How to Query for All Dates Greater Than a Certain Date in PostgreSQL?
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2024
When working with temporal data, querying for all dates greater than a given date is a common task in PostgreSQL. PostgreSQL offers several methods for executing these kinds of queries, providing flexibility to meet various needs and preferences. By leveraging date functions, intervals, and comparison operators, users can effectively filter and obtain pertinent data from a PostgreSQL database, enabling efficient analysis and reporting.
In this article, we will examine various approaches to running date-based queries in PostgreSQL and show how to use them to retrieve entries that have dates that are more than a predetermined threshold.
Efficient PostgreSQL Queries: Retrieve Dates Beyond a Specific Date
Querying for dates beyond a set threshold in PostgreSQL involves various methods. Whether using standard operators, functions like EXTRACT, or INTERVAL, PostgreSQL offers flexibility to efficiently filter and analyze temporal data.
In PostgreSQL, you can query for all dates greater than a certain date using various methods. Here are some common ways to achieve this:
Setting Up the Environment
To understand How to query for all dates greater than a certain date in PostgreSQL, we need a table on which we will perform various operations. So we create a table sample_table.
Creating the table sample_table :
PostgreSQL
CREATE TABLE sample_table (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
date_column DATE
);
INSERT INTO sample_table (date_column) VALUES
('2022-02-23'),
('2022-02-24'),
('2022-02-25'),
('2022-02-26'),
('2022-02-27');
--show table data
SELECT * FROM sample_table;
Output:
 Showing contents of sample_table
Showing contents of sample_tableMethods to Query Dates Greater Than a Specific Date
1. Using Greater Than Operator
This method employs the standard greater than operator to filter rows where the date column is later than the specified date. It's a straightforward and commonly used approach for date comparisons.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM your_table
WHERE your_date_column > date_value
Replace your_date_column with the name of the column containing the date datatype and your_table with the name of the table. Change date_value to the desired value found in the column.
Query:
SELECT * FROM sample_table
WHERE date_column > '2022-02-23';
Output:
 Output for Greater Than Operator
Output for Greater Than OperatorExplanation: The output displays rows from "sample_table" where the "date_column" is later than '2022-02-23', filtering entries based on date comparison.
2. Using EXTRACT Function
The EXTRACT function is used to extract the epoch value from the date column and the specified date. It then compares the epoch values, providing a numeric basis for date comparison.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM your_table
WHERE EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM your_date_column) > EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM date_value::timestamp);
Replace your_date_column with the name of the column containing the date datatype and your_table with the name of the table. Change date_value to the desired value found in the column.
Query:
SELECT * FROM sample_table
WHERE EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM date_column) > EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM '2022-02-23'::timestamp);
Output:
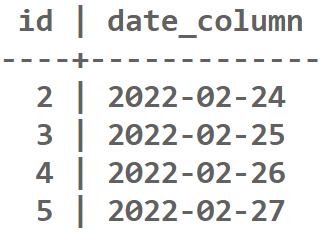 Output for Extract Function
Output for Extract FunctionExplanation: The given SQL query retrieves rows from the "sample_table" where the "date_column" is later than '2022-02-23'. The output would include dates '2022-02-24', '2022-02-25', '2022-02-26', '2022-02-27'.
This method utilizes the INTERVAL keyword to add a specified duration (in this case, one day) to the specified date. The query then selects dates greater than this modified date.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM your_table
WHERE your_date_column > date_value::date + INTERVAL '0 day';
Replace your_date_column with the name of the column containing the date datatype and your_table with the name of the table. Change date_value to the desired value found in the column.
Query:
SELECT * FROM sample_table
WHERE date_column > '2022-02-23'::date + INTERVAL '0 day';
Output:
 Output for Interval Keyword
Output for Interval KeywordExplanation: The query selects rows from "sample_table" with dates after '2022-02-23', including '2022-02-24', '2022-02-25', '2022-02-26', '2022-02-27'.
The DATE_PART function calculates the epoch values similarly to the EXTRACT method. It provides an alternative way to compare dates based on their epoch representations.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM your_table
WHERE DATE_PART('epoch', your_date_column) > DATE_PART('epoch', date_value::timestamp);
Replace your_date_column with the name of the column containing the date datatype and your_table with the name of the table. Change date_value to the desired value found in the column.
Query:
SELECT * FROM sample_table
WHERE DATE_PART('epoch', date_column) > DATE_PART('epoch', '2022-02-23'::timestamp);
Output:
 Output for Date_Part Function
Output for Date_Part FunctionExplanation: The query selects rows from "sample_table" with dates after '2022-02-23', including '2022-02-24', '2022-02-25', '2022-02-26', '2022-02-27'.
5. Using TO_DATE Function
The TO_DATE function converts the specified date string into a date type, allowing direct date comparisons. It's useful when the date format needs explicit conversion.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM your_table
WHERE your_date_column > TO_DATE(date_value, 'YYYY-MM-DD');
Replace your_date_column with the name of the column containing the date datatype and your_table with the name of the table. Change date_value to the desired value found in the column.
Query:
SELECT * FROM sample_table
WHERE date_column > TO_DATE('2022-02-23', 'YYYY-MM-DD');
Output:
 Output for TO_DATE Function
Output for TO_DATE FunctionExplanation: This query retrieves rows from "sample_table" where the "date_column" is later than '2022-02-23', displaying entries starting from '2022-02-24'. The TO_DATE function ensures accurate date comparisons.
Conclusion
In conclusion, querying for dates greater than a specific date in PostgreSQL offers multiple approaches, including standard operators, functions like 'EXTRACT' and 'DATE_PART', and the use of 'INTERVAL' and 'TO_DATE'. The choice among these methods depends on factors such as simplicity, performance, and specific use cases. PostgreSQL's diverse tools for date manipulation provide users with flexibility and efficiency in handling temporal data.