How to Find the Length of a Series Using Window Functions in SQL
Last Updated :
30 Apr, 2024
In data analysis, understanding the sequential patterns within datasets is crucial for informed decision-making. SQL's window functions offer a powerful toolset for such tasks, allowing efficient calculations across related rows. This article delves into utilizing window functions to determine the length of series within datasets.
Beginning with an overview of window functions, we delve into practical examples, showcasing their efficacy in finding consecutive series of numbers. Additionally, we explore scenarios where gap thresholds between values are considered, highlighting the versatility of SQL window functions in addressing diverse analytical requirements.
Window Functions
The Window function in SQL operates on a set of rows related to the current row. They allow you to perform calculations across a subset of rows, without collapsing the result into a single value. They also known as windowing or analytic functions, operate on a set of related values of a row to the current row. This makes them perfect for tasks like series length determination.
Examples of Finding a Length of a Series Using Window Functions
Let's start by creating a table inserting some data into it and then performing some queries to find the length of a series using window functions.
CREATE TABLE series_data (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
value INT
);
-- Insert some sample data
INSERT INTO series_data (value) VALUES
(1), (2), (3), (5), (6), (8), (9), (10), (12);
Output:
You can see the content of the table by executing the below command:
SELECT * FROM series_data;
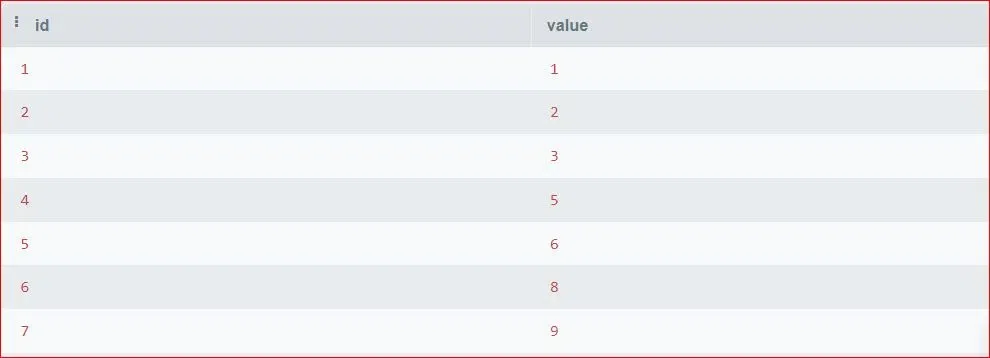 Series Data Table
Series Data TableNow, let's proceed with two examples of finding the length of a series using window functions:
Example 1: Finding the Length of Consecutive Series
In this example, we'll find the length of consecutive series of numbers in the value column.
SELECT
value,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY grp ORDER BY id) AS series_length
FROM (
SELECT
value,
id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY id) -
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY value ORDER BY id) AS grp
FROM
series_data
) AS subquery
ORDER BY
id;
Explanation:
Inner Subquery:
We start by selecting the value and id columns from the series_data table.
- Within this subquery, we use window functions:
- ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY id): This assigns a sequential row number to each row in the result set, ordered by the id column.
- ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY value ORDER BY id): This assigns a sequential row number to each row within each distinct value partition, ordered by the id column. This effectively groups consecutive values together.
- We calculate the difference between these row numbers for each row, effectively creating a grouping identifier (grp). When the values are consecutive, the difference will be constant, creating a unique group identifier for each consecutive series.
Outer Query:
- We select the value column and apply another ROW_NUMBER() function over the partition defined by the grp column.
- This function calculates the length of each series within its respective group, providing the length of consecutive series.
Output:
This output indicates that each value in the dataset forms a series of length 1, as there are no consecutive sequences of numbers.
 Length of Consecutive Series
Length of Consecutive SeriesExample 2: Finding the Length of Series with a Gap Threshold
In this example, we'll find the length of series of numbers in the value column, considering only series with a maximum gap of 1 between consecutive values.
SELECT
value,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY grp ORDER BY id) AS series_length
FROM (
SELECT
value,
id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY id) -
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY CASE WHEN id - LAG(id) OVER (ORDER BY id) <= 1 THEN value END ORDER BY id) AS grp
FROM
series_data
) AS subquery
ORDER BY
id;
Explanation:
Inner Subquery:
- Similar to Example 1, we select the value and id columns from the series_data table.
- Within this subquery, we use additional window functions:
- LAG(id) OVER (ORDER BY id): This accesses the id value of the previous row in the ordered sequence.
- CASE WHEN id - LAG(id) OVER (ORDER BY id) <= 1 THEN value END: This conditionally assigns the value when the gap between the current id and the previous id is less than or equal to 1.
- By partitioning with this modified condition, we group only consecutive values within a threshold of 1.
Outer Query:
- Similar to Example 1, we select the value column and apply another ROW_NUMBER() function over the partition defined by the grp column.
- This function calculates the length of each series within its respective group, providing the length of series with a gap threshold of 1 between consecutive values.
Output:
This output indicates the length of each series of consecutive numbers in the dataset. In this case, the consecutive series are:
- Series starting with 1, 2, and 3 has a length of 3.
- Series starting with 5 and 6 has a length of 2.
- Series starting with 8, 9, and 10 has a length of 3.
- The value 12 forms a series of length 1 as it is not followed by consecutive numbers.
 Length of Series with a Gap Threshold
Length of Series with a Gap ThresholdConclusion
In summary, SQL window functions are an immensely valuable feature which facilitates advanced analytical operations in an effortless and time-effective way. With these as the core, we are ready to do complex data manipulation and rendering data output in a visually appealing manner. Whether it is calculating the length of series or performing aggregation on data, or performing time-based calculations, window function helps sql developers and analysts to address complex problems in a precise and neat manner.
Similar Reads
Find the Length of a Series Using Window Functions in SQL Server
Window functions in SQL Server are a powerful tool for performing calculations across a series of rows related to the current row. Unlike aggregate functions, which combine rows into a single result, SQL Server window functions allow for row-by-row analysis while maintaining the entire dataset.This
4 min read
How to find last value from any table in SQL Server
We could use LAST_VALUE() in SQL Server to find the last value from any table. LAST_VALUE() function used in SQL server is a type of window function that results the last value in an ordered partition of the given data set. Syntax : SELECT *, FROM tablename LAST_VALUE ( scalar_value ) OVER ( [PARTIT
2 min read
How to Use SELECT With Aggregate Functions in SQL?
SQL aggregate functions are essential tools for summarizing and processing data. These functions help us perform calculations on a set of values to produce a single result, such as SUM, COUNT, AVG, MAX, and MIN. These functions work with the SELECT statement to process data and derive meaningful ins
4 min read
Using LENGTH() Function in SQL
Understanding the length of strings within a database is a fundamental aspect of effective data management and analysis. In the world of SQL, the LENGTH() function provides an essential tool for measuring the number of characters in a string, which can be invaluable for various tasks such as data va
4 min read
SQL Server Window Functions ROWS vs. RANGE
We will cover the important concept of the MS SQL Server which is the difference between Row and Range. The confusion between the row and range and where it is used will be eradicated by reading this article. So, be with the flow of the article for a better understanding and keep practicing side by
5 min read
How To Find the Sum of Digits in a String in SQL Server?
Given a string with digits and characters. The task is to find the sum of digits in that string. So, let's start by creating a database first. Step 1: Create a Database. Query : CREATE DATABASE GFG Step 2: Use the GFG Database. Query : USE GFG Step 3 : Â a) Select each character as a row by traversin
1 min read
How to Get the First Day of the Month in PL/SQL?
In PL/SQL programming, efficiently manipulating dates is crucial for various tasks, such as generating reports, calculating durations, or scheduling events. One common requirement is retrieving the first day of the month from a given date. In this article, we'll explore different approaches to achie
4 min read
How to find first value from any table in SQL Server
We could use FIRST_VALUE() in SQL Server to find the first value from any table. FIRST_VALUE() function used in SQL server is a type of window function that results in the first value in an ordered partition of the given data set. Syntax : SELECT *, FROM tablename; FIRST_VALUE ( scalar_value ) OVER
2 min read
Filtering Rows Using Aggregate Functions in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is an advanced relational database system that supports both relational (SQL) and non-relational (JSON) queries. It is free and open-source. Filtering rows based on conditions is a regular operation in database administration. Although filtering rows by each column value is easily done, m
5 min read
How to Select Data Between Two Dates and Times in SQL Server?
In SQL, some transactions need to be extracted based on their completion times and dates. Here, the DATETIME2 data type in SQL to perform such operations. For this article, we will be using the Microsoft SQL Server as our database. Note: Here, we will use the two dates and times given in the query a
2 min read