Hibernate - Many-to-Many Mapping
Last Updated :
04 Sep, 2025
A Many-to-Many relationship occurs when multiple records in one table are associated with multiple records in another table. For example:
- An employee can have multiple skills.
- A skill can belong to multiple employees.
To represent this scenario, we use three tables:
- geekEmployeeData: stores employee details.
- SkillsetData: stores skill details.
- geekEmployeeSkill: a join table that maps employees to their skillsets using foreign keys.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1. Create Database Tables
Java
-- Employee table
create table geeksforgeeks.geekEmployeeData (
id INT NOT NULL auto_increment,
first_name VARCHAR(20) default NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(20) default NULL,
salary INT default NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
-- Skills table
create table geeksforgeeks.SkillsetData (
id INT NOT NULL auto_increment,
skillName VARCHAR(30) default NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
-- Junction table for Many-to-Many mapping
create table geekEmployeeSkill (
geekEmpId INT NOT NULL,
skillId INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (geekEmpId,skillId)
);
Step 2. Create POJO Classes
- In this step, we create the tables needed for storing employees, skills, and their relationships.
- The geekEmployeeSkill table acts as a join table to maintain the Many-to-Many mapping.
2.1 GeekEmployeeData.java: For geekEmployeeData table data CRUD operations, this is required
Java
import java.util.Set;
public class GeekEmployeeData {
private int id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int salary;
// Many-to-Many: employee can have multiple skills
private Set skillSets;
public GeekEmployeeData() {}
public GeekEmployeeData(String firstName, String lastName, int salary) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.salary = salary;
}
// Getters & Setters
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getFirstName() { return firstName; }
public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; }
public String getLastName() { return lastName; }
public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; }
public int getSalary() { return salary; }
public void setSalary(int salary) { this.salary = salary; }
public Set getSkillSets() { return skillSets; }
public void setSkillSets(Set skillSets) { this.skillSets = skillSets; }
}
Explanation:
- This class represents the geekEmployeeData table and stores basic employee info.
- The Set<SkillsetData> models the Many-to-Many relationship with skills.
2.2 SkillsetData.java : For SkillsetData table data CRUD operations, this is required
Java
public class SkillsetData {
private int id;
private String skillName;
public SkillsetData() {}
public SkillsetData(String skillName)
{
this.skillName = skillName;
}
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getSkillName() { return skillName; }
public void setSkillName(String skillName)
{
this.skillName = skillName;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
// This method is definitely required in order to check whether any two elements/objects are equal
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (!this.getClass().equals(obj.getClass()))
return false;
SkillsetData obj2 = (SkillsetData)obj;
if ((this.id == obj2.getId())
&& (this.skillName.equals(
obj2.getSkillName()))) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// collections calculate the hash value for a given key using the hashCode() method.
public int hashCode()
{
// This method is definitely required in order to check whether any two elements/objects are equal
int tmp = 0;
tmp = (id + skillName).hashCode();
return tmp;
}
}
Explanation:
- Represents the SkillsetData table and contains skill information.
- equals() and hashCode() ensure that Set collections properly manage duplicates.
Step 3. Hibernate Mapping File
In many-to-many relationships, Hibernate uses a mapping file to define associations between entities. The <set> element specifies the relationship and how related objects should be persisted.
geekEmployeeData.hbm.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD//EN"
"http://hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<!-- Employee mapping -->
<class name="com.geeksforgeeks.GeekEmployeeData" table="geekEmployeeData">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<set name="skillSets" cascade="save-update" table="geekEmployeeSkill">
<key column="geekEmpId"/>
<many-to-many column="skillId" class="com.geeksforgeeks.SkillsetData"/>
</set>
<property name="firstName" column="first_name" type="string"/>
<property name="lastName" column="last_name" type="string"/>
<property name="salary" column="salary" type="int"/>
</class>
<!-- Skill mapping -->
<class name="com.geeksforgeeks.SkillsetData" table="SkillsetData">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="skillName" column="skillName" type="string"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Explanation:
- Maps Java classes to database tables, including the Many-to-Many relationship.
- <set> and <many-to-many> elements define how skills are associated with employees.
Step 4. Hibernate Configuration File
hibernate.cfg.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/geeksforgeeks</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<!-- Change your appropriate password here -->
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">xxxx</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update </property>
<mapping resource="geekEmployeeData.hbm.xml" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Explanation:
- Configures database connection, Hibernate dialect, and mapping resources.
- hbm2ddl.auto=update ensures schema is automatically updated when the app runs.
Step 5. Implementation Class
GeekEmployeeManytoManyExample.java
Java
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import org.hibernate.*;
public class GeekEmployeeManytoManyExample {
private static SessionFactory factory;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
factory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println("Failed to create sessionFactory object." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
GeekEmployeeManytoManyExample app = new GeekEmployeeManytoManyExample();
HashSet skillSets = new HashSet();
skillSets.add(new SkillsetData("Java"));
skillSets.add(new SkillsetData("Python"));
skillSets.add(new SkillsetData("R Programming"));
HashSet databaseSkillSets = new HashSet();
databaseSkillSets.add(new SkillsetData("MySQL"));
databaseSkillSets.add(new SkillsetData("SQL Server"));
databaseSkillSets.add(new SkillsetData("MongoDB"));
app.addEmployee("GeekA", "GeekA", 100000, skillSets);
app.addEmployee("GeekB", "GeekB", 50000, databaseSkillSets);
app.addEmployee("GeekC", "GeekC", 50000, skillSets);
app.listGeekEmployeeData();
}
public Integer addEmployee(String fname, String lname, int salary, Set skillSets) {
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
Integer employeeID = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
GeekEmployeeData employee = new GeekEmployeeData(fname, lname, salary);
employee.setSkillSets(skillSets);
employeeID = (Integer) session.save(employee);
tx.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
session.close();
}
return employeeID;
}
public void listGeekEmployeeData() {
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(GeekEmployeeData.class);
List employees = criteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator = employees.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployeeData emp = (GeekEmployeeData) iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: " + emp.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: " + emp.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: " + emp.getSalary());
Set skillSets = emp.getSkillSets();
for (Iterator it = skillSets.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SkillsetData skill = (SkillsetData) it.next();
System.out.println("SkillName: " + skill.getSkillName());
}
}
tx.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
}
Explanation:
- Implements adding employees with multiple skills and listing them using Hibernate.
- Demonstrates fetching related entities in a Many-to-Many relationship easily with Hibernate criteria queries.
Run and Varify

Parallelly Checking the table values:

 geekemployeeskill data
geekemployeeskill dataLet us list the records by using hibernate criteria query.
The following method retrieves all employees along with their associated skillsets.
Java
public void listGeekEmployeeData() {
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// Create criteria for GeekEmployeeData
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria = session.createCriteria(GeekEmployeeData.class);
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator = geekEmployeeList.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployeeData employeeData = (GeekEmployeeData) iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: " + employeeData.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: " + employeeData.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: " + employeeData.getSalary());
// Iterate over skill sets
Set skillSets = employeeData.getSkillSets();
for (Iterator it = skillSets.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SkillsetData skill = (SkillsetData) it.next();
System.out.println("SkillName: " + skill.getSkillName());
}
}
tx.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
Uses:
Java
/* List down all the employees by using Hibernate criteria */
geekEmployeeObject.listGeekEmployeeData();

Filtering Employee Records
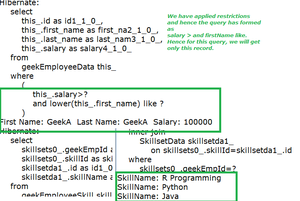
You can filter employees based on multiple criteria, such as salary greater than 50,000 and first name starting with 'Geek'.
Java
public void listGeekEmployeesByNameAndSalaryCriteria() {
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// Create criteria for GeekEmployeeData
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria = session.createCriteria(GeekEmployeeData.class);
// Define restrictions
Criterion salaryExpectation = Restrictions.gt("salary", 50000);
Criterion nameExpectation = Restrictions.ilike("firstName", "Geek%");
// Combine restrictions with AND
LogicalExpression logicalAndExpression = Restrictions.and(salaryExpectation, nameExpectation);
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(logicalAndExpression);
// Fetch list
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator = geekEmployeeList.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployeeData employeeData = (GeekEmployeeData) iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: " + employeeData.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: " + employeeData.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: " + employeeData.getSalary());
// Iterate over skill sets
Set skillSets = employeeData.getSkillSets();
for (Iterator it = skillSets.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SkillsetData skill = (SkillsetData) it.next();
System.out.println("SkillName: " + skill.getSkillName());
}
}
tx.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
Explanation:
- Demonstrates filtering employees based on multiple conditions (salary > 50000 AND firstName LIKE 'Geek%').
- Shows how Hibernate criteria queries simplify complex SQL joins with Many-to-Many relationships.
Uses:
Java
// Let us add filter data by using Restrictions
geekEmployeeObject.listGeekEmployeesByNameAndSalaryCriteria();
Video explanation:
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java