Iterative diagonal traversal of binary tree
Last Updated :
26 Sep, 2024
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to print the diagonal traversal of the binary tree.
Note: If the diagonal element are present in two different subtrees, then left subtree diagonal element should be taken first and then right subtree.
Example:
Input:
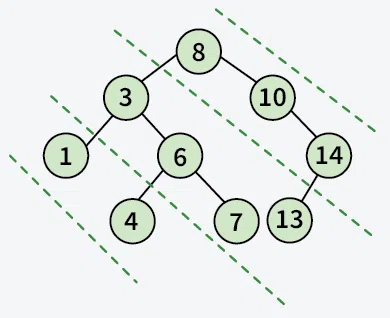
Output: 8 10 14 3 6 7 13 1 4
Explanation: The above is the diagonal elements in a binary tree that belong to the same line.
[Expected Approach - 1] Using Queue with delimiter - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to traverse the binary tree in level order manner using a queue. Push the root node and null pointer into the queue. For each node (starting from root), append its value to the resultant list. Push its left child node into queue if it exists, and set it to its right child node. If the current node is null, it means the starting of the next diagonal. So set the current node to the front node of the queue and pop from queue.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to print diagonal view
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node (int x) {
data = x;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
vector<int> diagonal(Node* root) {
vector<int> ans;
// base case
if (root == nullptr)
return ans;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
q.push(nullptr);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// if current is delimiter then insert another
// null for next diagonal
if (curr == nullptr) {
// if tree has been traversed
if (q.empty()) break;
q.push(nullptr);
}
// Else print the current diagonal
else {
while (curr != nullptr) {
ans.push_back(curr->data);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr->left != nullptr)
q.push(curr->left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr->right;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
void printList(vector<int> v) {
int n = v.size();
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
Node* root = new Node(8);
root->left = new Node(3);
root->right = new Node(10);
root->left->left = new Node(1);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(14);
root->right->right->left = new Node(13);
root->right->left->left = new Node(4);
root->right->left->right = new Node(7);
vector<int> ans = diagonal(root);
printList(ans);
}
// Java Program to print diagonal view
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
static ArrayList<Integer> diagonalPrint(Node root) {
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
// base case
if (root == null)
return ans;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
q.add(null);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = q.poll();
// if current is delimiter then insert another
// null for next diagonal
if (curr == null) {
// if tree has been traversed
if (q.isEmpty()) break;
q.add(null);
}
// Else print the current diagonal
else {
while (curr != null) {
ans.add(curr.data);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr.left != null)
q.add(curr.left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
static void printList(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.right.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.left.right = new Node(7);
ArrayList<Integer> ans = diagonalPrint(root);
printList(ans);
}
}
# Python Program to print diagonal view
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Iterative function to print diagonal view
def diagonal_print(root):
ans = []
if root is None:
return ans
q = []
q.append(root)
q.append(None)
while len(q) > 0:
curr = q.pop(0)
# if current is delimiter then insert another
# null for next diagonal
if curr is None:
# if tree has been traversed
if len(q) == 0:
break
q.append(None)
# Else print the current diagonal
else:
while curr is not None:
ans.append(curr.data)
# if left child is present
# push into queue
if curr.left is not None:
q.append(curr.left)
# current equals to right child
curr = curr.right
return ans
def print_list(v):
for i in range(len(v)):
print(v[i], end=" ")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Create a hard coded tree
# 8
# / \
# 3 10
# / / \
# 1 6 14
# / \ /
# 4 7 13
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.right.left.left = Node(4)
root.right.left.right = Node(7)
ans = diagonal_print(root)
print_list(ans)
// C# Program to print diagonal view
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
static List<int> DiagonalPrint(Node root) {
List<int> ans = new List<int>();
// base case
if (root == null)
return ans;
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
q.Enqueue(null);
while (q.Count > 0) {
Node curr = q.Dequeue();
// if current is delimiter then insert another
// null for next diagonal
if (curr == null) {
// if tree has been traversed
if (q.Count == 0) break;
q.Enqueue(null);
}
// Else print the current diagonal
else {
while (curr != null) {
ans.Add(curr.data);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr.left != null)
q.Enqueue(curr.left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
static void PrintList(List<int> v) {
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++) {
Console.Write(v[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main() {
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.right.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.left.right = new Node(7);
List<int> ans = DiagonalPrint(root);
PrintList(ans);
}
}
// JavaScript Program to print diagonal view
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.key = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
function diagonalPrint(root) {
let ans = [];
// base case
if (root === null)
return ans;
let q = [];
// push root
q.push(root);
// push delimiter
q.push(null);
while (q.length > 0) {
let curr = q.shift();
// if current is delimiter then insert another
// null for next diagonal
if (curr === null) {
// if tree has been traversed
if (q.length === 0) break;
q.push(null);
}
// Else print the current diagonal
else {
while (curr !== null) {
ans.push(curr.key);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr.left !== null)
q.push(curr.left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
function printList(v) {
for (let i = 0; i < v.length; i++) {
process.stdout.write(v[i] + " ");
}
console.log();
}
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
let root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.right.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.left.right = new Node(7);
let ans = diagonalPrint(root);
printList(ans);
Output8 10 14 3 6 7 13 1 4
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the total number of nodes in the binary tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
[Expected Approach - 2] Using Queue without delimiter - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is similar to level order traversal, use a queue, but here delimiter is not used. Little modification is to be done.
- if(curr.left != null), then add it to the queue and move curr pointer to right of curr.
- if curr = null, then remove a node from queue.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to print diagonal view
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node (int x) {
data = x;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
vector<int> diagonalPrint(Node* root) {
vector<int> ans;
// base case
if (root == nullptr)
return ans;
queue<Node*> q;
// push root
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
while (curr != nullptr) {
ans.push_back(curr->data);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr->left != nullptr)
q.push(curr->left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr->right;
}
}
return ans;
}
void printList(vector<int> v) {
int n = v.size();
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
Node* root = new Node(8);
root->left = new Node(3);
root->right = new Node(10);
root->left->left = new Node(1);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(14);
root->right->right->left = new Node(13);
root->right->left->left = new Node(4);
root->right->left->right = new Node(7);
vector<int> ans = diagonalPrint(root);
printList(ans);
}
// Java Program to print diagonal view
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
static ArrayList<Integer> diagonalPrint(Node root) {
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
// base case
if (root == null)
return ans;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
// push root
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = q.poll();
while (curr != null) {
ans.add(curr.data);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr.left != null)
q.add(curr.left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
static void printList(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.right.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.left.right = new Node(7);
ArrayList<Integer> ans = diagonalPrint(root);
printList(ans);
}
}
# Python Program to print diagonal view
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Iterative function to print diagonal view
def diagonal_print(root):
ans = []
# base case
if root is None:
return ans
q = []
# push root
q.append(root)
while len(q) > 0:
curr = q.pop(0)
while curr is not None:
ans.append(curr.data)
# if left child is present
# push into queue
if curr.left is not None:
q.append(curr.left)
# current equals to right child
curr = curr.right
return ans
def print_list(v):
for i in range(len(v)):
print(v[i], end=" ")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Create a hard coded tree
# 8
# / \
# 3 10
# / / \
# 1 6 14
# / \ /
# 4 7 13
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.right.left.left = Node(4)
root.right.left.right = Node(7)
ans = diagonal_print(root)
print_list(ans)
// C# Program to print diagonal view
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
static List<int> DiagonalPrint(Node root) {
List<int> ans = new List<int>();
// base case
if (root == null)
return ans;
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
// push root
q.Enqueue(root);
while (q.Count > 0) {
Node curr = q.Dequeue();
while (curr != null) {
ans.Add(curr.data);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr.left != null)
q.Enqueue(curr.left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
static void PrintList(List<int> v) {
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++) {
Console.Write(v[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main() {
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.right.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.left.right = new Node(7);
List<int> ans = DiagonalPrint(root);
PrintList(ans);
}
}
// JavaScript Program to print diagonal view
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.key = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
function diagonalPrint(root) {
let ans = [];
// base case
if (root === null)
return ans;
let q = [];
// push root
q.push(root);
while (q.length > 0) {
let curr = q.shift();
while (curr !== null) {
ans.push(curr.key);
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (curr.left !== null)
q.push(curr.left);
// current equals to right child
curr = curr.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
function printList(v) {
for (let i = 0; i < v.length; i++) {
process.stdout.write(v[i] + " ");
}
console.log();
}
// Create a hard coded tree
// 8
// / \
// 3 10
// / / \
// 1 6 14
// / \ /
// 4 7 13
let root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.right.left.left = new Node(4);
root.right.left.right = new Node(7);
let ans = diagonalPrint(root);
printList(ans);
Output8 10 14 3 6 7 13 1 4
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the total number of nodes in the binary tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Related articles:
Similar Reads
Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to print the diagonal traversal of the binary tree.Note: If the diagonal element are present in two different subtrees, then left subtree diagonal element should be taken first and then right subtree. Example:Input: Output: 8 10 14 3 6 7 13 1 4Explanation: The above
7 min read
Kth node in Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree and a value K. The task is to print the k-th node in the diagonal traversal of the binary tree. If no such node exists then print -1.Examples: Input : 8 / \ 3 10 / / \ 1 6 14 / \ / 4 7 13 k = 5 Output : 6 Diagonal Traversal of the above tree is: 8 10 14 3 6 7 13 1 4 Input : 1 / \
9 min read
Inorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Inorder traversal is a depth-first traversal method that follows this sequence:Left subtree is visited first.Root node is processed next.Right subtree is visited last.How does Inorder Traversal work?Key Properties:If applied to a Binary Search Tree (BST), it returns elements in sorted order.Ensures
5 min read
Boundary Traversal of binary tree
Given a binary tree, the task is to find the boundary nodes of the binary tree Anti-Clockwise starting from the root.The boundary includes:left boundary (nodes on left excluding leaf nodes)leaves (consist of only the leaf nodes)right boundary (nodes on right excluding leaf nodes)The left boundary is
15+ min read
Binary Tree Iterator for Inorder Traversal
Given a Binary Tree and an input array. The task is to create an Iterator that utilizes next() and hasNext() functions to perform Inorder traversal on the binary tree. Examples: Input: 8 Input Array = [next(), hasNext(), next(), next(), next(), hasNext(), next(), next(), hasNext()] / \ 3 9 / \ 2 4 \
13 min read
Double Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to find its Double Order Traversal. Double Order Traversal is a tree traversal technique in which every node is traversed twice in the following order: Visit the Node.Traverse the Left Subtree.Visit the Node.Traverse the Right Subtree.Examples:Input: Output: 1 7 4 4
6 min read
Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Preorder traversal is a tree traversal method that follows the Root-Left-Right order:The root node of the subtree is visited first.Next, the left subtree is recursively traversed.Finally, the right subtree is recursively traversed.How does Preorder Traversal work?Key Properties: Used in expression t
5 min read
Boundary Level order traversal of a Binary Tree
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to print all levels of this tree in Boundary Level order traversal. Boundary Level order traversal: In this traversal, the first element of the level (starting boundary) is printed first, followed by last element (ending boundary). Then the process is repeated for th
11 min read
Postorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Postorder traversal is a tree traversal method that follows the Left-Right-Root order:The left subtree is visited first.The right subtree is visited next.The root node is processed last.How does Postorder Traversal work?Key Properties:It is used for tree deletion because subtrees are deleted before
5 min read
Inorder traversal of an N-ary Tree
Given an N-ary tree containing, the task is to print the inorder traversal of the tree. Examples:Â Input: N = 3Â Â Output: 5 6 2 7 3 1 4Input: N = 3Â Â Output: 2 3 5 1 4 6Â Approach: The inorder traversal of an N-ary tree is defined as visiting all the children except the last then the root and finall
6 min read