Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain in Computer Network
Last Updated :
15 Mar, 2023
Prerequisite - Network Devices, Transmission Modes
The most common network devices used are routers and switches. But we still hear people talking about hubs, repeaters, and bridges. Do you ever wonder why these former devices are preferred over the latter ones? One reason could be: 'because they are more efficient and powerful'. But what actually is the reason behind their efficiency? This is when terms like "Collision Domains" and "Broadcast Domains" come into the picture.
Before going further, let us recall that a hub is a multiple-port repeater. Similarly, a switch is a multiple-port bridge so that you can understand why repeaters and bridges are not typically used in production networks(because of less number of ports).
Now, narrowing it down to Hubs, Switches and Routers, let us discuss them in reference to the below domains.
- Collision Domain -
A Collision Domain is a scenario in which when a device sends out a message to the network, all other devices which are included in its collision domain have to pay attention to it, no matter if it was destined for them or not. This causes a problem because, in a situation where two devices send out their messages simultaneously, a collision will occur leading them to wait and re-transmit their respective messages, one at a time. Remember, it happens only in the case of a half-duplex mode. - Broadcast Domain -
A Broadcast Domain is a scenario in which when a device sends out a broadcast message, all the devices present in its broadcast domain have to pay attention to it. This creates a lot of congestion in the network, commonly called LAN congestion, which affects the bandwidth of the users present in that network.
From this, we can realize that the more the number of collision domains and the more the number of broadcast domains, the more efficient is the network providing better bandwidth to all its users.
So, which of our network devices break collision domains, and which of them break broadcast domains?
- HUB -
We start with a hub because we should get rid of it as soon as possible. The reason being, it neither breaks a collision domain nor a broadcast domain,i.e a hub is neither a collision domain separator nor a broadcast domain separator. All the devices connected to a hub are in a single collision and single broadcast domain. Remember, hubs do not segment a network, they just connect network segments. - SWITCH -
Coming to switches, we have an advantage over the hub. Every port on a switch is in a different collision domain, i.e a switch is a collision domain separator. So messages that come from devices connected to different ports never experience a collision. This helps us during designing networks but there is still a problem with switches. They never break broadcast domains, which means it is not a broadcast domain separator. All the ports on the switch are still in a single broadcast domain. If a device sends a broadcast message, it will still cause congestion. - ROUTER -
Last, but not least, we have our savior. A router not only breaks collision domains but also breaks broadcast domains, which means it is both collisions as well as broadcast domain separators. A router creates a connection between two networks. A broadcast message from one network will never reach the other one as the router will never let it pass.
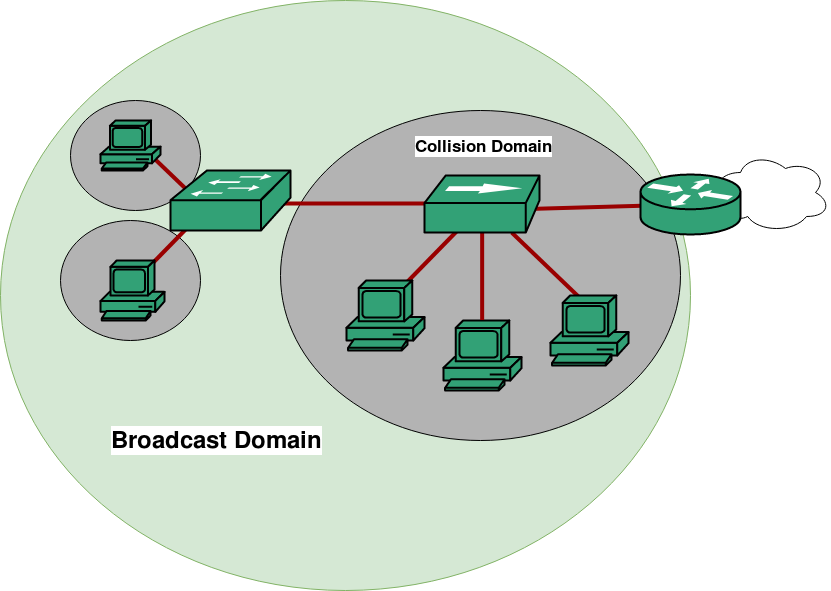
Also, as repeaters and bridges differ from hubs and switches only in terms of the number of ports, a repeater does not break collision and broadcast domains, while a bridge breaks only collision domains.
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain in Computer Network:
Advantages of Collision Domain:
High Network Performance: Collision Domain helps to improve network performance by reducing collisions on the network, which can improve data transmission and reduce packet loss.
Efficient Use of Network Resources: Collision Domain enables efficient use of network resources, such as bandwidth, by reducing the number of collisions and avoiding wastage of network resources.
Better Network Security: Collision Domain can help to improve network security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access and network attacks, which can occur due to network congestion.
Disadvantages of Collision Domain:
Limited Scalability: Collision Domain may not be scalable in larger networks, as the number of devices connected to the network increases, which can lead to network congestion and performance degradation.
Complex Network Management: Collision Domain can be complex to manage, requiring the use of protocols such as Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD), which can be difficult to configure and maintain.
Advantages of Broadcast Domain:
Efficient Network Communication: Broadcast Domain enables efficient network communication by allowing multiple devices to receive the same message simultaneously.
Simplified Network Management: Broadcast Domain can simplify network management by allowing administrators to manage network devices and policies more easily.
Improved Collaboration: Broadcast Domain can improve collaboration by enabling real-time communication and collaboration among network users.
Disadvantages of Broadcast Domain:
Increased Network Congestion: Broadcast Domain can lead to increased network congestion, particularly in larger networks, which can impact network performance and lead to packet loss.
Reduced Network Security: Broadcast Domain can reduce network security by increasing the risk of unauthorized access and network attacks, particularly in environments with a large number of devices.
References -
CCNA, Todd Lammle
Similar Reads
CCNA Tutorial for Beginners This CCNA Tutorial is well-suited for the beginner as well as professionals, and It will cover all the basic to advanced concepts of CCNA like Components of Computer Networking, Transport Layer, Network Layer, CCNA training, Cisco Networking, Network Design, Routing and Switching, etc. which are req
8 min read
Basics of Computer Networking
Components of Computer Networking
NIC Full Form - Network Interface CardNIC stands for Network Interface Card. NIC is additionally called Ethernet or physical or network card. NIC is one of the major and imperative components of associating a gadget with the network. Each gadget that must be associated with a network must have a network interface card. Even the switches
4 min read
What is a Network Switch and How Does it Work?The Switch is a network device that is used to segment the networks into different subnetworks called subnets or LAN segments. It is responsible for filtering and forwarding the packets between LAN segments based on MAC address. Switches have many ports, and when data arrives at any port, the destin
9 min read
What is Network Hub and How it Works?Hub in networking plays a vital role in data transmission and broadcasting. A hub is a hardware device used at the physical layer to connect multiple devices in the network. Hubs are widely used to connect LANs. A hub has multiple ports. Unlike a switch, a hub cannot filter the data, i.e. it cannot
6 min read
Introduction of a RouterNetwork devices are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with one another. For example Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Routers, Gateway, Router, and NIC, etc. What is a Router?A Router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer
12 min read
Types of Ethernet CableAn ethernet cable allows the user to connect their devices such as computers, mobile phones, routers, etc, to a Local Area Network (LAN) that will allow a user to have internet access, and able to communicate with each other through a wired connection. It also carries broadband signals between devic
5 min read
Transport Layer
Transport Layer responsibilitiesThe transport Layer is the second layer in the TCP/IP model and the fourth layer in the OSI model. It is an end-to-end layer used to deliver messages to a host. It is termed an end-to-end layer because it provides a point-to-point connection rather than hop-to-hop, between the source host and destin
5 min read
Introduction of Ports in ComputersA port is basically a physical docking point which is basically used to connect the external devices to the computer, or we can say that A port act as an interface between the computer and the external devices, e.g., we can connect hard drives, printers to the computer with the help of ports. Featur
3 min read
What is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)?Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a connection-oriented protocol for communications that helps in the exchange of messages between different devices over a network. It is one of the main protocols of the TCP/IP suite. In OSI model, it operates at the transport layer(Layer 4). It lies between th
5 min read
TCP 3-Way Handshake ProcessThe TCP 3-Way Handshake is a fundamental process that establishes a reliable connection between two devices over a TCP/IP network. It involves three steps: SYN (Synchronize), SYN-ACK (Synchronize-Acknowledge), and ACK (Acknowledge). During the handshake, the client and server exchange initial sequen
6 min read
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a Transport Layer protocol. UDP is a part of the Internet Protocol suite, referred to as UDP/IP suite. Unlike TCP, it is an unreliable and connectionless protocol. So, there is no need to establish a connection before data transfer. The UDP helps to establish low-late
10 min read
Network Layer
IPv4 Addressing
Subnetting
Data Link Layer
Physical Layer
Cisco Networking Devices
Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Network devices are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with each other. Network devices like hubs, repeaters, bridges, switches, routers, gateways, and brouter help manage and direct data flow in a network. They ensure efficient communication betwe
9 min read
Collision Detection in CSMA/CDCSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/ Collision Detection) is a media access control method that was widely used in Early Ethernet technology/LANs when there used to be shared Bus Topology and each node ( Computers) was connected by Coaxial Cables. Nowadays Ethernet is Full Duplex and Topology is
7 min read
Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain in Computer NetworkPrerequisite - Network Devices, Transmission Modes The most common network devices used are routers and switches. But we still hear people talking about hubs, repeaters, and bridges. Do you ever wonder why these former devices are preferred over the latter ones? One reason could be: 'because they ar
5 min read
Difference between layer-2 and layer-3 switchesA switch is a device that sends a data packet to a local network. What is the advantage of a hub? A hub floods the network with the packet and only the destination system receives that packet while others just drop due to which the traffic increases a lot. To solve this problem switch came into the
5 min read