MATLAB which is also known as "Matrix Laboratory" allows its user to manipulate matrixes, plotting of functions and data, creation of algorithms, and user interfaces written in different programming languages by providing a computing environment. MATLAB is software designed and powered by mathworks.com. One can install it in different operating systems like Windows, Mac OS, and Linux as well as get access to the online platform.
Whereas, Simulink is an additional package to MATLAB that allows model-based design for the embedded systems as well as a dynamic system along with the graphical multi-dimension simulation.
In this article, the interfaces that will be shown via screenshots will be the online platform based.
To use the online interface of MATLAB, follow the steps listed below.
Step 1. First, Visit the mathworks.com.

Step 2. Click on the sign-in button.
Step 3. A box as shown below appears on your screen, click on the Create account link. It will redirect you to the account creation section.


Step 4. Fill up all the necessary information and your account has been created. Now, you will enter the page where you will be shown different ways of using MATLAB. One can use the license key, if have one, or can either install it in the system or one can use the trial for 30 days as I did. Make sure you have your work or university email for accessing 30 days trial pack for using it online, else you can always download it once you sign in to the MATLAB. All the steps for accessing Simulink in MATLAB will be the same in the installed version, too.
Step 5. So, once you select the option that you like, you will enter the interface like this, if you selected the Trial version. Now, click on the Open online Platform.
Step 6. You will be taken to the screen. Now, take a minute or two to get familiar with the environment.

Step 7. The screen that you first enter is the MATLAB's interface. Go to the navbar, where you will find the Simulink, else you can type Simulink in the MATLAB interface. And you will be taken to the Simulink. Pictures shown here will be your interfaces.

Step 8. Now to use Simulink, select create a blank model, and you will be taken to the screen like mine.

Step 9. Now, here we will show you to choose an RLC resistor and just have a single resistor from the RLC. For that, go to the navbar and select Library Browser. You will be taken to the library which contains a whole bunch of exciting circuits, components, and related kinds of information.
When you will enter the Library on the left side you will see all the categories and the subcategories from where you can see and find the components, whereas, on the right side you will see the same thing but the subcategories in a descriptive way. You can even type the components that you need in the search box, but for that, you must know what you need and what it is called in the library.
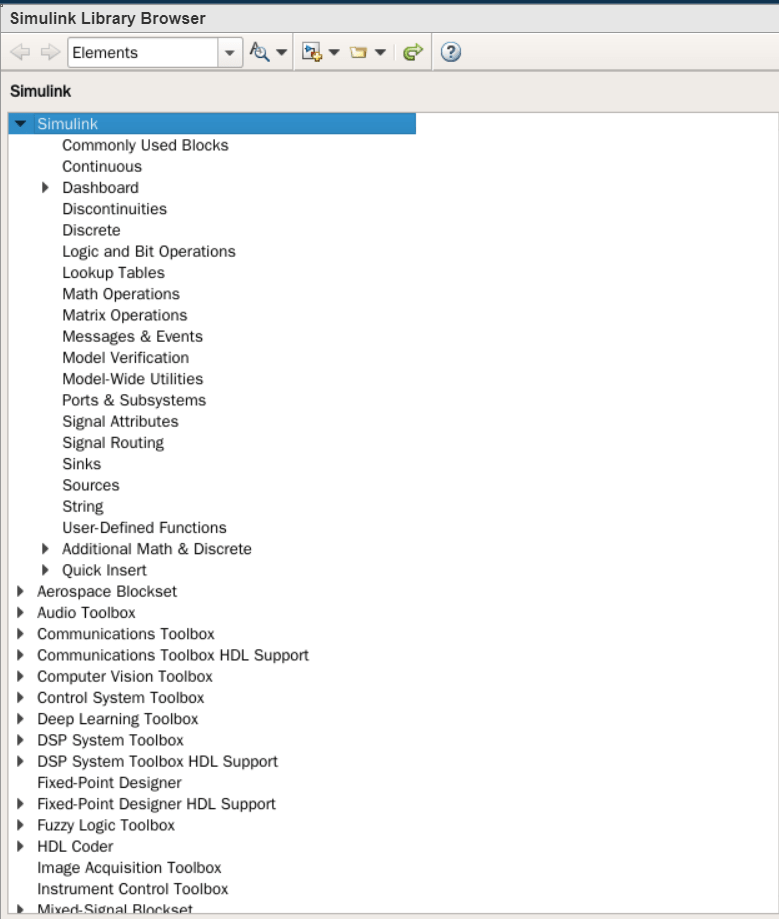

Step 10. Now for choosing an RLC circuit, you need to scroll down and locate Simscape. Select that and the dropdown menu will give you the options, and from that find Specialized power Systems. Select that and on the right side, you will see various categories the power systems contain. Head to the passive and select the RLC circuit.


Step 11. To select the component and bring it to our blank model, click the right button, where a box appears and select add a block to the untitled [name of your document] block. [ Note: You can name your design beforehand, too. I prefer to name it at last]
Step 12. After that, you can see it present on your blank model. Now, double-tap on the component, and you will see Block parameter properties appear on your screen. It allows a user to customize and add the values as a user likes.

Since we want to make a resistor, so selected R and added the value which results in something like this. You can even rename the component. For that, double click on the name written for the component, it will be selected, erase the name and give it yours.


Similarly, try adding other components, and make a full circuit. For learning more about the components, you can visit the official website for accessing the documents.
Similar Reads
Up-sampling in MATLAB Interpolation or up-sampling is the specific inverse of decimation. It is a data saving operation, in that all examples of x[n] are available in the extended signal y[n]. Interpolation works by adding (L–1) zero-valued examples for each input sample. We will be using the interp() function to interp
1 min read
Down-sampling in MATLAB The two basic operations in a multi-rate system are decreasing/down-sampling (decimation) and increasing (interpolation) the sampling rate of a signal. In down-sampling we start with a constant time signal x(t) and convert it into a succession of tests x[n], in decimation we start with a discrete-ti
2 min read
Tables in MATLAB Table is an array data type in MATLAB that stores column-based or tabular data of same or different types. A table stores each column-oriented data under a variable name (column name). These table columns can have different data types in each however, the number of data points in every column must b
2 min read
polyval() in MATLAB polyval is a built-in function in MATLAB that allows you to evaluate a polynomial at a specific point. It evaluates the polynomial let's p at the points in x and it returns the corresponding function values in y . The syntax for polyval is as follows: Syntax: y = polyval(p,x) %returns the value of a
2 min read
Variable Names in MATLAB A variable is a named-memory location that stores different types of data which can be used to perform a specific set of operations. It can be thought of as a container that holds some value in memory. The Matlab workspace store all the variables being used during a session. This workspace not only
5 min read
Polynomials in MATLAB A polynomial is an expression that is made up of variables, constants, and exponents, that are combined using mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division (No division operation by a variable). Polynomials in MATLAB are represented as row of a vector containing
2 min read