Render a HTML Template as Response - Django Views
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2025
A view function, or view for short, is simply a Python function that takes a Web request and returns a Web response. This article revolves around how to render an HTML page from Django using views. Django has always been known for its app structure and ability to manage applications easily. Let's dive in to see how to render a template file through a Django view.
Django Render a HTML Template as Response Explanation
Illustration of
How to render a HTML Template in a view using an Example. Consider a project named
geeksforgeeks having an app named
geeks.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
After you have a project and an app, open
views.py and let's start creating a view called geeks_view which is used print "
Hello world" through a template file. A django view is a python function which accept an argument called
request and returns an
response.
Enter following code into views.py of app
Python3 1==
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
def geeks_view(request):
# render function takes argument - request
# and return HTML as response
return render(request, "home.html")
but this code won't work until into define a proper mapping of URL. Mapping means you need to tell Django what a user enters in the browser to render your particular view. For example
www.geeksforgeeks.org tells django to execute its home page view. So let's modify urls.py to start our view.
Include your app's urls into main urls by adding following code to
geeksforgeeks > urls.py
Python3 1==
"""geeksforgeeks URL Configuration
The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see:
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/5.2/ / en / 2.2 / topics / http / urls / Examples:
Function views
1. Add an import: from my_app import views
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name ='home')
Class-based views
1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name ='home')
Including another URLconf
1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls'))
"""
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include("geeks.urls")),
]
Now lets create a path to our view from
geeks > urls.py
Python3 1==
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
# importing views from views..py
from .views import geeks_view
urlpatterns = [
path('', geeks_view ),
]
Done. Now go to check if our template gets rendered or not. visit here -
http://localhost:8000/
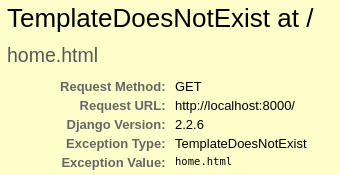
It is giving an error that you don't have a template home.html. So let's create our template now, in
geeks folder create a folder called templates and create a file home.html into it. Now let's check again -
http://localhost:8000/.

This way you can render any template file using the same procedure -
1. Create a view in views.py
2. Create a template file which is to be rendered and link it to the view.
3. Create a URL to map to that view.
We used this error because during your process of learning on
how to create a project using django? you may encounter a lot of errors, there you dont need to hyper, just take a long breath and simply google the error you will have solution to everything.
Similar Reads
TemplateView - Class Based Generic View Django Django provides several class based generic views to accomplish common tasks. The simplest among them is TemplateView. It Renders a given template, with the context containing parameters captured in the URL. TemplateView should be used when you want to present some information on an HTML page. Templ
2 min read
Handle and Iterate Nested Dictionaries in Django Templates Django templates offer various tags and filters to work with data. they are designed to readable and expressive. To iterate through a dictionary which contains a dictionary itself as a Value we can use the " { % for % } " template tag to iterate over dictionary that contains dictionary. But Django t
4 min read
extends - Django Template Tags Django’s {% extends %} tag allows you to reuse a base template across multiple pages, so you don’t have to repeat the same HTML code in every template. This makes your templates cleaner, easier to maintain, and helps keep a consistent layout throughout your site.Syntax: {% extends 'base_template.htm
2 min read
extends - Django Template Tags Django’s {% extends %} tag allows you to reuse a base template across multiple pages, so you don’t have to repeat the same HTML code in every template. This makes your templates cleaner, easier to maintain, and helps keep a consistent layout throughout your site.Syntax: {% extends 'base_template.htm
2 min read
extends - Django Template Tags Django’s {% extends %} tag allows you to reuse a base template across multiple pages, so you don’t have to repeat the same HTML code in every template. This makes your templates cleaner, easier to maintain, and helps keep a consistent layout throughout your site.Syntax: {% extends 'base_template.htm
2 min read
Django Templates | Set - 2 Prerequisite: Django Templates | Set-1, Views In Django. Navigate to brand/views.py and add following code to brand/views.py Python3 1== from django.shortcuts import render from django.http import HttpResponse # Create your views here. def ViewDemo(request): return HttpResponse("<h1>Hello
2 min read