How to Design a Database for Whatsapp
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Database design is important for messaging platforms like WhatsApp and enables efficient management of user accounts, contacts, messages, and media files. A well-structured database supports easy communication, real-time message delivery, and enhanced user privacy and security.
In this article, we will learn about How Database Design Essentials for WhatsApp by understanding various aspects of the article in detail.
Database Design Essentials for WhatsApp
- Designing a database for a messaging platform like WhatsApp involves considerations such as user management, message storage, contact lists, real-time updates, and security.
- The database must handle high volumes of data, ensure fast response times, and maintain data integrity and privacy.
Features of Databases for Messaging Platforms
Databases for messaging platforms offer a range of features designed to support user management, real-time communication, message storage, and analytics. These features typically include:
- User Management: Managing user accounts, profiles, and authentication.
- Contact Lists: Storing user contacts and relationships.
- Message Storage: Handling the storage and retrieval of messages and media files.
- Real-time Updates: Ensuring real-time message delivery and status updates.
- Encryption and Security: Implementing end-to-end encryption and secure data storage.
- Analytics and Reporting: Generating insights and reports on user activity and platform performance.
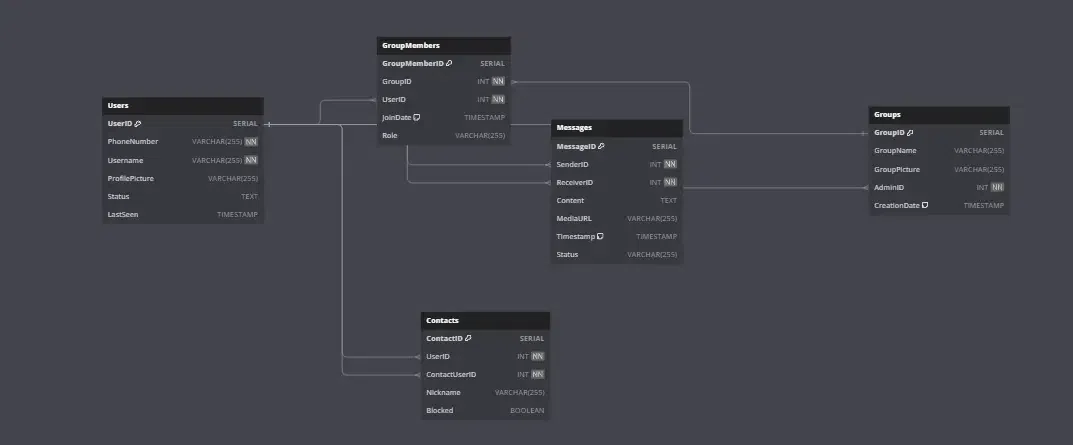
Entities and Attributes in Databases for Messaging Platforms
Entities in a messaging platform database represent various aspects of user management, message storage, contact lists, and real-time updates, while attributes describe their characteristics.
1. User Table
- UserID (Primary Key): It is a Unique identifier for each user.
- PhoneNumber: User's phone number used for registration.
- Username: User's display name.
- ProfilePicture: It is a URL or reference to the user's profile picture.
- Status: User's status message.
- LastSeen: Timestamp of the user's last activity.
2. Contact Table
- ContactID (Primary Key): Unique identifier for each contact entry.
- UserID: Identifier for the user who has the contact.
- ContactUserID: Identifier for the contact user.
- Nickname: Optional nickname for the contact.
- Blocked: Boolean indicating if the contact is blocked.
3. Message Table
- MessageID (Primary Key): Unique identifier for each message.
- SenderID: Identifier for the user who sent the message.
- ReceiverID: Identifier for the user who received the message.
- Content: The text content of the message.
- MediaURL: URL or reference to any media attached to the message.
- Timestamp: It is a Date and time when the message was sent.
- Status: Status of the message (e.g., sent, delivered, read).
4. Group Table
- GroupID (Primary Key): Unique identifier for each group.
- GroupName: Name of the group.
- GroupPicture: URL or reference to the group's profile picture.
- AdminID: Identifier for the user who is the group admin.
- CreationDate: Date when the group was created.
5. GroupMember Table
- GroupMemberID (Primary Key): Unique identifier for each group member entry.
- GroupID: Identifier for the associated group.
- UserID: Identifier for the user who is a member of the group.
- JoinDate: The date when the user joined the group.
- Role: Role of the user in the group (e.g., member, admin).
Relationships Between Entities
Based on the entities and their attributes provided, relationships between them can be defined to establish data flows and dependencies within the messaging platform database.
1. One-to-Many Relationship between User and Contact:
- One user can have multiple contacts.
- Each contact entry is associated with one user.
- Therefore, the relationship between the User and the Contact is one-to-many.
2. One-to-Many Relationship between User and Message:
- One user can send multiple messages.
- Each message is sent by one user.
- Therefore, the relationship between the User and the Message is one-to-many.
3. One-to-Many Relationship between Group and GroupMember:
- One group can have multiple members.
- Each group member entry is associated with one group.
- Therefore, the relationship between Group and GroupMember is one-to-many.
4. Many-to-Many Relationship between User and Group:
- One user can be a member of multiple groups.
- One group can have multiple users as members.
- Therefore, the relationship between the User and the Group is many-to-many, implemented via the GroupMember table.
Entities Structures in SQL Format
Here's how the entities mentioned above can be structured in SQL format:
-- Create User Table
CREATE TABLE Users (
UserID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
PhoneNumber VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
Username VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
ProfilePicture VARCHAR(255),
Status TEXT,
LastSeen TIMESTAMP
);
-- Create Contact Table
CREATE TABLE Contacts (
ContactID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
UserID INT NOT NULL,
ContactUserID INT NOT NULL,
Nickname VARCHAR(255),
Blocked BOOLEAN,
FOREIGN KEY (UserID) REFERENCES Users(UserID),
FOREIGN KEY (ContactUserID) REFERENCES Users(UserID)
);
-- Create Message Table
CREATE TABLE Messages (
MessageID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
SenderID INT NOT NULL,
ReceiverID INT NOT NULL,
Content TEXT,
MediaURL VARCHAR(255),
Timestamp TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
Status VARCHAR(255),
FOREIGN KEY (SenderID) REFERENCES Users(UserID),
FOREIGN KEY (ReceiverID) REFERENCES Users(UserID)
);
-- Create Group Table
CREATE TABLE Groups (
GroupID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
GroupName VARCHAR(255),
GroupPicture VARCHAR(255),
AdminID INT NOT NULL,
CreationDate TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (AdminID) REFERENCES Users(UserID)
);
-- Create GroupMember Table
CREATE TABLE GroupMembers (
GroupMemberID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
GroupID INT NOT NULL,
UserID INT NOT NULL,
JoinDate TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
Role VARCHAR(255),
FOREIGN KEY (GroupID) REFERENCES Groups(GroupID),
FOREIGN KEY (UserID) REFERENCES Users(UserID)
);
Database Model for Messaging Platforms
The database model for a messaging platform revolves around efficiently managing user accounts, contact lists, message storage, group management, and real-time updates to ensure a seamless and secure communication experience.
Tips & Best Practices for Enhanced Database Design
- Scalability: Design the database to scale with the growing number of users, messages, and groups.
- Indexing: Implement indexing on frequently queried columns (e.g., UserID, MessageID) to optimize query performance.
- Caching: Use caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed data, such as user profiles and contact lists, to reduce database load.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect user data, including end-to-end encryption, access controls, and secure storage.
- Real-time Processing: Implement real-time data processing for features such as live message delivery and status updates.
- Data Redundancy: Use data redundancy and replication techniques to ensure high availability and reliability.
Conclusion
Designing a database for a messaging platform like WhatsApp is essential for managing user accounts, contact lists, message storage, real-time updates, and security effectively. By following best practices in database design and using modern technologies, messaging platforms can optimize operations, enhance user engagement, and ensure data security.
Similar Reads
How to Design a Database for Zomato Database design is fundamental for food delivery platforms like Zomato and enables efficient management of restaurant information, user profiles, order processing, and real-time tracking. A well-structured database supports seamless operations, personalized recommendations, and enhanced user engagem
5 min read
How to Design a Database for Twitter Database design is critical for social media platforms like Twitter where efficient management of user accounts, tweets, retweets, likes, and multimedia content is essential. A robust database architecture supports seamless user interactions, real-time updates, and enhanced privacy and security. In
5 min read
How to Design a Database for Uber Database design is important for ride-sharing platforms like Uber which enables efficient management of drivers, passengers, ride requests, payments and location data. A well-structured database supports seamless operations, real-time tracking, and personalized services, ensuring a smooth and reliab
5 min read
How to Design a Database For MVP? When creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), database design is crucial as it shapes the foundation of the product's functionality, scalability, and performance. The database must efficiently support core features while allowing flexibility for future enhancements. In this article, we'll look at th
4 min read
How to Design a Database For Spotify? Spotify is a top music streaming service, that serves millions of users with tons of songs and podcasts. To make everything run smoothly, Spotify uses a smart database system that handles user info, playlists, music catalogs, and recommendations. In this article, we'll look at how databases are desi
6 min read
How to Design a Database for Instagram Database design is important for social media platforms like Instagram and enables efficient management of user accounts, posts, comments, likes, and multimedia content. A robust database architecture supports easy user interactions, real-time updates, and enhanced privacy and security. In this arti
5 min read