PySpark Collect() – Retrieve data from DataFrame
Last Updated :
17 Jun, 2021
Collect() is the function, operation for RDD or Dataframe that is used to retrieve the data from the Dataframe. It is used useful in retrieving all the elements of the row from each partition in an RDD and brings that over the driver node/program.
So, in this article, we are going to learn how to retrieve the data from the Dataframe using collect() action operation.
Syntax: df.collect()
Where df is the dataframe
Example 1: Retrieving all the Data from the Dataframe using collect().
After creating the Dataframe, for retrieving all the data from the dataframe we have used the collect() action by writing df.collect(), this will return the Array of row type, in the below output shows the schema of the dataframe and the actual created Dataframe.
Python
# importing necessary libraries
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# function to create new SparkSession
def create_session():
spk = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Corona_cases_statewise.com") \
.getOrCreate()
return spk
# function to create RDD
def create_RDD(sc_obj,data):
df = sc.parallelize(data)
return df
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_data = [("Uttar Pradesh",122000,89600,12238),
("Maharashtra",454000,380000,67985),
("Tamil Nadu",115000,102000,13933),
("Karnataka",147000,111000,15306),
("Kerala",153000,124000,5259)]
# calling function to create SparkSession
spark = create_session()
# creating spark context object
sc = spark.sparkContext
# calling function to create RDD
rd_df = create_RDD(sc,input_data)
schema_lst = ["State","Cases","Recovered","Deaths"]
# creating the dataframe using createDataFrame function
df = spark.createDataFrame(rd_df,schema_lst)
# printing schema of the dataframe and showing the dataframe
df.printSchema()
df.show()
# retrieving the data from the dataframe using collect()
df2= df.collect()
print("Retrieved Data is:-")
print(df2)
Output:

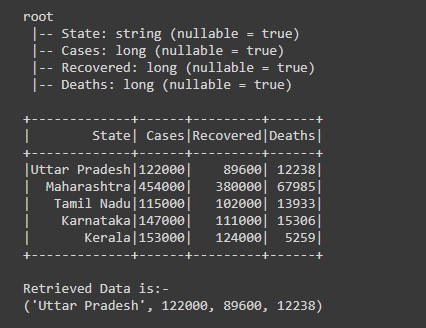
Example 2: Retrieving Data of specific rows using collect().
After creating the Dataframe, we have retrieved the data of 0th row Dataframe using collect() action by writing print(df.collect()[0][0:]) respectively in this we are passing row and column after collect(), in the first print statement we have passed row and column as [0][0:] here first [0] represents the row that we have passed 0 and second [0:] this represents the column and colon(:) is used to retrieve all the columns, in short, we have retrieve the 0th row with all the column elements.
Python
# importing necessary libraries
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# function to create new SparkSession
def create_session():
spk = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Corona_cases_statewise.com") \
.getOrCreate()
return spk
# function to create RDD
def create_RDD(sc_obj,data):
df = sc.parallelize(data)
return df
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_data = [("Uttar Pradesh",122000,89600,12238),
("Maharashtra",454000,380000,67985),
("Tamil Nadu",115000,102000,13933),
("Karnataka",147000,111000,15306),
("Kerala",153000,124000,5259)]
# calling function to create SparkSession
spark = create_session()
# creating spark context object
sc = spark.sparkContext
# calling function to create RDD
rd_df = create_RDD(sc,input_data)
schema_lst = ["State","Cases","Recovered","Deaths"]
# creating the dataframe using createDataFrame function
df = spark.createDataFrame(rd_df,schema_lst)
# printing schema of the dataframe and showing the dataframe
df.printSchema()
df.show()
print("Retrieved Data is:-")
# Retrieving data from 0th row
print(df.collect()[0][0:])
Output:
Example 3: Retrieve data of multiple rows using collect().
After creating the Dataframe, we are retrieving the data of the first three rows of the dataframe using collect() action with for loop, by writing for row in df.collect()[0:3], after writing the collect() action we are passing the number rows we want [0:3], first [0] represents the starting row and using ":" semicolon and [3] represents the ending row till which we want the data of multiple rows.
Here is the number of rows from which we are retrieving the data is 0,1 and 2 the last index is always excluded i.e, 3.
Python
# importing necessary libraries
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
# function to create new SparkSession
def create_session():
spk = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Corona_cases_statewise.com") \
.getOrCreate()
return spk
# function to create RDD
def create_RDD(sc_obj,data):
df = sc.parallelize(data)
return df
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_data = [("Uttar Pradesh",122000,89600,12238),
("Maharashtra",454000,380000,67985),
("Tamil Nadu",115000,102000,13933),
("Karnataka",147000,111000,15306),
("Kerala",153000,124000,5259)]
# calling function to create SparkSession
spark = create_session()
# creating spark context object
sc = spark.sparkContext
# calling function to create RDD
rd_df = create_RDD(sc,input_data)
schema_lst = ["State","Cases","Recovered","Deaths"]
# creating the dataframe using createDataFrame function
df = spark.createDataFrame(rd_df,schema_lst)
# showing the dataframe and schema
df.printSchema()
df.show()
print("Retrieved Data is:-")
# Retrieving multiple rows using collect() and for loop
for row in df.collect()[0:3]:
print((row["State"]),",",str(row["Cases"]),",",
str(row["Recovered"]),",",str(row["Deaths"]))
Output:

Example 4: Retrieve data from a specific column using collect().
After creating the Dataframe, we are retrieving the data of 'Cases' column using collect() action with for loop. By iterating the loop to df.collect(), that gives us the Array of rows from that rows we are retrieving and printing the data of 'Cases' column by writing print(col["Cases"]);
As we are getting the rows one by iterating for loop from Array of rows, from that row we are retrieving the data of "Cases" column only. By writing print(col["Cases"]) here from each row we are retrieving the data of 'Cases' column by passing 'Cases' in col.
Python
# importing necessary libraries
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
# function to create new SparkSession
def create_session():
spk = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Corona_cases_statewise.com") \
.getOrCreate()
return spk
# function to create RDD
def create_RDD(sc_obj,data):
df = sc.parallelize(data)
return df
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_data = [("Uttar Pradesh",122000,89600,12238),
("Maharashtra",454000,380000,67985),
("Tamil Nadu",115000,102000,13933),
("Karnataka",147000,111000,15306),
("Kerala",153000,124000,5259)]
# calling function to create SparkSession
spark = create_session()
# creating spark context object
sc = spark.sparkContext
# calling function to create RDD
rd_df = create_RDD(sc,input_data)
schema_lst = ["State","Cases","Recovered","Deaths"]
# creating the dataframe using createDataFrame function
df = spark.createDataFrame(rd_df,schema_lst)
# showing the dataframe and schema
df.printSchema()
df.show()
print("Retrieved Data is:-")
# Retrieving data from the "Cases" column
for col in df.collect():
print(col["Cases"])
Output:

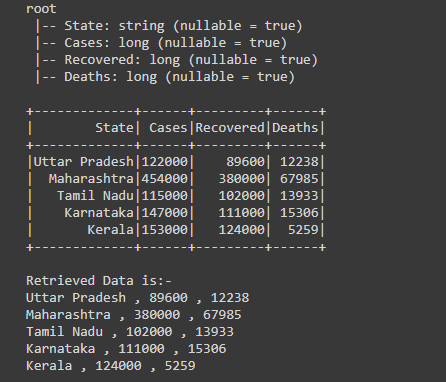
Example 5: Retrieving the data from multiple columns using collect().
After creating the dataframe, we are retrieving the data of multiple columns which include "State", "Recovered" and "Deaths".
For retrieving the data of multiple columns, firstly we have to get the Array of rows which we get using df.collect() action now iterate the for loop of every row of Array, as by iterating we are getting rows one by one so from that row we are retrieving the data of "State", "Recovered" and "Deaths" column from every column and printing the data by writing, print(col["State"],",",col["Recovered"],",",col["Deaths"])
Python
# importing necessary libraries
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
# function to create new SparkSession
def create_session():
spk = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Corona_cases_statewise.com") \
.getOrCreate()
return spk
# function to create RDD
def create_RDD(sc_obj,data):
df = sc.parallelize(data)
return df
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_data = [("Uttar Pradesh",122000,89600,12238),
("Maharashtra",454000,380000,67985),
("Tamil Nadu",115000,102000,13933),
("Karnataka",147000,111000,15306),
("Kerala",153000,124000,5259)]
# calling function to create SparkSession
spark = create_session()
# creating spark context object
sc = spark.sparkContext
# calling function to create RDD
rd_df = create_RDD(sc,input_data)
schema_lst = ["State","Cases","Recovered","Deaths"]
# creating the dataframe using createDataFrame function
df = spark.createDataFrame(rd_df,schema_lst)
# showing the dataframe and schema
df.printSchema()
df.show()
print("Retrieved Data is:-")
# Retrieving data of the "State",
# "Recovered" and "Deaths" column
for col in df.collect():
print(col["State"],",",col["Recovered"],",
",col["Deaths"])
Output:
Similar Reads
Python Tutorial | Learn Python Programming Language Python Tutorial – Python is one of the most popular programming languages. It’s simple to use, packed with features and supported by a wide range of libraries and frameworks. Its clean syntax makes it beginner-friendly.Python is:A high-level language, used in web development, data science, automatio
10 min read
Python Interview Questions and Answers Python is the most used language in top companies such as Intel, IBM, NASA, Pixar, Netflix, Facebook, JP Morgan Chase, Spotify and many more because of its simplicity and powerful libraries. To crack their Online Assessment and Interview Rounds as a Python developer, we need to master important Pyth
15+ min read
Non-linear Components In electrical circuits, Non-linear Components are electronic devices that need an external power source to operate actively. Non-Linear Components are those that are changed with respect to the voltage and current. Elements that do not follow ohm's law are called Non-linear Components. Non-linear Co
11 min read
Python OOPs Concepts Object Oriented Programming is a fundamental concept in Python, empowering developers to build modular, maintainable, and scalable applications. By understanding the core OOP principles (classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and abstraction), programmers can leverage the full p
11 min read
Python Projects - Beginner to Advanced Python is one of the most popular programming languages due to its simplicity, versatility, and supportive community. Whether you’re a beginner eager to learn the basics or an experienced programmer looking to challenge your skills, there are countless Python projects to help you grow.Here’s a list
10 min read
Python Exercise with Practice Questions and Solutions Python Exercise for Beginner: Practice makes perfect in everything, and this is especially true when learning Python. If you're a beginner, regularly practicing Python exercises will build your confidence and sharpen your skills. To help you improve, try these Python exercises with solutions to test
9 min read
Python Programs Practice with Python program examples is always a good choice to scale up your logical understanding and programming skills and this article will provide you with the best sets of Python code examples.The below Python section contains a wide collection of Python programming examples. These Python co
11 min read
Spring Boot Tutorial Spring Boot is a Java framework that makes it easier to create and run Java applications. It simplifies the configuration and setup process, allowing developers to focus more on writing code for their applications. This Spring Boot Tutorial is a comprehensive guide that covers both basic and advance
10 min read
Class Diagram | Unified Modeling Language (UML) A UML class diagram is a visual tool that represents the structure of a system by showing its classes, attributes, methods, and the relationships between them. It helps everyone involved in a project—like developers and designers—understand how the system is organized and how its components interact
12 min read
Enumerate() in Python enumerate() function adds a counter to each item in a list or other iterable. It turns the iterable into something we can loop through, where each item comes with its number (starting from 0 by default). We can also turn it into a list of (number, item) pairs using list().Let's look at a simple exam
3 min read