JUnit Testing For MySQL Project in Java
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
For testing a software project, automated testing is always good and that will produce error-prone results. In the case of manual testing, there are possibilities of human errors. In this article let us take a sample project and let us see how to write JUnit test cases for it.
Example Project
Project Structure:

As this is the Maven-driven project, let us see
pom.xml
Relevant Maven dependency for JUnit. This has to be available in pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
XML
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>geeksforgeeks</groupId>
<artifactId>geeksforgeeks.jdbc.com</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>geeksforgeeks.jdbc.com</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- MySQL usage dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JUNIT dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Let us assume that MySQL got installed in the system and there is a database named "geeksforgeeks" is available

Let us see the important files of the project.
ds-connection.properties
# DataSource
ds.database-driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
ds.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/geeksforgeeks
ds.username=root
ds.password=***** # Provide your correct password
ConnectionClass.java
Java
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ConnectionClass {
public Connection getFileFromResources()
{
Properties prop = new Properties();
try {
prop.load(getClass().getResourceAsStream(
"/resources/ds-connection.properties"));
String dname
= (String)prop.get("ds.database-driver");
String dbConnUrl = (String)prop.get("ds.url");
String dbUserName
= (String)prop.get("ds.username");
String dbPassword
= (String)prop.get("ds.password");
Class.forName(dname);
Connection dbConn = DriverManager.getConnection(
dbConnUrl, dbUserName, dbPassword);
if (dbConn != null) {
System.out.println("Connection Successful");
}
else {
System.out.println(
"Failed to make connection!");
}
return dbConn;
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static void close(Connection conn)
{
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
}
catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(
"SQL Exception in close connection method");
}
}
}
public static void close(Statement stmt)
{
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
}
catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(
"SQL Exception in close statement method");
}
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet rSet)
{
if (rSet != null) {
try {
rSet.close();
}
catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(
"SQL Exception in close resultset method");
}
}
}
}
Model Class:
Freelancer.java
Each and every field should match with the corresponding freelancer table(MySQL) column
Java
public class Freelancer {
private int freelancerId;
private String freelancerName;
private int freelancerAge;
private int pricePerHour;
public int getFreelancerId() {
return freelancerId;
}
public void setFreelancerId(int freelancerId) {
this.freelancerId = freelancerId;
}
public String getFreelancerName() {
return freelancerName;
}
public void setFreelancerName(String freelancerName) {
this.freelancerName = freelancerName;
}
public int getFreelancerAge() {
return freelancerAge;
}
public void setFreelancerAge(int freelancerAge) {
this.freelancerAge = freelancerAge;
}
public int getPricePerHour() {
return pricePerHour;
}
public void setPricePerHour(int pricePerHour) {
this.pricePerHour = pricePerHour;
}
}
FreelancerQueries.java
Java
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class FreelancerQueries {
// To get all the rows of Freelancer table data and
// adding in the list
public List<Freelancer> listFreelancerDetails()
{
ConnectionClass connClass = new ConnectionClass();
Connection con = connClass.getFileFromResources();
List<Freelancer> list = new ArrayList<Freelancer>();
Freelancer freelancer = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Statement stmt = null;
// Write the SQL query
String query = "select * from freelancer";
try {
stmt = con.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery(query);
// Iterate the whole resultset and add the data
// in the list
while (rs.next()) {
freelancer = new Freelancer();
freelancer.setFreelancerId(rs.getInt(1));
freelancer.setFreelancerName(
rs.getString(2));
freelancer.setFreelancerAge(rs.getInt(3));
freelancer.setPricePerHour(rs.getInt(4));
// System.out.println(rs.getInt(1) + " " +
// rs.getString(2));
list.add(freelancer);
}
}
catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
connClass.close(con);
connClass.close(stmt);
connClass.close(rs);
}
return list;
}
// Retrieve Freelancer Name by Means of Freelancer Id
public String getFreelancerNameById(int freelancerId)
{
ConnectionClass connClass = new ConnectionClass();
Connection con = connClass.getFileFromResources();
PreparedStatement pStmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
String freelancerName = null;
try {
// Retrieve the row for the matching
// freelancerId
String query
= "select * from freelancer where freelancerId=?";
pStmt = con.prepareStatement(query);
pStmt.setInt(1, freelancerId);
rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
// Get the freelancerName
freelancerName = rs.getString(2);
System.out.println(rs.getString(2));
}
}
catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
connClass.close(con);
connClass.close(pStmt);
connClass.close(rs);
}
return freelancerName;
}
// Retrieve PriceOerHour for the given freelanceId
public int getFreelancerPricePerHour(int freelancerId)
{
ConnectionClass connClass = new ConnectionClass();
Connection con = connClass.getFileFromResources();
PreparedStatement pStmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
int pricePerHour = 0;
try {
String query
= "select * from freelancer where freelancerId=?";
pStmt = con.prepareStatement(query);
pStmt.setInt(1, freelancerId);
rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
pricePerHour = rs.getInt(4);
System.out.println(pricePerHour);
}
}
catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
connClass.close(con);
connClass.close(pStmt);
connClass.close(rs);
}
return pricePerHour;
}
}
Now, let us see the JUnit test case preparation file. Here we have to include positive, and negative scenarios for each and every requirement. Multiple assert statements we can write in a method and all should get passed and that will tell about our software code is correct in all aspects and for any test data, the written code will be correct.
AppTest.java
Each and every method has to start with @Test and inside the method, the methods written in "FreelancerQueries.java" should be called. Testcases can be written with
- assertEquals (Equality checking)
- assertNotEquals(Not equality checking)
- assertTrue(Checking for True) etc.,
Java
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotEquals;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
public class AppTest {
FreelancerQueries freelancerQueriesObject = new FreelancerQueries();
@Test
public void listFreelancerDetails_positive() {
List<Freelancer> listFreelancerDetails = freelancerQueriesObject.listFreelancerDetails();
// Checking whether totally 2 freelancers are available
assertEquals(listFreelancerDetails.size(), 2);
// Checking whether first freelancer id is 1
assertEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(0).getFreelancerId(),1);
// Checking whether first freelancer name is Freelancer A
assertEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(0).getFreelancerName(),"Freelancer A");
// Checking whether second freelancer age is 20
assertEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(1).getFreelancerAge(),20);
// Checking whether second freelancer price per hour is 2000
assertEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(1).getPricePerHour(),2000);
}
@Test
public void listFreelancerDetails_negative() {
List<Freelancer> listFreelancerDetails = freelancerQueriesObject.listFreelancerDetails();
// As this is negative testing we need to check with assertNotEquals
assertNotEquals(listFreelancerDetails.size(), 11);
// Checking whether first freelancer id is not 10
assertNotEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(0).getFreelancerId(),10);
// Checking whether first freelancer name is not Rachel
assertNotEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(0).getFreelancerName(),"Rachel");
// Checking whether second freelancer age is not 30
assertNotEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(1).getFreelancerAge(),30);
// Checking whether second freelancer price per hour is not 4000
assertNotEquals(listFreelancerDetails.get(0).getPricePerHour(),4000);
}
@Test
public void getFreelancerName_PositiveTestCase() {
String freelancerName = freelancerQueriesObject.getFreelancerNameById(1);
assertEquals(freelancerName, "Freelancer A");
freelancerName = freelancerQueriesObject.getFreelancerNameById(2);
assertEquals(freelancerName, "Freelancer B");
}
@Test
public void getdFreelancerName_NegativeTestCase() {
String freelancerName = freelancerQueriesObject.getFreelancerNameById(2);
assertNotEquals(freelancerName, "Phoebe");
}
@Test
public void getFirstFreelancerPricePerHour_PositiveTestCase() {
int pricePerHour = freelancerQueriesObject.getFreelancerPricePerHour(1);
assertEquals(pricePerHour, 1000);
}
@Test
public void getSecondFreelancerPricePerHour_NegativeTestCase() {
int pricePerHour = freelancerQueriesObject.getFreelancerPricePerHour(2);
assertNotEquals(pricePerHour, 5000);
}
}
Let us execute the JUnit test cases now. We have to run the test cases in the following way

Once everything is successful, we will get the output as follows

In cases of any error, it will be clearly indicated as follows :
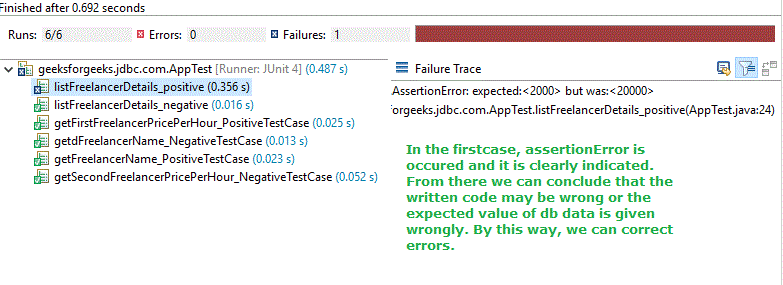
Conclusion
Testing with JUnit has become mandatory nowadays and in the software industry, software quality testing is handled by JUnit in these ways.