How To Host Tomcat In Kubernetes?
Last Updated :
15 Mar, 2024
A popular technique for deploying Java-based web applications that can be scaled using containers is to host Apache Tomcat on a Kubernetes server. You can scale and manage containerized apps with the aid of Kubernetes.
What Is Tomcat?
Apache Tomcat server: Apache Tomcat is a web container. It allows the users to run Servlet and JAVA Server Pages that are based on the web applications. It can be used as an HTTP server. The performance of the Tomcat server is not as good as the designated web server. It can be used as a separate product with its internal Web server. It can also be used as mutually with the other Web-servers which include Apache, Microsoft Internet Information Server, and Microsoft Personal Web-server.
Why To Host Tomcat On Kubernetes?
There are various benefits to running Tomcat on Kubernetes when it comes to delivering and maintaining Java-based web applications. The following are some advantages of Tomcat hosting on Kubernetes:
- Container Orchestration
- Scalability
- Resource Management
- Isolation and Encapsulation
- Declarative Configuration
Step-by-Step Guide To Setup Tomcat On Kubernetes Cluster
Step 1: Create Namespace
You have two options for hosting Tomcat: either make your namespace or use the Kubernetes cluster's default namespace. I was in the process of establishing my namespace, which I wanted to use for deploying my application.
Create a namespace using the command
kubectl create namespace <namespace-name>
kubectl create namespace tomcat-ps
Create a namespace using the YAML
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: tomcat-ps
labels:
team: prod-team
.webp)
Step 2: Create Tomcat pod
Creating a Tomcat pod in Kubernetes involves defining a YAML configuration file that describes the pod's specifications. Below are the steps and an explanation for creating a simple Tomcat pod:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: tomcatapp
namespace: tomcat-ps
labels:
app: tomcatapp
spec:
containers:
- name: tomcat
image: tomcat:latest # image
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
Explanation of the YAML:
- apiVersion: Specifies the Kubernetes API version being used.
- kind: Indicates the type of resource being created, in this case, a Pod.
- metadata: Contains metadata about the Pod, including its name.
- spec: Describes the specification of the Pod.
- containers: Defines the containers running in the Pod.
- name: Specifies the name of the container.
- image: Specifies the Docker image to use for the Tomcat container (in this case, tomcat:latest).
- ports: Specifies the ports to expose on the container.
Step 3: Create NodePort Service for tomcat
To expose the Tomcat pod using a NodePort service in Kubernetes, you'll need to create a service configuration file. Below are the steps to create a NodePort service for the Tomcat pod:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: tomcatappsvc
namespace: tomcat-ps
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: tomcatapp
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
Kubernetes allows us to mention the service and pod yaml in single file.
Explanation of each section:
- apiVersion: v1: Specifies the Kubernetes API version being used. In this case, it's version 1.
- kind: Service: Indicates the type of resource being created, which is a Service. A Service in Kubernetes provides a way to expose a set of Pods as a network service.
- metadata: Contains metadata about the service, including its name (tomcatappsvc) and the namespace (tomcat-ps) in which it should be created.
- spec: Describes the specification of the service, defining its behavior and how it should route traffic to the associated Pods.
- type: NodePort: Specifies the type of service. In this case, it's a NodePort service. NodePort services make a specific port on each node in the cluster accessible externally. The service will be reachable on a randomly assigned port within a specified range (usually 30000-32767).
- selector: Identifies the Pods that this service will route traffic to. In this example, it selects Pods with the label app: tomcatapp. This label is used to match the service with the corresponding Pods.
- ports: Specifies the ports to expose on the service.
- port: 80: Defines the port on the service itself. In this case, it's port 80, the standard port for HTTP traffic.
- targetPort: 8080: Specifies the port on the Pods to which traffic should be forwarded. In this example, it's port 8080, which is a common port for Tomcat applications.
In summary, this Service configuration (tomcatappsvc) creates a NodePort service in the tomcat-ps namespace. The service will route external traffic on port 80 to the Pods with the label app: tomcatapp on port 8080. Ensure that your Tomcat Pods have the specified label (app: tomcatapp) so that they are correctly associated with this service.
.webp)
Step 4: List every pod in the namespace you defined by applying the yaml file in Kubernetes.
For that use the following command.
kubectl get all -n <namespace>
Namespace you have created: List all the pods in it.
kubectl get all -n tomcat-ps
.webp)
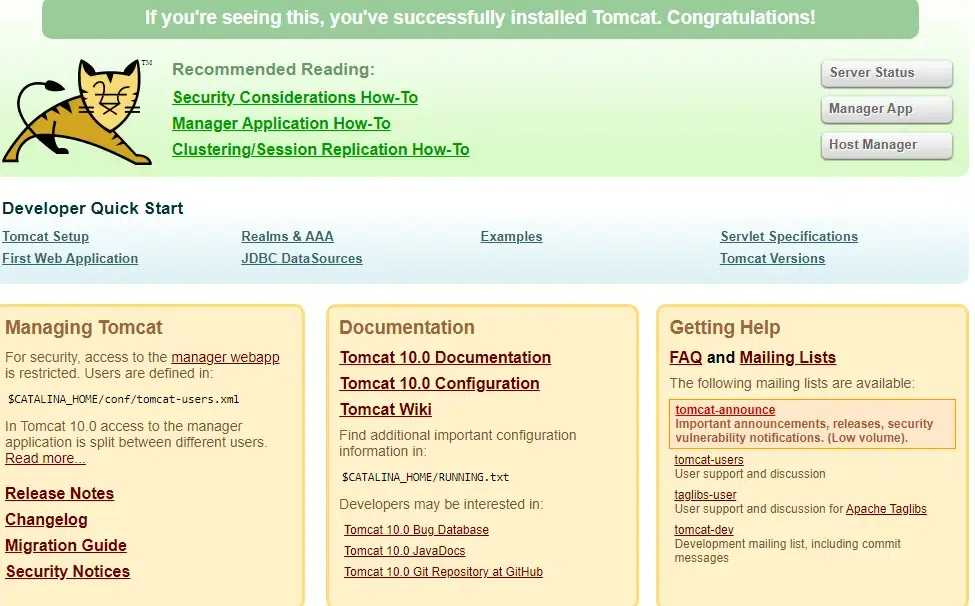
The screenshot above shows that the Tomcat pod is now operating on port "32014".
Step 5: Accessthe Tomcat from the internet.
http://IPaddress:<port number>
Similar Reads
How To Stop Pod In Kubernetes ?
In the Kubernetes cluster stopping a pod is typically deleting the pod. Pods are meant to be ephemeral, meaning they can be created, destroyed, and replaced dynamically as needed. When the pod is deleted in Kubernetes the resources associated with the pod will be released. What Is Kubernetes Pod? In
5 min read
How To Host Website On Tomcat Server ?
Deploying a website on a Tomcat server is a direct interaction that permits you to host and manage web applications built by utiliz ng Java innovations. Apache Tomcat, commonly referred to as Tomcat, is an open-source web server and servlet container created by the Apache Software Foundation. It is
6 min read
How to Restart Container in Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is a platform for container orchestration created to simplify application deployment, scaling, and administration. Suppose you have a big package of LEGO parts and you want to use them to make something very spectacular. But as your LEGO creation becomes larger, it becomes harder to organ
8 min read
How To Deploy Nginx In Kubernetes ?
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration tool used to deploy, scale, and manage containerized applications. On the other hand, NGINX is a web service used for proxying and load balancing. Here in this article, I have first discussed what is Kubernetes and its features. Then I have discus
8 min read
How to Careate Static Pod in Kubernetes ?
Static pods in Kubernetes make it simple to run pods directly on individual cluster nodes without the Kubernetes API server being involved. Not at all like ordinary pods oversaw by the Kubernetes control plane, static pods are characterized and overseen straight by the Kubelet, the essential node ag
7 min read
How to Resart Pod In kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration tool that helps in scaling, deploying, and managing containerized applications. In Kubernetes, the pods are the smallest deployable unit. In this guide, I will first discuss what Kubernetes is. Then I will discuss what is pods in Kubernetes. After
5 min read
How to Setup Jenkins on Kubernetes Cluster
Setting up Jenkins on a Kubernetes cluster is an efficient way to automate your CI/CD pipelines and streamline your software development lifecycle. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of installing Jenkins on Kubernetes, why you should do it, and the steps you need to follow to make
7 min read
How To Use Kind To Deploy Kubernetes Clusters?
Kind also referred to as Kubernetes in Docker is a popular open-source tool used for running a Kubernetes cluster locally. Kind uses Docker containers as Cluster Nodes making it substantially faster than its alternatives like Minikube or Docker Desktop which uses a Virtual Machine. Kind is commonly
10 min read
How to Deploy Kubernetes on AWS?
Kubernetes, the open-supply box orchestration platform, has emerged as the solution for dealing with containerized applications. When deploying Kubernetes in the cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS) gives a robust and scalable environment. In this manual, we can walk you through the manner of deploying
7 min read
How to Deploy Kubernetes on GCP?
Kubernetes, the open-supply field orchestration platform, has emerged as the standard for coping with containerized applications. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides a robust and scalable surrounding for deploying Kubernetes clusters. In this comprehensive manual, we are able to walk you through th
5 min read