How to Format USB Drives On Linux
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
It may be essential to format the USB device on occasion (for example, when changing the file system or deleting data). Many Linux users, on the other hand, are hesitant to begin the formatting process, believing it to be either difficult or time-consuming.
We'll learn how to format a USB drive in Linux using three quick and easy methods in this tutorial:
- Using the Disks Application
- Using the GParted tool
- Using the Terminal
Format a USB Drive on Linux
Method 1: Using the Disks Application
Step 1: Launch the 'Disks' app on our Linux Operating System.
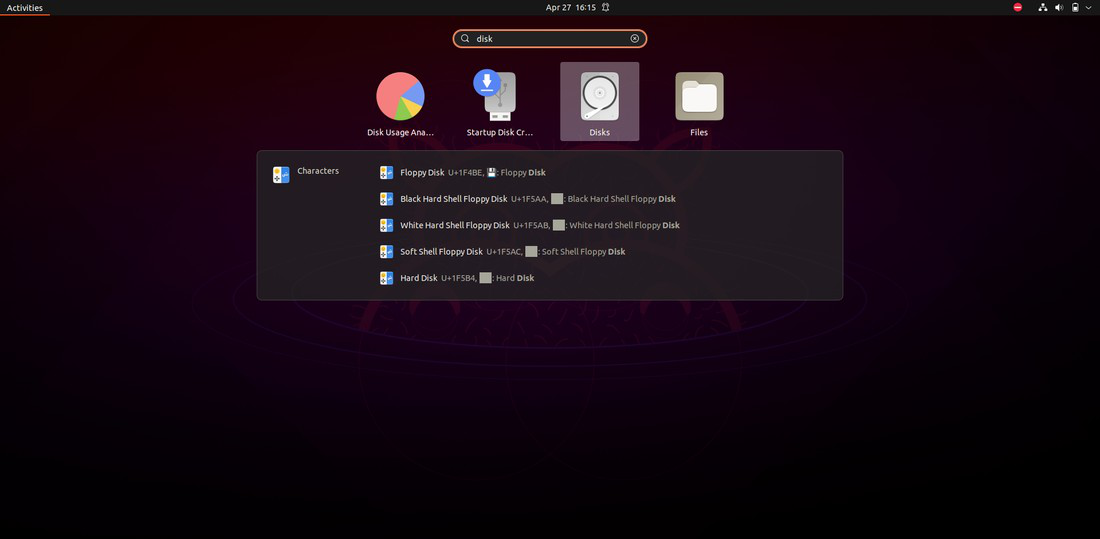
Step 2: From the list on the left, choose our USB Drive.

Step 3: On the right panel, below the USB Drive, select the 'Additional Partition Options' button, as seen in the image below.

Step 4: From the menu, select 'Format Partition Option,' as seen in the screenshot below.

Step 5: Now type in a new name for our formatted USB drive and choose 'FAT' as the 'type' so that you may use it with any operating system, then click 'Next' as shown below.

Step 6: Click on the Format button for formatting the USB.

Our USB drive has been successfully formatted.
Method 2: Using the GParted tool
Step 1: If you don't already have 'GParted' installed on our computer, you can do so with the apt command.
sudo apt install gparted

Step 2: Use the following command to start the 'GParted' utility.
sudo gparted

Select our USB drive from the list in the top right corner once the software has started.
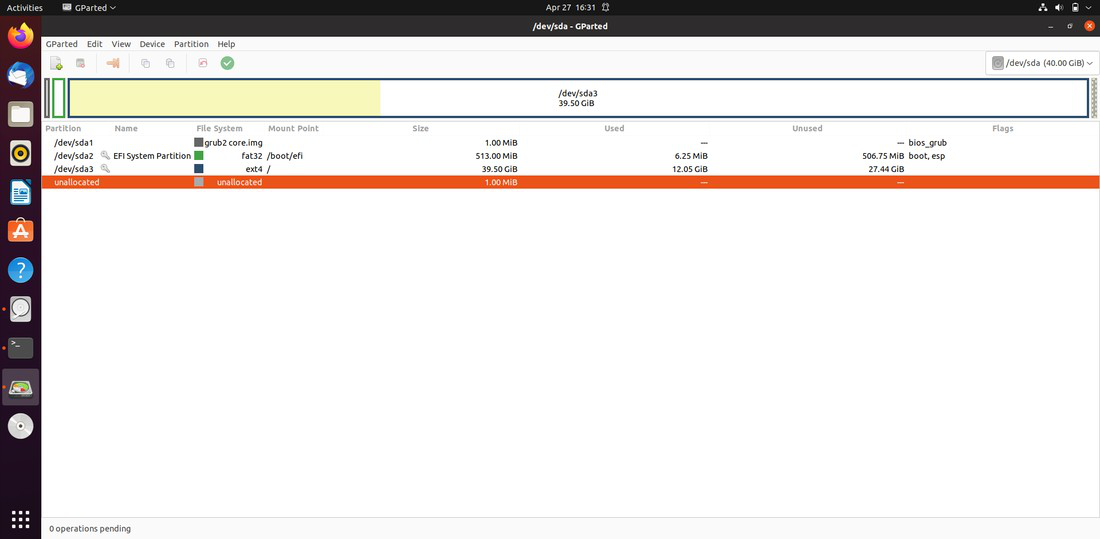
Step 3: To begin formatting, select the 'Format to' option from the 'right-click menu on the drive. Choose 'FAT32' from the drop-down selection.

Step 4: On the top menu, select the "green-colored" 'Tick' button.
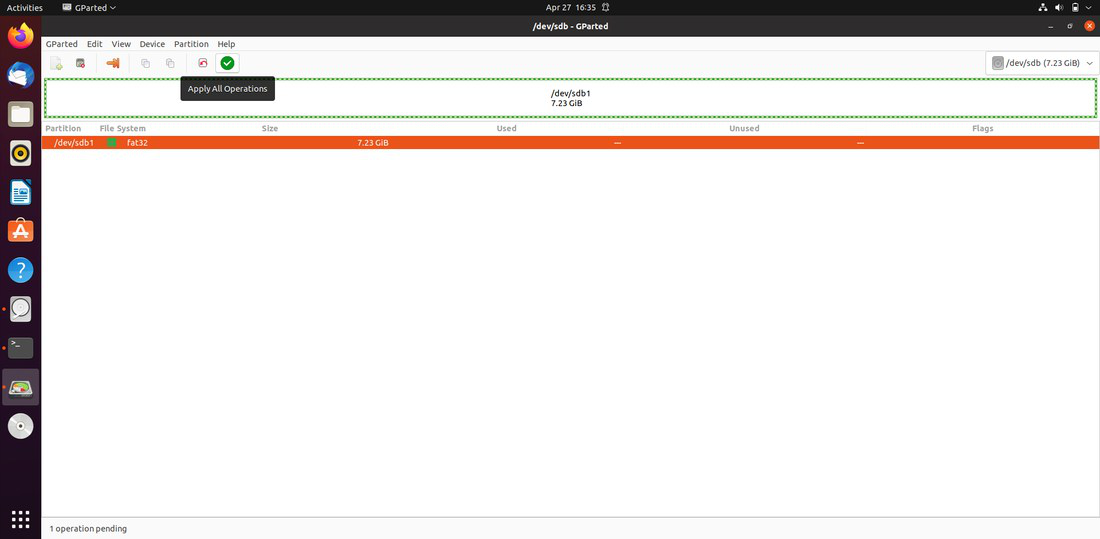
Step 5: Wait for the procedure to finish before clicking 'Apply.'

Now the process of formatting begins if we change our mind then click to 'Cancel' button to stop the formatting process.

Now, Our USB finally gets Formatted.
Method 3: Using the Terminal
Step 1: The first step is to open the terminal. CTRL + SHIFT + T is the default keyboard shortcut for launching the Terminal. And then run the command below.
df

Step 2: The terminal outputs a list of all mounted partitions, together with the following data: utilized space, available space, used space percentage, and path.
Step 3: Use the following command to unmount the USB disc.
sudo umount /dev/sdb1

Step 4: Use the following command to format the USB drive using the FAT32 file system (which is compatible with all operating systems).
sudo mkfs.ntfs /dev/sdb1

Step 5: Run the following command to see if the USB has been correctly formatted.
sudo fsck /dev/sdb1

The presence of 0 files on our USB drive shows that our device was successfully formatted.

Similar Reads
How to Format a Hard Drive in Windows? Formatting a hard drive in Windows is a crucial task that prepares the drive for data storage, resolves system errors, and clears unwanted data. Whether you're setting up a new hard drive, cleaning an old one, or solving file system issues, knowing how to format your drive correctly is essential. Th
4 min read
Formatting the Drive in Linux Formatting drives is easy(if you know what you are doing) in Linux but with a tiny mistake, you can lose data or due to wrong formatting you may also corrupt some important files. So in this article, we will tell you about some basic formatting commands in Linux. Even though you can use number graph
7 min read
How to Mount and Unmount Drives on Linux In the Linux operating system, everything is treated as a file. Every Linux administrator must know how to organize and access files better. In this article, we will learn about the Mount and Unmount commands.What are mounting and unmounting in Linux?Mounting and Unmounting are essential tasks in an
4 min read
How to Recover Deleted Files Using Foremost in Linux? Foremost is a digital forensic application that is used to recover lost or deleted files. Foremost can recover the files for hard disk, memory card, pen drive, and another mode of memory devices easily. It can also work on the image files that are being generated by any other Application. It is a fr
3 min read
How to Format a Write–Protected Pen Drive? When you receive the error "The disk is write-protected", it means you tried formatting your Pendrive but were not able to. This may be due to external software or encryption that was probably used to lock the contents of the Pendrive and the contents within the drive are read-only. In this case, th
3 min read
How to Create Bootable USB for Arch Linux? A bootable USB or live USB is a USB flash drive that contains a bootable operating system. We create these USB flash drives when we wanted to refresh or change our operating system. Let's discuss how we can create a Bootable USB flash drive for Arch Linux. Download the Arch ISO image from the Arch d
2 min read