How to Setup Encrypted Filesystems and Swap Space Using ‘Cryptsetup’ Tool in Linux
Last Updated :
02 Apr, 2025
An LFCE is in charge of the design, implementation, and continuous maintenance of the system architecture and is qualified and experienced to install, administer, and troubleshoot network services in Linux systems. Hard disc encryption for Linux Introduction to The Linux Foundation Certification Program for Linux Filesystem Encryption (LFCE). Encryption is designed to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing your sensitive data and to prevent it from becoming lost or stolen along with your computer or hard drive. Simply said, a key is used to "lock" access to your information, making it accessible only while the system is active and when a trusted person unlocks it. This means that if someone attempts to look at the standard kernel-level encryption tool, dm-crypt (short for device-mapper and cryptographic), will be covered in this article's discussion of how to set up encrypted file systems. Please be aware that dm-crypt can only be used to encrypt full devices, partitions, or loop devices because it is a block-level tool.
Encryption Preparation for a Drive, Partition, or Loop Device
Step 1: In Linux, create LFCS series partitions and filesystems.
# dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sdb bs=4096

Step 2: Testing for Support for Encryption
We must first confirm that our kernel has been built with support for encryption before moving on.
# grep -i config_dm_crypt /boot/config-$(uname -r)

Step 3: Installation of Cryptsetup
Cryptsetup is a frontend interface for creating, configuring, accessing, and managing encrypted file systems using dm-crypt
# aptitude update && aptitude install cryptsetup

Step 4: Constructing a Secure Partition
The default operating mode for cryptsetup is LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) therefore we’ll continue with that. Setting the LUKS partition and the passphrase will be our first step.
# cryptsetup -y luksFormat /dev/sdb1

Step 5: Cryptsetup Version
To know the version type the following command
# cryptsetup --version
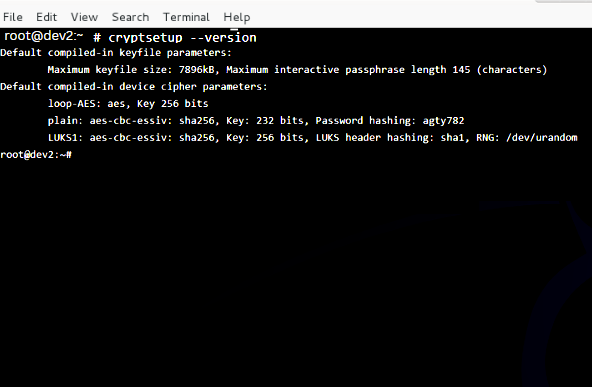
Testing Encryption
Step 1: Launch the LUKS partition and type the below command
# cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb1 my_encrypted_partition

Note: In this command, /dev/sdb1 is the encrypted partition, and my_encrypted_partition is a mapping name that you assign to the decrypted partition. You can replace my_encrypted_partition with any name you like. After entering this command, you will be prompted to enter the password that was used to encrypt the partition
Step 2: The partition be mounted as a standard file system
The partition should be mounted as a standard file system. It should serve as a warning. To get the partition run the following command.
# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/enc

Step 3: Create a dummy file inside the mount point.
# echo “This is article series about the LFCE certification” > /mnt/enc/testfile.txt

Step 4: Check to see whether you can open the newly produced file.
# cat /mnt/enc/testfile.txt

Step 5: Unmount the file system
# umount /mnt/enc

Step 6: Close the LUKS partition
# cryptsetup luksClose my_encrypted_partition

Step 7: The partition should be mounted as a standard file system. It should be an error indication.
# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/enc

Encrypting the Swap Space for Further Security
When the encrypted partition is open, the passphrase you previously provided to access it is kept in RAM memory. The data can be decrypted if someone can get his hands on this key. Since the RAM contents are stored on the swap partition while a laptop is in hibernation, doing this is extremely simple.
Step 1: Create a partition to be used as a swap with the appropriate size (/dev/sdd1 in our case) and encrypt it as explained earlier. Name it just “swap” for convenience.’
# swapon --show
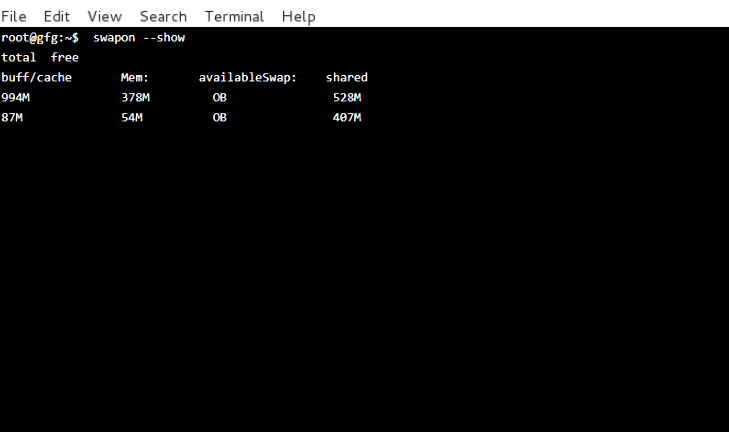
Step 2: Set it as swap and activate it
# mkswap /dev/mapper/swap
# swapon /dev/mapper/swap

Step 3: Next, change the corresponding entry in /etc/fstab
/dev/mapper/swap none swap sw 0 0

Step 4: Finally, edit /etc/crypttab and reboot
swap /dev/sdd1 /dev/urandom swap

Step 5: Once the system has finished booting, you can verify the status of the swap space:
# cryptsetup status swap

Conclusion:
For all of your data, you now have an encrypted partition. LUKS encrypts whole block devices, so it is ideal for securing the data on portable storage devices like USB flash drives and laptop hard drives. Additionally, you may utilize your NAS server to safeguard backups. AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard Instruction Set) equipped Intel and AMD processors can speed up dm-crypt-based encryption for Linux kernel versions 2.6.32 and higher. Hard disc encryption will speed up as a result. Works with the swap partition as well, allowing you to use the hibernation function (also known as suspend-to-disk), which copies the RAM contents to the swap partition before shutting off the computer. LUKS only allows for a maximum of 8 passwords, meaning that only 8 users can each have their own unique access keys.
Similar Reads
How to Use Cryptmount Utility to Create Encrypted Filesystems in Linux? Cryptmount a utility which allows user to access encrypted files, which is developed by Linux Operating Systems here they do not require root privileges. Cryptmount requires Linux Distributions with kernel 2.6 or later. Encrypted files and encrypted partitions, both are handled by Cryptmount. Simple
5 min read
Encrypting and Decrypting the Files Using GnuPG in Linux GnuPG is an encryption module that uses OpenPGP at its core. PGP stands for Pretty Good Privacy. It is an encryption program that provides authentication and cryptographic privacy for data communication. In the age where data is the new oil, the modern age thieves won't intrude in through doors, win
3 min read
Encrypt/Decrypt Files in Linux using Ccrypt Ccrypt is a command line tool for encryption and decryption of data. Ccrypt is based on the Rijndael cipher, the same cipher used in the AES standard. On the other hand, in the AES standard, a 128-bit block size is used, whereas ccrypt uses a 256-bit block size. Ccrypt commonly uses the .cpt file ex
3 min read
How to Encrypt and Decrypt Text in Android Using Cryptography? Cryptography is a technique of securing information and communications through the use of codes so that only those people for whom the information is intended can understand it and process it. Thus preventing unauthorized access to information. The prefix “crypt†means “hidden†and suffix graphy mea
15+ min read
Encrypt and Decrypt Files using Python Encryption is the process of converting readable data into an unreadable format to protect its contents. This is useful when storing or sharing sensitive information. In Python, we can encrypt and decrypt files using the cryptography library’s Fernet module, which uses symmetric encryption. This mea
3 min read
How to Create Btrfs Filesystem in Linux and its Features Btrfs was a project which was started back in 2007, it is a part of the Linux kernel. It is a copy-on-write filesystem that uses advanced features. It is highly scalable, and easy to maintain and repair. Since 2013 this file system is considered stable in the Linux kernel. The core and the most vita
5 min read