different types of software testing, each designed to validate specific aspects of an application, such as functionality, performance, se
15+ min read
Testing Guidelines - Software EngineeringSoftware testing is an essential component of software development, ensuring that applications function correctly, meet user expectations, and are ready for deployment. Effective software testing involves a structured approach guided by well-defined principles and best practices. This article explor
3 min read
What is Debugging in Software Engineering?Debugging in Software Engineering is the process of identifying and resolving errors or bugs in a software system. It's a critical aspect of software development, ensuring quality, performance, and user satisfaction. Despite being time-consuming, effective debugging is essential for reliable and com
11 min read
Verification & Validation
Practice Questions