Logical and Physical Address in Operating System
Last Updated :
24 May, 2024
A logical address is generated by the CPU while a program is running. The logical address is a virtual address as it does not exist physically, therefore, it is also known as a Virtual Address. The physical address describes the precise position of necessary data in a memory. Before they are used, the MMU must map the logical address to the physical address. In operating systems, logical and physical addresses are used to manage and access memory. Here is an overview of each in detail.
What is a Logical Address?
A logical address, also known as a virtual address, is an address generated by the CPU during program execution. It is the address seen by the process and is relative to the program's address space. The process accesses memory using logical addresses, which are translated by the operating system into physical addresses. An address that is created by the CPU while a program is running is known as a logical address. Because the logical address is virtual—that is, it doesn't exist physically—it is also referred to as such. The CPU uses this address as a reference to go to the actual memory location. All logical addresses created from a program's perspective are referred to as being in the "logical address space". This address is used as a reference to access the physical memory location by CPU. The term Logical Address Space is used for the set of all logical addresses generated by a program's perspective.
What is a Physical Address?
A physical address is the actual address in the main memory where data is stored. It is a location in physical memory, as opposed to a virtual address. Physical addresses are used by the Memory Management Unit (MMU) to translate logical addresses into physical addresses. The user must use the corresponding logical address to go to the physical address rather than directly accessing the physical address. For a computer program to function, physical memory space is required. Therefore, the logical address and physical address need to be mapped before the program is run.
The term "physical address" describes the precise position of necessary data in a memory. Before they are used, the MMU must map the logical address to the physical address. This is because the user program creates the logical address and believes that the program is operating in this logical address. However, the program requires physical memory to execute. All physical addresses that match the logical addresses in a logical address space are collectively referred to as the "physical address space"
The translation from logical to physical addresses is performed by the operating system's memory management unit (MMU) within the computer's hardware architecture. The MMU uses a page table to translate logical addresses into physical addresses. The page table maps each logical page number to a physical frame number. While the operating system plan this process, it's important to note that the MMU itself is a hardware component separate from the software-based elements of the operating system.
Similarities Between Logical and Physical Addresses in the Operating System
- Both logical and physical addresses are used to identify a specific location in memory.
- Both logical and physical addresses can be represented in different formats, such as binary, hexadecimal, or decimal.
- Both logical and physical addresses have a finite range, which is determined by the number of bits used to represent them.
Important Points about Logical and Physical Addresses in Operating Systems
- The use of logical addresses provides a layer of abstraction that allows processes to access memory without knowing the physical memory location.
- Logical addresses are mapped to physical addresses using a page table. The page table contains information about the mapping between logical and physical addresses.
- The MMU translates logical addresses into physical addresses using the page table. This translation is transparent to the process and is performed by hardware.
- The use of logical and physical addresses allows the operating system to manage memory more efficiently by using techniques such as paging and segmentation.
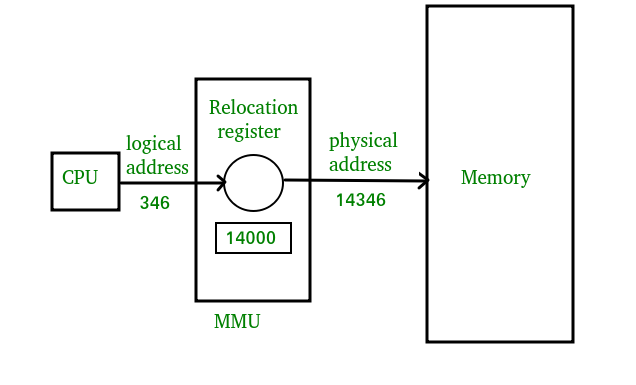
What is Memory Management Unit ?
The physical hardware of a computer that manages its virtual memory and caching functions is called the memory management unit (MMU). The MMU is sometimes housed in a separate Integrated Chip (IC), but it is typically found inside the central processing unit (CPU) of the computer. The MMU receives all inputs for data requests and decides whether to retrieve the data from ROM or RAM storage.
Difference Between Logical address and Physical Address
| Parameter | LOGICAL ADDRESS | PHYSICAL ADDRESS |
|---|
| Basic | generated by CPU | location in a memory unit |
| Address Space | Logical Address Space is set of all logical addresses generated by CPU in reference to a program. | Physical Address is set of all physical addresses mapped to the corresponding logical addresses. |
| Visibility | User can view the logical address of a program. | User can never view physical address of program. |
| Generation | generated by the CPU | Computed by MMU |
| Access | The user can use the logical address to access the physical address. | The user can indirectly access physical address but not directly. |
| Editable | Logical address can be change. | Physical address will not change. |
| Also called | virtual address. | real address. |
Some reference books on operating system concepts that cover logical and physical addressing include:
- "Operating System Concepts" by Abraham Silberschatz, Peter Baer Galvin, and Greg Gagne.
- "Modern Operating Systems" by Andrew S. Tanenbaum.
- "Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces" by Remzi H. Arpaci-Dusseau and Andrea C. Arpaci-Dusseau.
These books provide detailed coverage of operating system concepts, including memory management and addressing techniques.
Similar Reads
Physical and Logical File Systems 1. Physical files: Physical files contain the actual data that is stored on an iSeries system, and a description of how data is to be presented to or received from a program. They contain only one record format and one or more members. Records in database files can be described using either a field-
5 min read
Virtual Address Space in Operating System In operating systems, Virtual memory plays a very vital role, in managing the memory allotted to different processes and efficiently isolating the different memory addresses. The role of the virtual address is to assign a space to the ledger of all the virtual memory areas that are provided to diffe
5 min read
Hashed Page Tables in Operating System There are several common techniques for structuring page tables like Hierarchical Paging, Hashed Page Tables, and Inverted Page Tables. In this article, we will discuss the Hashed Page Table. Hashed Page Tables are a type of data structure used by operating systems to efficiently manage memory mappi
4 min read
Paging in Operating System Paging is the process of moving parts of a program, called pages, from secondary storage (like a hard drive) into the main memory (RAM). The main idea behind paging is to break a program into smaller fixed-size blocks called pages.To keep track of where each page is stored in memory, the operating s
8 min read
Address Binding and its Types Address Binding is the mapping of a physical address to a logical address known as a virtual address, it allocates a physical memory region to a logical pointer. In this article, We are going to cover address binding with the help of an example and Its types like compile time, load time, and executi
5 min read
Operating System as an Extended Machine The architecture of a computer is very primitive and awkward to program at the machine level language. So it is obvious that the user would not want to interact directly with the storage devices or hardware to get the work done. Example: Let's understand this thing more clearly with the help of an e
3 min read