How to Create Database Objects in MYSQL
Last Updated :
17 Apr, 2024
MySQL, the widely used relational database management system, offers a robust set of tools for creating and managing database objects. To organize and manipulate data effectively, users can utilize SQL commands such as CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, CREATE INDEX, and CREATE PROCEDURE.
In this article, We will explore the creation of these database objects in MySQL by understanding various methods along with the examples in detail.
How to Create Database Objects in MYSQL
The process of creating database objects in MySQL involves several key components. First, tables are created using the CREATE TABLE command, defining the structure of the data. Then Views can be created with the CREATE VIEW command and offering customized perspectives on the data. Indexes can enhance performance by creating efficient data retrieval paths using the CREATE INDEX command. Lastly, stored procedures can be implemented with the CREATE PROCEDURE command and enable the execution of predefined logic on the database. Below are the approaches which we will discuss in the article.
- Using Basic Regular Expression Patterns
- Using Advanced Regular Expression Features
Let's set up an Environment:
To understand How to Create Database Objects in MYSQL we need a table on which we will perform various operations and queries. Here we will consider a table called employees which contains id, name, salary, and age as Columns.
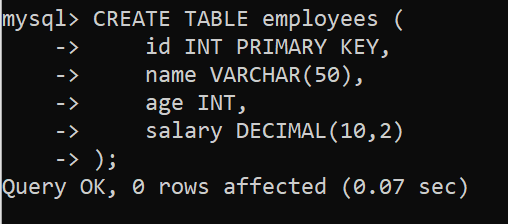 create table
create tableLet's Creating Views
Syntax:
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
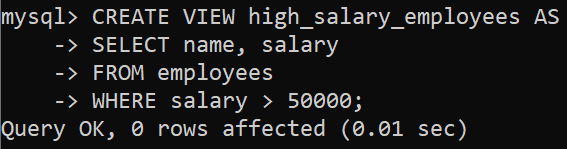
Example:
CREATE VIEW high_salary_employees AS
SELECT name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary > 50000;
In this query its creating a view named high_salary_employees, which returns those data as name and salaries from the employees table for those employees who has salaries more than 50000.
Output:
 create view
create viewLet's Create Indexes
CREATE INDEX idx_age
ON employees (age);
Output:
 create index
create indexIn the SQL query its creating a index for the age column of the employees table, and because of this created index the data retrievel operations will much be fast. Because Indexes improve the efficiency of data retrieval operations by allowing faster lookup of rows based on the indexed column.
Let's Creating Stored Procedures
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE increase_salary(IN empid INT, IN amount DECIMAL(10,2))
BEGIN
UPDATE employees
SET salary = salary + amount
WHERE id = empid;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Output:
 create procedure
create procedureIn this SQL query its created a stored procedure with name of increase_salary, it takes arguments empid and amount. It will update the salary value of specified empid by the given amount.
1. Using Basic Regular Expression Patterns
By the regular expression gives a basic way to match text in the string. Because its have defined Literals, Characters and metacharacters that define the pattern to be matched.
Let's say we want to match email addresses in a given text.
SELECT * FROM employees
WHERE email REGEXP '^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$';
Output:
 regexp
regexpExplanation:
- ^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+ : This will match the username part of the email address, which begins with one or more letters, numbers, dots, underscores, percent signs, plus signs or hyphens.
- @ : It matches the symbol “@”.
- [a-zA-Z0-9.-]+ : This matches the domain part of the email address that consists of at least one letter or number followed by a period and/or hyphen.
- \. : The dot is escaped to get dot from domain
- [a-zA-Z]{2,}$ : It matches top-level domain (TLD) part of the email address and it consists of at least two alphabets.
2. Using Advanced Regular Expression Features
This includes advanced regex features that go beyond simple patterns to incorporate more complex matching options such as quantifiers, anchors and lookaheads/lookbehinds.
Suppose we would like to find phone numbers of a particular format.
SELECT mobile
FROM employees
WHERE mobile REGEXP '^(\\+\\d{1,2}\\s?)?(\\d{3}[-\\s]?)?\\d{3}[-\\s]?\\d{4}$';
Output:
 regexp
regexpExplanation:
- ^ : It signifies the start of a given string.
- (\\+\\d{1,2}\\s?)? : This is an optional international dialing code like +1 or +91 and could be followed by an optional space.
- (\\d{3}[-\\s]?)? : Three digits that make up the area code might be followed by an optional dash or space.
- \d{3}\s?-? : The phone number’s first three digits are then followed by a dash or space if necessary.
- \d{4}$ : This is the last four digits of the phone number, which come before the end of any string.
Conclusion
Overall, By mastering the creation of database objects in MySQL, users can effectively organize and manage their data. Whether it's creating tables to structure data, views to provide customized data perspectives, indexes to improve data retrieval performance, or stored procedures to automate common tasks.
Similar Reads
How to Check MySQL Database
SQL stands for Structured Query Language which is a computer language for storing, manipulating, and retrieving data stored in relational database management systems (RDBMS). SQL was developed at IBM by Donald Chamberlin, Donald C. Messerli, and Raymond F. Boyce in the year 1970s. MySQL is an open-s
4 min read
How to Show/List Tables in MySQL Database
In MySQL, the SHOW TABLES command is a powerful tool used to list the tables within a specific database. This command provides a convenient way to view the tables that exist in a database without needing to query the database schema directly. In this article, we are going to explore various ways whe
5 min read
How to Show a List of All Databases in MySQL
MySQL is a popular open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that is uniquely used to construct expandable and high-productivity databases. MySQL, which was created by MySQL AB and later acquired by its current owner Oracle Corporation, was originally introduced in 1995.MySQL is repu
7 min read
How to Show Schema of a Table in MySQL Database?
A table schema in MySQL database defines the structure of table, including columns, data types, relationships between columns, etc. It is a blueprint for the table, describing how data is organized in the table and how it relates to other tables in the database. To see the schema of a table in MySQL
2 min read
MySQL Create Database Statement
The MySQL CREATE DATABASE statement is used to create a new database. It allows you to specify the database name and optional settings, such as character set and collation, ensuring the database is ready for storing and managing data. In this article, we are going to learn how we can create database
4 min read
Create Database in MS SQL Server
Databases in Microsoft SQL Server are crucial for managing data, categorized into system databases, which are auto-created and user databases, created by users. In this article, We will learn about the basics of system and user databases along with methods for creating and managing them using T-SQL
5 min read
How to Create Database and Collection in MongoDB
MongoDB is a widely used NoSQL database renowned for its flexibility, scalability, and performance in managing large volumes of unstructured data. Whether you’re building a small application or handling big data, MongoDB offers an easy-to-use structure for managing your data. In this article, we wil
6 min read
How to Connect Python with SQL Database?
In this article, we will learn how to connect SQL with Python using the MySQL Connector Python module. Below diagram illustrates how a connection request is sent to MySQL connector Python, how it gets accepted from the database and how the cursor is executed with result data.SQL connection with Pyth
2 min read
SQL CREATE DATABASE
Creating a database is one of the fundamental tasks in SQL and is the first step in structuring your data for efficient management. Whether you're a developer or a database administrator, understanding the CREATE DATABASE statement is essential. Understanding how to use this command effectively is c
6 min read
Minimal Permission to Create SQL Database
In SQL Server, the ability to create a database is governed by specific permissions and roles that can be granted to users. Understanding these permissions is essential for ensuring security and maintaining the principle of least privilege in our database environment.In this article, we will learn a
4 min read