Minimum cost to connect all houses in a city
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Given a 2D array houses[][] consisting of n 2D coordinates {x, y} where each coordinate represents the location of each house, the task is to find the minimum cost to connect all the houses of the city.
Note: Cost of connecting two houses is the Manhattan Distance between the two points (xi, yi) and (xj, yj) i.e., |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where |p| denotes the absolute value of p.
Examples:
Input: houses[][] = [[0, 7], [0, 9], [20, 7], [30, 7], [40, 70]]
Output: 105
Explanation:
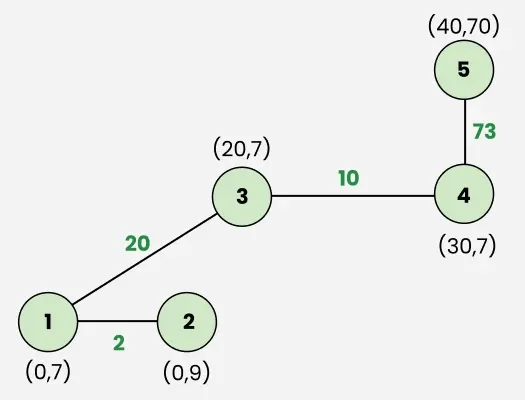
Connect house 1 (0, 7) and house 2 (0, 9) with cost = 2
Connect house 1 (0, 7) and house 3 (20, 7) with cost = 20
Connect house 3 (20, 7) with house 4 (30, 7) with cost = 10
At last, connect house 4 (30, 7) with house 5 (40, 70) with cost 73.
All the houses are connected now.
The overall minimum cost is 2 + 10 + 20 + 73 = 105.
Input: houses[][] = [[4, 12], [15, 20], [17, 0]]
Output: 41
Explanation:
Connect house 1 (4, 12) and house 2 (15, 20) with cost = 19
Connect house 2 (15, 20) and house 3 (17, 0) with cost = 22
All the houses are connected now.
The overall minimum cost is 19 + 22 = 41.
[Approach 1] Using Prim’s Algorithm - Time O(n^2*log(n)) and Space O(n^2)
We can think of each house as a node in a graph, and the Manhattan distance between any two houses as the weight of the edge connecting those two nodes. With this interpretation, the problem of connecting all houses with the minimum total cost becomes equivalent to finding a Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) of a complete graph.
Step by Step implementations:
- Start with any house (we start with house 0).
- Push all distances from this house to other houses into a min-heap (priority queue).
- At every step: Pick the house with the smallest connection cost that hasn't been visited.
- Add that cost to the total cost and mark the house as visited.
- Push distances from this new house to all unvisited houses into the heap.
- Repeat until all houses are visited and return the total cost.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
// Calculates Manhattan Distance between two houses
int manhattanDistance(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {
return abs(a[0] - b[0]) + abs(a[1] - b[1]);
}
// Returns the minimum cost to connect
// all houses using Prim's algorithm
int minCost(vector<vector<int>>& houses) {
int n = houses.size();
// Min-heap to store {cost, house_index}
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>,
greater<>> minHeap;
// Marks whether a house is already connected
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
// Start with the first house (index 0)
minHeap.push({0, 0});
int totalCost = 0;
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
pair<int, int> p = minHeap.top(); minHeap.pop();
int cost = p.first;
int u = p.second;
// Skip if already connected
if (visited[u]) continue;
// Mark the house as connected and add the cost
visited[u] = true;
totalCost += cost;
// Calculate distance to all unvisited houses and add to heap
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) {
if (!visited[v]) {
int dist = manhattanDistance(houses[u], houses[v]);
minHeap.push({dist, v});
}
}
}
return totalCost;
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> houses = {
{0, 7}, {0, 9}, {20, 7}, {30, 7}, {40, 70}
};
int result = minCost(houses);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Calculates Manhattan Distance between two houses
static int manhattanDistance(int[] a, int[] b) {
return Math.abs(a[0] - b[0]) + Math.abs(a[1] - b[1]);
}
// Returns the minimum cost to connect
// all houses using Prim's algorithm
static int minCost(int[][] houses) {
int n = houses.length;
// Min-heap to store {cost, houseIndex}
PriorityQueue<int[]> minHeap =
new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
// Marks whether a house is already connected
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
// Start with the first house (index 0)
minHeap.offer(new int[]{0, 0});
int totalCost = 0;
while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = minHeap.poll();
int cost = curr[0];
int u = curr[1];
// Skip if already connected
if (visited[u]) continue;
// Mark as connected and add the cost
visited[u] = true;
totalCost += cost;
// Add distances to all unvisited houses
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (!visited[v]) {
int dist = manhattanDistance(houses[u], houses[v]);
minHeap.offer(new int[]{dist, v});
}
}
}
return totalCost;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] houses = {
{0, 7}, {0, 9}, {20, 7}, {30, 7}, {40, 70}
};
int result = minCost(houses);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
import heapq
# Calculates Manhattan Distance between two houses
def manhattanDistance(a, b):
return abs(a[0] - b[0]) + abs(a[1] - b[1])
# Returns the minimum cost to connect
# all houses using Prim's algorithm
def minCost(houses):
n = len(houses)
# Min-heap to store {cost, house_index}
minHeap = [(0, 0)]
# Marks whether a house is already connected
visited = [False] * n
# Start with the first house (index 0)
totalCost = 0
while minHeap:
cost, u = heapq.heappop(minHeap)
# Skip if already connected
if visited[u]:
continue
# Mark the house as connected and add the cost
visited[u] = True
totalCost += cost
# Calculate distance to all
# unvisited houses and add to heap
for v in range(n):
if not visited[v]:
dist = manhattanDistance(houses[u], houses[v])
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (dist, v))
return totalCost
if __name__ == "__main__":
houses = [
[0, 7], [0, 9], [20, 7], [30, 7], [40, 70]
]
result = minCost(houses)
print(result)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
// Calculates Manhattan Distance between two houses
static int manhattanDistance(int[,] houses, int i, int j) {
return Math.Abs(houses[i, 0] - houses[j, 0]) +
Math.Abs(houses[i, 1] - houses[j, 1]);
}
// Returns the minimum cost to connect
// all houses using Prim's algorithm
static int minCost(int[,] houses) {
int n = houses.GetLength(0);
// Min-heap to store {cost, house_index, tieBreaker}
var minHeap = new SortedSet<(int cost, int index, int tieBreaker)>();
int tie = 0;
minHeap.Add((0, 0, tie++));
// Marks whether a house is already connected
bool[] visited = new bool[n];
// Start with the first house (index 0)
int totalCost = 0;
while (minHeap.Count > 0) {
var p = minHeap.Min;
minHeap.Remove(p);
int cost = p.cost;
int u = p.index;
// Skip if already connected
if (visited[u]) continue;
// Mark the house as connected and add the cost
visited[u] = true;
totalCost += cost;
// Calculate distance to all unvisited houses and add to heap
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) {
if (!visited[v]) {
int dist = manhattanDistance(houses, u, v);
minHeap.Add((dist, v, tie++));
}
}
}
return totalCost;
}
static void Main() {
int[,] houses = new int[,]
{ {0, 7}, {0, 9}, {20, 7},{30, 7},{40, 70}
};
int result = minCost(houses);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
// Calculates Manhattan Distance between two houses
function manhattanDistance(a, b) {
return Math.abs(a[0] - b[0]) + Math.abs(a[1] - b[1]);
}
// Returns the minimum cost to connect
// all houses using Prim's algorithm
function minCost(houses) {
const n = houses.length;
// Min-heap to store [cost, house_index]
const minHeap = [[0, 0]];
// Marks whether a house is already connected
const visited = Array(n).fill(false);
let totalCost = 0;
while (minHeap.length > 0) {
// Extract the house with minimum connection cost
minHeap.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
// Sort to simulate min-heap
const [cost, u] = minHeap.shift();
// Skip if already connected
if (visited[u]) continue;
// Mark the house as connected and add the cost
visited[u] = true;
totalCost += cost;
// Calculate distance to all unvisited houses and add to heap
for (let v = 0; v < n; ++v) {
if (!visited[v]) {
const dist = manhattanDistance(houses[u], houses[v]);
minHeap.push([dist, v]);
}
}
}
return totalCost;
}
// Driver Code
const houses = [[0, 7], [0, 9], [20, 7], [30, 7], [40, 70]];
const result = minCost(houses);
console.log(result);
[Approach 2] Using Kruskal's Algorithm - Time O(n^2*log(n)) and Space O(n^2)
To solve the problem, we model it as a weighted graph, where each house is a node, and the edge weight between any two houses is the Manhattan distance (i.e., the cost to connect them).
We generate all possible edges between houses and store their corresponding weights. Then, we use Kruskal’s algorithm to find the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) of this graph. To efficiently detect and avoid cycles while building the MST, we use a Disjoint Set Union (DSU) data structure with path compression and union by rank.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
// DSU data structure
// path compression + rank by union
class DSU {
vector<int> parent;
vector<int> rank;
public:
DSU(int n) {
parent.resize(n, -1);
rank.resize(n, 1);
}
// Find function
int find(int i) {
if (parent[i] == -1)
return i;
return parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
// Union function
void unite(int x, int y) {
int s1 = find(x);
int s2 = find(y);
if (s1 != s2) {
if (rank[s1] < rank[s2]) {
parent[s1] = s2;
}
else if (rank[s1] > rank[s2]) {
parent[s2] = s1;
}
else {
parent[s2] = s1;
rank[s1] += 1;
}
}
}
};
class Graph {
vector<vector<int>> edgelist;
int V;
public:
Graph(int V) {
this->V = V;
}
// Function to add edge in a graph
void addEdge(int x, int y, int w) {
edgelist.push_back({w, x, y});
}
int kruskalsMST() {
// Sort all edges
sort(edgelist.begin(), edgelist.end());
// Initialize the DSU
DSU s(V);
// Stores the final answer
int ans = 0;
int count = 0; // no of edges in MST
for (auto edge : edgelist) {
int w = edge[0];
int x = edge[1];
int y = edge[2];
// Take this edge in MST if it does
// not form a cycle
if (s.find(x) != s.find(y)) {
s.unite(x, y);
ans += w;
count++;
}
if (count == V - 1) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
int minCost(vector<vector<int>> &houses) {
int n = houses.size();
// Create graph with n nodes
Graph g(n);
// Add all possible edges
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
int cost = abs(houses[i][0] - houses[j][0]) +
abs(houses[i][1] - houses[j][1]);
g.addEdge(i, j, cost);
}
}
return g.kruskalsMST();
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> houses = {{0, 7}, {0, 9}, {20, 7}, {30, 7},
{40, 70}};
cout << minCost(houses);
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class DSU {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
public DSU(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(parent, -1);
Arrays.fill(rank, 1);
}
// Find function with path compression
public int find(int i) {
if (parent[i] == -1)
return i;
return parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
// Union function with union by rank
public void unite(int x, int y) {
int s1 = find(x);
int s2 = find(y);
if (s1 != s2) {
if (rank[s1] < rank[s2]) {
parent[s1] = s2;
} else if (rank[s1] > rank[s2]) {
parent[s2] = s1;
} else {
parent[s2] = s1;
rank[s1] += 1;
}
}
}
}
class Graph {
private List<int[]> edgelist;
private int V;
public Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
edgelist = new ArrayList<>();
}
// Function to add an edge to the graph
public void addEdge(int x, int y, int w) {
edgelist.add(new int[]{ w, x, y });
}
// Function to calculate MST using Kruskal's Algorithm
public int kruskalsMST() {
// Sort all edges by weight
edgelist.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
// Initialize DSU
DSU s = new DSU(V);
int ans = 0; // Stores total cost
int count = 0; // Tracks number of edges added to MST
for (int[] edge : edgelist) {
int w = edge[0];
int x = edge[1];
int y = edge[2];
// Include edge if it doesn't form a cycle
if (s.find(x) != s.find(y)) {
s.unite(x, y);
ans += w;
count++;
}
// Stop if MST has V-1 edges
if (count == V - 1) break;
}
return ans;
}
}
class GfG {
public static int minCost(int[][] houses) {
int n = houses.length;
Graph g = new Graph(n);
// Create edges between every pair of houses
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
int cost = Math.abs(houses[i][0] - houses[j][0]) +
Math.abs(houses[i][1] - houses[j][1]);
g.addEdge(i, j, cost);
}
}
// Return the minimum total cost
return g.kruskalsMST();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] houses = {
{ 0, 7 },
{ 0, 9 },
{ 20, 7 },
{ 30, 7 },
{ 40, 70 }
};
System.out.println(minCost(houses));
}
}
# Disjoint Set Union (DSU) or Union-Find class
class DSU:
def __init__(self, n):
# Initialize parent and rank arrays
self.parent = [-1] * n
self.rank = [1] * n
# Find function with path compression
def find(self, i):
if self.parent[i] == -1:
return i
self.parent[i] = self.find(self.parent[i])
return self.parent[i]
# Union function with union by rank
def unite(self, x, y):
s1 = self.find(x)
s2 = self.find(y)
if s1 != s2:
if self.rank[s1] < self.rank[s2]:
self.parent[s1] = s2
elif self.rank[s1] > self.rank[s2]:
self.parent[s2] = s1
else:
self.parent[s2] = s1
self.rank[s1] += 1
# Graph class to build and process edges
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.edgelist = []
# Adds an edge between house u and house v with given cost
def addEdge(self, x, y, w):
self.edgelist.append((w, x, y))
# Runs Kruskal's algorithm to return the MST total cost
def kruskalsMST(self):
# Sort edges based on weight
self.edgelist.sort()
s = DSU(self.V)
# Total cost of MST
ans = 0
# Number of edges included in MST
count = 0
for w, x, y in self.edgelist:
# Include edge if it doesn't form a cycle
if s.find(x) != s.find(y):
s.unite(x, y)
ans += w
count += 1
# If MST contains V - 1 edges, stop
if count == self.V - 1:
break
return ans
# Function to compute minimum cost to connect all houses
def minCost(houses):
n = len(houses)
g = Graph(n)
# Add edges between every pair of houses with
# Manhattan distance as cost
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
cost = abs(houses[i][0] - houses[j][0]) + abs(houses[i][1] - houses[j][1])
g.addEdge(i, j, cost)
# Compute MST cost
return g.kruskalsMST()
if __name__ == "__main__":
houses = [[0, 7], [0, 9], [20, 7], [30, 7], [40, 70]]
print(minCost(houses))
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Disjoint Set Union (Union-Find) with path
// compression and union by rank
class DSU {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
public DSU(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = -1;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
// Finds the representative (root) of the set that contains i
public int find(int i) {
if (parent[i] == -1)
return i;
return parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
// Unites two sets by rank
public void unite(int x, int y) {
int s1 = find(x);
int s2 = find(y);
if (s1 != s2) {
if (rank[s1] < rank[s2])
parent[s1] = s2;
else if (rank[s1] > rank[s2])
parent[s2] = s1;
else {
parent[s2] = s1;
rank[s1]++;
}
}
}
}
// Edge class to store a weighted
// connection between two houses
class Edge : IComparable<Edge> {
public int u, v, w;
public Edge(int u, int v, int w) {
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
}
// Compare edges by weight
public int CompareTo(Edge other) {
return this.w.CompareTo(other.w);
}
}
class GFG {
// Calculates the Manhattan distance between two points
static int manhattan(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
return Math.Abs(x1 - x2) + Math.Abs(y1 - y2);
}
// Returns the minimum cost to connect all houses
static int minCost(int[,] houses) {
int n = houses.GetLength(0);
List<Edge> edges = new List<Edge>();
// Create edges between all pairs of houses
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
int cost = manhattan(houses[i, 0], houses[i, 1],
houses[j, 0], houses[j, 1]);
edges.Add(new Edge(i, j, cost));
}
}
// Sort edges by cost
edges.Sort();
DSU dsu = new DSU(n);
int totalCost = 0;
int count = 0;
// Apply Kruskal's algorithm to find MST
foreach (Edge e in edges) {
if (dsu.find(e.u) != dsu.find(e.v)) {
dsu.unite(e.u, e.v);
totalCost += e.w;
count++;
if (count == n - 1)
break; // MST complete
}
}
return totalCost;
}
static void Main() {
int[,] houses = {
{ 0, 7 },
{ 0, 9 },
{ 20, 7 },
{ 30, 7 },
{ 40, 70 }
};
Console.WriteLine(minCost(houses));
}
}
// JavaScript program to find the minimum
// cost of connecting houses using Kruskal's algorithm
class DSU {
constructor(n) {
this.parent = Array(n).fill(-1);
this.rank = Array(n).fill(1);
}
// Find with path compression
find(i) {
if (this.parent[i] === -1) return i;
return (this.parent[i] = this.find(this.parent[i]));
}
// Union by rank
unite(x, y) {
const s1 = this.find(x);
const s2 = this.find(y);
if (s1 !== s2) {
if (this.rank[s1] < this.rank[s2]) {
this.parent[s1] = s2;
} else if (this.rank[s1] > this.rank[s2]) {
this.parent[s2] = s1;
} else {
this.parent[s2] = s1;
this.rank[s1]++;
}
}
}
}
class Graph {
constructor(V) {
this.V = V;
this.edgelist = [];
}
// Add edge to the graph
addEdge(x, y, w) {
this.edgelist.push([w, x, y]);
}
// Kruskal's algorithm to find MST
kruskalsMST() {
this.edgelist.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
const dsu = new DSU(this.V);
let totalCost = 0;
let count = 0;
for (const [w, x, y] of this.edgelist) {
if (dsu.find(x) !== dsu.find(y)) {
dsu.unite(x, y);
totalCost += w;
count++;
if (count === this.V - 1) break;
}
}
return totalCost;
}
}
// Returns the minimum cost to connect all houses
function minCost(houses) {
const n = houses.length;
const g = new Graph(n);
// Add all possible edges based on Manhattan distance
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
const cost =
Math.abs(houses[i][0] - houses[j][0]) +
Math.abs(houses[i][1] - houses[j][1]);
g.addEdge(i, j, cost);
}
}
return g.kruskalsMST();
}
// Driver Code
const houses = [
[0, 7],
[0, 9],
[20, 7],
[30, 7],
[40, 70]
];
console.log(minCost(houses));
Time Complexity: O(n²*log(n)), This includes generating all possible edges between n houses O(n²), sorting them for Kruskal's algorithm O(n²*log(n)), and performing efficient union-find operations O(n*log(n)) due to path compression.
Space Complexity: O(n²), to store all the edges.
Similar Reads
Basics & Prerequisites
Data Structures
Array Data StructureIn this article, we introduce array, implementation in different popular languages, its basic operations and commonly seen problems / interview questions. An array stores items (in case of C/C++ and Java Primitive Arrays) or their references (in case of Python, JS, Java Non-Primitive) at contiguous
3 min read
String in Data StructureA string is a sequence of characters. The following facts make string an interesting data structure.Small set of elements. Unlike normal array, strings typically have smaller set of items. For example, lowercase English alphabet has only 26 characters. ASCII has only 256 characters.Strings are immut
2 min read
Hashing in Data StructureHashing is a technique used in data structures that efficiently stores and retrieves data in a way that allows for quick access. Hashing involves mapping data to a specific index in a hash table (an array of items) using a hash function. It enables fast retrieval of information based on its key. The
2 min read
Linked List Data StructureA linked list is a fundamental data structure in computer science. It mainly allows efficient insertion and deletion operations compared to arrays. Like arrays, it is also used to implement other data structures like stack, queue and deque. Here’s the comparison of Linked List vs Arrays Linked List:
2 min read
Stack Data StructureA Stack is a linear data structure that follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out). LIFO implies that the element that is inserted last, comes out first and FILO implies that the element that is inserted first
2 min read
Queue Data StructureA Queue Data Structure is a fundamental concept in computer science used for storing and managing data in a specific order. It follows the principle of "First in, First out" (FIFO), where the first element added to the queue is the first one to be removed. It is used as a buffer in computer systems
2 min read
Tree Data StructureTree Data Structure is a non-linear data structure in which a collection of elements known as nodes are connected to each other via edges such that there exists exactly one path between any two nodes. Types of TreeBinary Tree : Every node has at most two childrenTernary Tree : Every node has at most
4 min read
Graph Data StructureGraph Data Structure is a collection of nodes connected by edges. It's used to represent relationships between different entities. If you are looking for topic-wise list of problems on different topics like DFS, BFS, Topological Sort, Shortest Path, etc., please refer to Graph Algorithms. Basics of
3 min read
Trie Data StructureThe Trie data structure is a tree-like structure used for storing a dynamic set of strings. It allows for efficient retrieval and storage of keys, making it highly effective in handling large datasets. Trie supports operations such as insertion, search, deletion of keys, and prefix searches. In this
15+ min read
Algorithms
Searching AlgorithmsSearching algorithms are essential tools in computer science used to locate specific items within a collection of data. In this tutorial, we are mainly going to focus upon searching in an array. When we search an item in an array, there are two most common algorithms used based on the type of input
2 min read
Sorting AlgorithmsA Sorting Algorithm is used to rearrange a given array or list of elements in an order. For example, a given array [10, 20, 5, 2] becomes [2, 5, 10, 20] after sorting in increasing order and becomes [20, 10, 5, 2] after sorting in decreasing order. There exist different sorting algorithms for differ
3 min read
Introduction to RecursionThe process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly is called recursion and the corresponding function is called a recursive function. A recursive algorithm takes one step toward solution and then recursively call itself to further move. The algorithm stops once we reach the solution
14 min read
Greedy AlgorithmsGreedy algorithms are a class of algorithms that make locally optimal choices at each step with the hope of finding a global optimum solution. At every step of the algorithm, we make a choice that looks the best at the moment. To make the choice, we sometimes sort the array so that we can always get
3 min read
Graph AlgorithmsGraph is a non-linear data structure like tree data structure. The limitation of tree is, it can only represent hierarchical data. For situations where nodes or vertices are randomly connected with each other other, we use Graph. Example situations where we use graph data structure are, a social net
3 min read
Dynamic Programming or DPDynamic Programming is an algorithmic technique with the following properties.It is mainly an optimization over plain recursion. Wherever we see a recursive solution that has repeated calls for the same inputs, we can optimize it using Dynamic Programming. The idea is to simply store the results of
3 min read
Bitwise AlgorithmsBitwise algorithms in Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) involve manipulating individual bits of binary representations of numbers to perform operations efficiently. These algorithms utilize bitwise operators like AND, OR, XOR, NOT, Left Shift, and Right Shift.BasicsIntroduction to Bitwise Algorit
4 min read
Advanced
Segment TreeSegment Tree is a data structure that allows efficient querying and updating of intervals or segments of an array. It is particularly useful for problems involving range queries, such as finding the sum, minimum, maximum, or any other operation over a specific range of elements in an array. The tree
3 min read
Pattern SearchingPattern searching algorithms are essential tools in computer science and data processing. These algorithms are designed to efficiently find a particular pattern within a larger set of data. Patten SearchingImportant Pattern Searching Algorithms:Naive String Matching : A Simple Algorithm that works i
2 min read
GeometryGeometry is a branch of mathematics that studies the properties, measurements, and relationships of points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids. From basic lines and angles to complex structures, it helps us understand the world around us.Geometry for Students and BeginnersThis section covers key br
2 min read
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem