ORDER BY Statement in MariaDB
Last Updated :
01 Dec, 2023
In MariaDB, the ORDER BY clause is an important component for organizing the result set of a query in a certain order. Being aware of the complexities of ORDER BY can significantly improve your capacity to get and evaluate data effectively, regardless of whether you're working with one or more columns, ascending or descending sorting, or both. This article will explore the ORDER BY statement in MariaDB, including its syntax, uses, and best practices.
ORDER BY Clause
The results of a statement are sorted using the ORDER BY clause. It offers the choice to sort the data in either ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order and describes the sequence in which the data is performed. If the order is not specified, the order is assumed to be ascending.
Syntax:
SELECT field1, filed2, ... FROM table_name [WHERE condition] ORDER BY field1 [ASC | DESC], filed2 [ASC | DESC], ...;
- SELECT Clause: It specifies the columns you want to retrieve from the table.
- FROM Clause: It specifies the table from which the data will be retrieved.
- WHERE Clause: It filters the rows based on specific conditions.
- ORDER BY Clause: Sorts the result set in either descending (DESC) or ascending (ASC) order according to one or more columns.
Let's create a table products and insert some data into this
CREATE TABLE
Query:
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(100),
category VARCHAR(50),
unit_price DECIMAL(10, 2),
stock_quantity INT
);
INSERT DATA
Query:
INSERT INTO products VALUES
(1, 'Laptop', 'Electronics', 1200.00, 50),
(2, 'Smartphone', 'Electronics', 800.00, 100),
(3, 'Coffee Maker', 'Appliances', 50.00, 30),
(4, 'Backpack', 'Fashion', 40.00, 80),
(5, 'Desk Chair', 'Furniture', 150.00, 20);
Sorting Based on a Single Column in Ascending Order
Query:
SELECT * FROM products ORDER BY product_name ASC;
This pulls every column from the "products" table and arranges the result set in ascending alphabetical order by product name.
Output:
 ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY Clause
Sorting Based on a Single Column in Descending Order
Query:
SELECT product_name, unit_price FROM products ORDER BY unit_price DESC;
This extracts the unit prices and product names from the "products" table and arranges them according to the unit price in decreasing order.
Output:
 ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY Clause
Sorting Based on a Multiple Columns
Query:
SELECT * FROM products ORDER BY category ASC, unit_price DESC;
This arranges the result set in ascending order by category and descending order by unit price.
Output:
 ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY ClauseSorting by Column Number
SELECT product_name, category FROM products ORDER BY 1;
This retrieves the product name and category from the products table and sort the first selected column which is product_name.
Output:
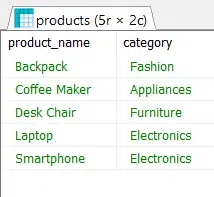 ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY ClauseSort and Filter Based on Stock Quantity
Query:
SELECT * FROM products WHERE category = 'Electronics' ORDER BY stock_quantity ;
The result set is sorted ascendingly by stock amount after retrieving every column for products in the "Electronics" category.
Note:
When using the ORDER BY clause, ASC is the default value.
Therefore, by default, the result will be sorted in ascending order in the ORDER BY clause if nothing is specified after the column name.
Output:
 ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY Clause
Conclusion
Using the ORDER BY statement in MariaDB is like to possessing superpowers when it comes to organizing and interpreting data from database queries. You may quickly arrange and analyze your data by following the examples provided below. It's like having a tool that allows you to filter information in the way that best suits your requirements. Try out multiple examples to figure out how this feature may help you get the most out of MariaDB until you get an idea of it.
Similar Reads
MariaDB INSERT Statement
MariaDB is a famous open-source relational database management system. It is renowned for its performance, scalability, and robust functions. One essential thing about operating with databases is the ability to insert information, and the INSERT statement plays a crucial role in this technique. In t
3 min read
What is Nested Select Statement in MariaDB
Nested select statements, normally named subqueries, represent an advanced feature for MariaDB which enables more efficient and thorough querying of the data. Therefore, the nesting of a SELECT statement within another allows us to perform operations and filtering that could be hardly possible with
4 min read
MariaDB UPDATE Statement
MariaDB uses SQL (Structured Query Language) and it is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) for managing and manipulating data. MariaDB is known for its high performance, even on large datasets. This makes it a good choice for applications that require fast data access. Maria
6 min read
Union Operator in MariaDB
MariaDB is an Open-Source Database system and MariaDB offers similar security features to MySQL, including access control, user authentication, and encryption. UNION operator is a fundamental part of MariaDB, a well-known database systeÂm. The UNION operator mergeÂs results from different SELECT que
5 min read
Show Tables in MariaDB
MariaDB is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). MariaDB is a very successful RDBMS that is known for its performance, scalability, and ease of use. When dealing with databases, understanding the structure and organization of their table type becomes important. MariaDB provid
4 min read
Truncate Table in MariaDB
MariaDB is an open-source relational database management system. It offers faster query execution and data manipulation as compared to other RDBMS. Also, it handles large datasets very efficiently. MariaDB Provides plugins for various functionalities like backup, performance monitoring, security, an
4 min read
Drop Table in MariaDB
MariaDB is one of the most widely used open-source relational database management systems, it offers many useful commands for manipulating database structures. It supports the same features that MySQL does but with additional features. Some of the most significant features are new storage engines, J
4 min read
Alter Table in MariaDB
MariaDB is an open-source RDBMS, that offers an extensive collection of features for handling database structures effectively. One important part of database management is changing tables to meet needs or improve performance. The ALTER TABLE command in MariaDB assists in these changes, allowing user
5 min read
Intersect Operator in MariaDB
MariaDB, a popular open-source relational database management system (RDBMS), offers a plethora of powerful features for data manipulation and querying. Among these features is the Intersect operator, a valuable tool for performing set operations on query results. In this article, We will learn bout
4 min read
Comparison Operator in MariaDB
In the world of database management, precise comparisons are essential for accurate data retrieval and manipulation. MariaDB, a powerful open-source relational database system, offers a range of comparison operators to help us filter and query our data effectively. In this article, We will learn abo
5 min read