How to Save Data in Session and Local Storage [Full Guide]
Last Updated :
05 Apr, 2025
When working with web applications, session storage and local storage are essential tools for storing data on the client side. These storage mechanisms allow you to persist user data between page reloads or sessions, helping improve user experience and performance. Session storage is useful for temporary data that you want to persist only during a user's session, while local storage allows you to store data persistently across sessions. In this guide, we’ll show you how to easily save data in session storage and local storage using JavaScript.
What is Web Storage?
Web storage provides web applications with the ability to store data directly on a user’s device, and it's more efficient than cookies. There are two types of web storage in modern browsers:
- Session Storage: Data is stored for the duration of the page session and is cleared when the tab or browser is closed.
- Local Storage: Data is stored even after the browser or tab is closed and persists until the user clears it manually or through code.
Both types of storage are part of the Web Storage API and allow you to store data as key-value pairs.
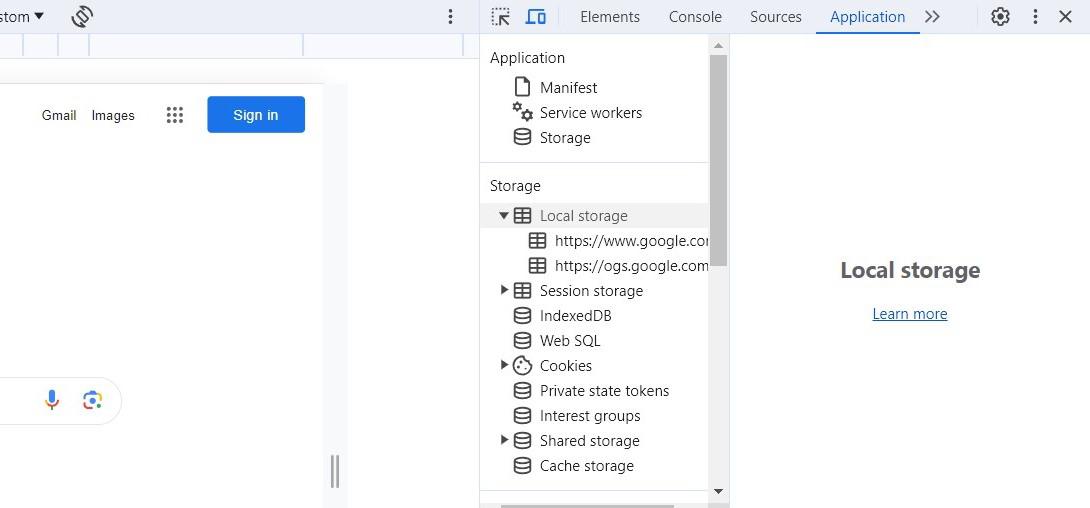
How to Open Session Storage and Local Storage in Developer Tools
If you're a web developer or just curious about how websites store data in your browser, Session Storage and Local Storage are two essential features to explore. Here's how you can access and inspect them in Google Chrome's Developer Tools.
Step 1: Open the Developer Console
- Launch Google Chrome on your computer and navigate to the webpage you want to inspect.
- Press F12 on your keyboard or right-click anywhere on the webpage and select Inspect to open the Developer Tools panel.
Step 2: Navigate to the Application Tab
In the Developer Tools panel, look at the top and click on the Application tab. This tab gives you access to various tools for managing and inspecting data related to the webpage, including storage options.
Step 3: Access the Storage Menu
- Once in the Application tab, you'll see a list of various sections on the left-hand side.
- Find and click on the Storage menu, which will display different types of storage used by the website, including Local Storage, Session Storage, Cookies, and more.
Step 4: View Data in Session Storage and Local Storage
- Under the Storage menu, you’ll see entries for Local Storage and Session Storage.
- Click on either one to explore their respective data. Local Storage persists even after the browser is closed, while Session Storage only lasts for the duration of the session (until the tab is closed).
Memory Capacity
- Session Storage: 5 MB
- Local Storage: 10 MB
Features of Session Storage :
- SessionStorage is used to store the session information of the user.
- A session is started when a user login or after visiting a web page.
- This session is said to be ended when the user signs out or closes the tab.
- Data persists if a page refreshes.
- This session storage data is automatically cleared by the browser when a session is ended.
- Data is stored in the form of key-value pairs.
- Each tab has its own session Storage. Other tabs or windows, even the same website or origin cannot access this data.
- Depending upon the browser, storage limit for a origin(domain + port + protocol) will be up to 5 MB on each tab.
Example: We visited a site A in Tab 1 , and the same site in Tab 2, each tab has it's own session storage up to 5 Mb. Other web pages from the same origin can use this data in that session.
When to use Session Storage?
- We want to store data only for a session.
- We want to maintain sessions.
- When dealing with transactions and sensitive information.
- When we do not want other tabs or windows to access or share the information.
- When we want the data to be erased when the session ends.
Methods of session storage object
sessionstorage.setItem(key,value); // Adds data in key-value pair
sessionstorage.getItem(key); // Gets the data for the given key
sessionStorage.removeItem(key); // Removes the (key, value) pair data for the given key
sessionstorage.key(index); // Gets the key based on the index position
sessionstorage.length; // Returns the length of the storage list.
sessionstorage.clear(); // Clears all the session storage
Demonstrating Session Storage
Example: The following example demonstrates session storage
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Session Storage Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Session Storage Example</h1>
<button onclick="setSessionData()">Set Session Data</button>
<button onclick="getSessionData()">Get Session Data</button>
<button onclick="clearSessionData()">Clear Session Data</button>
<button onclick="getSessionLength()">Get Session Length</button>
<button onclick="getSessionKey(1)">Get Session Data by Index</button>
<div id="output"></div>
<script>
// Function to set data in Session Storage
function setSessionData() {
sessionStorage.setItem("username", "JohnDoe");
sessionStorage.setItem("preferences", JSON.stringify({
theme: "dark", lang: "en"
}));
}
// Function to retrieve data from Session Storage
function getSessionData() {
let username = sessionStorage.getItem("username");
let preferences = JSON.parse(sessionStorage.getItem("preferences"));
document.getElementById("output").textContent =
"Username: " + username + ", Preferences: " + JSON.stringify(preferences);
}
// Function to clear all data from Session Storage
function clearSessionData() {
sessionStorage.clear();
document.getElementById("output")
.textContent = "Session Storage data cleared.";
}
// Function to get the length of Session Storage
function getSessionLength() {
let length = sessionStorage.length;
document.getElementById("output").textContent = "Session Storage length: "
+ length;
}
// Function to get Session Storage data by index
function getSessionKey(index) {
let key = sessionStorage.key(index);
let value = sessionStorage.getItem(key);
document.getElementById("output").textContent =
"Key at index " + index + ": " + key + ", Value: " + value;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output: In the left side of the screen, we are clicking on buttons which adds the data , modifies the data in sessionstorage and in the right side under application tab, we can see how this sessionstorage is getting modified.
Features of LocalStorage:
- LocalStorage is used to store the information of the user persistently in the browser.
- It does not get cleared unless JavaScript code running on that website deletes it or we erase it using browser settings.
- Data stored in local storage is not sent for the server upon every request.
- Data is not lost even if we close the browser, or restart the computer.
- Data is stored in the form of key- value pairs.
- The web pages from the same origin in the other tabs/windows can also use this local storage data.
- Depending upon the browser, storage limit for a origin(domain + port + protocol) will be up to 10 MB.
Example: We visited a site in Tab 1 and the same site in Tab 2 or another window. We stored some data from each tab or window; they are centrally stored at the same place (unlike for sessionstorage, where each tab has its own storage even though the origin is the same) and can be accessed from all the web pages originating from the same origin in the same tab.
When to use LocalStorage?
- We want to store data persistently.
- When we do not want to lose data if the tab or browser is closed.
- Want to store user activity and track user actions.
- Need not maintain sessions.
- Other tabs or windows can access the stored data, which can be shared with other tabs or windows with the same origin.
The browser provides local storage and session storage objects to work with. We use the objects to store and manage the data.
Methods of localstorage object
localStorage.setItem(key,value); // Adds data in key-value pair
localStorage.getItem(key); // Gets the data for the given key
localStorage.removeItem(key); // Removes the (key, value) pair data for the given key
localStorage.key(index); // Gets the key based on the index position
localStorage.length; // Returns the lenght of the storage list
localStorage.clear(); // Clears all the local storage associated with the origin.
Demonstrating LocalStorage Object
Example: The following example demonstrates Local Storage object
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Local Storage Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Local Storage Example</h1>
<button onclick="setLocalData()">Set Local Data</button>
<button onclick="getLocalData()">Get Local Data</button>
<button onclick="clearLocalData()">Clear Local Data</button>
<button onclick="getLocalLength()">Get Local Length</button>
<button onclick="getLocalKey(0)">Get Local Data by Index</button>
<div id="output"></div>
<script>
// Function to append content to output
function appendToOutput(content) {
let output = document.getElementById("output");
let existingContent = output.innerHTML;
output.innerHTML = existingContent + "<br>" + content;
}
// Function to set data in Local Storage
function setLocalData() {
localStorage.setItem("name", "Alice");
let preferences = { theme: "light", lang: "fr" };
localStorage.setItem("preferences", JSON.stringify(preferences));
appendToOutput("Local data set: Name: Alice, Preferences: " + JSON.stringify(preferences));
}
// Function to retrieve data from Local Storage
function getLocalData() {
let name = localStorage.getItem("name");
let preferences = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("preferences"));
appendToOutput("Local data retrieved: Name: " + name + ", Preferences: " + JSON.stringify(preferences));
}
// Function to clear all data from Local Storage
function clearLocalData() {
localStorage.clear();
appendToOutput("Local Storage data cleared.");
}
// Function to get the length of Local Storage
function getLocalLength() {
let length = localStorage.length;
appendToOutput("Local Storage length: " + length);
}
// Function to get Local Storage data by index
function getLocalKey(index) {
let key = localStorage.key(index);
let value = localStorage.getItem(key);
appendToOutput("Key at index " + index + ": " + key + ", Value: " + value);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output: In the left side of the screen, we are clicking on buttons which adds the data , modifies the data in localstorage and in the right side under application tab, we can see how this localstorage is getting modified..
Key Differences Between Session Storage and Local Storage
| Feature | Session Storage | Local Storage |
|---|
| Duration | Data is cleared when the page or tab is closed | Data persists until manually cleared or through code |
| Scope | Available only within the current tab or window | Available across tabs and windows |
| Storage Limit | 5MB per domain (varies by browser) | 5MB per domain (varies by browser) |
| Data Access | Can only be accessed within the current session | Can be accessed across sessions |
| Use Case | Temporarily store data for the current session | Store data that needs to persist across sessions |
Common Use Cases for Session and Local Storage
Session Storage Use Cases:
- Single-Session Forms: Store form data temporarily as users navigate between pages.
- Temporary Preferences: For example, language selection or filtering preferences during a session.
- Shopping Cart: Store cart data that disappears once the user exits the session.
Local Storage Use Cases:
- User Authentication: Save login states or authentication tokens between sessions.
- User Preferences: Retain settings like dark mode or language preferences across browser sessions.
- Progress Tracking: Store the progress of a multi-step form or survey.
Security Considerations
While session and local storage are helpful for many tasks, they do come with some important security considerations:
- Storage Limitations: Both session and local storage have limited capacity (about 5MB), so they should only be used for small amounts of data.
- Data Persistence: Data in local storage persists even after the user closes the browser. Be cautious about storing sensitive information, as this data is easily accessible by anyone using the device.
- No Encryption: Data stored in both session and local storage is not encrypted. For sensitive data, consider using encrypted storage methods or server-side storage solutions.
Conclusion
Saving data in session storage and local storage is a simple and effective way to enhance web applications by storing temporary or persistent information directly on the client side. Use session storage for short-term data that should disappear after the session ends, and local storage for long-term data that should remain accessible even after the browser is closed. By understanding how to leverage these storage options, you can create more interactive and efficient web applications.
Similar Reads
How to store an array in localStorage ?
To store an array in localStorage refers to saving an array of data in the web browser’s storage that persists across sessions. This is useful for keeping data, like user preferences or temporary information, accessible even after refreshing the page or reopening the browser. What is Javascript loca
3 min read
How to Save Data in Local Storage in JavaScript ?
LocalStorage is a client-side web storage mechanism provided by JavaScript, which allows developers to store key-value pairs directly in the user's browser. Unlike cookies, LocalStorage is persistent—data stored remains even after the browser is closed and reopened, making it ideal for retaining use
2 min read
Difference Between Local Storage, Session Storage And Cookies
The HTTP protocol is one of the most important protocols for smooth communication between the server and the client. The main disadvantage of the HTTP protocol is that it is a stateless protocol, which means it does not track any kind of response or request by the server or the client. So, to resolv
6 min read
How to Store Data in Local Storage using AngularJS ?
Angular JS is a typescript-based web application framework. It is supported by the Angular team of Google and open-source developers. It is a component-based framework allowing the developers to reuse the components created. It is well-suited for large and complex applications because of its well-de
5 min read
How to View and Edit local Storage in Microsoft Edge Browser
Local Storage in Microsoft Edge is a key component for web developers, allowing websites to store data locally in the user's browser. This feature is especially useful for saving preferences, session data, or even small-scale databases that need to persist between sessions. If you're looking to view
5 min read
How to Persist Data in Distributed Storage?
Do you know how your files stay safe and accessible in the digital world? It's all because of distributed storage systems. But what keeps your data from disappearing into thin air? That's where data persistence comes in. In this article, we'll break down the basics of how your data sticks around in
8 min read
How to Manage Sessions and Cookies in Express JS?
Express is a small framework that sits on top of NodeJS web server functionality to simplify its APIs and add helpful new features. It makes it easier to organize your application’s functionality with middleware and routing. It adds helpful utilities to NodeJS HTTP objects, it helps the rendering of
4 min read
How to Store an Object sent by a Function in JavaScript ?
When a function in JavaScript returns an object, there are several ways to store this returned object for later use. These objects can be stored in variables, array elements, or properties of other objects. Essentially, any data structure capable of holding values can store the returned object. Tabl
2 min read
How to save and load cookies in Selenium using Python
In web automation and testing, maintaining session information across different runs of scripts is often necessary. Cookies are a great way to save session data to avoid logging in repeatedly. Selenium, a popular tool for web testing, provides straightforward ways to save and load cookies using Pyth
4 min read
How to Store Username and Password in Flask
This article covers storing usernames and passwords in a Flask web app using MySQL. After logging in, users see a welcome message with their username. InstallationTo make our project we first create a virtual environment, to learn how to create and activate a virtual environment, refer to - Python v
6 min read