C# Decision Making (if, if-else, if-else-if ladder, nested if, switch, nested switch)
Last Updated :
13 Jan, 2025
Decision Making in programming is similar to decision making in real life. In programming too, a certain block of code needs to be executed when some condition is fulfilled.
A programming language uses control statements to control the flow of execution of program based on certain conditions. These are used to cause the flow of execution to advance and branch based on changes to the state of a program.
Conditional Statements of C#
There are few conditional statements of C# is mentioned below:
- if
- if-else
- if-else-if
- Nested if
- Switch
- Nested Switch
1. If Statement
The if statement checks the given condition. If the condition evaluates to be true then the block of code/statements will execute otherwise not.
Syntax:
if ( condition ) {
//code to be executed
}
Note: If the curly brackets { } are not used with if statements then the statement just next to it is only considered associated with the if statement.
Flowchart:
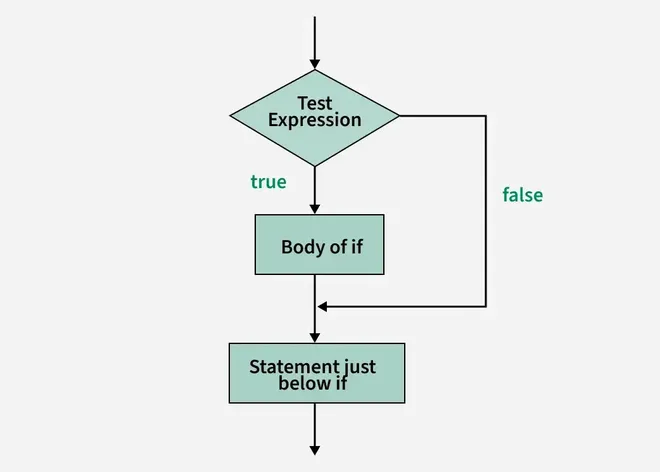
Example:
C#
// Using if statement
using System;
public class Geeks
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string name = "Geek";
// Using if statement
if (name == "Geek") {
Console.WriteLine("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
2. If-else Statement
The if statement evaluates the code if the condition is true but what if the condition is not true, here comes the else statement. It tells the code what to do when the if condition is false.
Syntax:
if(condition)
{
// code if condition is true
}
else
{
// code if condition is false
}
Flowchart:

Example:
C#
// Using if-else statement
using System;
public class Geeks
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string name = "Geek";
// Using if-else statement
if (name == "Geeks") {
Console.WriteLine("GeeksForGeeksr");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("Geeks");
}
}
}
3. If-else-if ladder Statement
The if-else-if ladder statement executes one condition from multiple statements. The execution starts from top and checked for each if condition. The statement of if block will be executed which evaluates to be true. If none of the if condition evaluates to be true then the last else block is evaluated.
Syntax:
if(condition1)
{
// code to be executed if condition1 is true
}
else if(condition2)
{
// code to be executed if condition2 is true
}
else if(condition3)
{
// code to be executed if condition3 is true
}
...
else
{
// code to be executed if all the conditions are false
}
Flowchart:

Example:
C#
// Using if-else-if ladder
using System;
class Geeks
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int i = 20;
// Using If-else-if ladder
if (i == 10)
Console.WriteLine("i is 10");
else if (i == 15)
Console.WriteLine("i is 15");
else if (i == 20)
Console.WriteLine("i is 20");
else
Console.WriteLine("i is not present");
}
}
4. Nested - If Statement
If statement inside an if statement is known as nested if. if statement in this case is the target of another if or else statement. When more than one condition needs to be true and one of the condition is the sub-condition of parent condition, nested if can be used.
Syntax:
if (condition1)
{
// code to be executed
// if condition2 is true
if (condition2)
{
// code to be executed
// if condition2 is true
}
}
Flowchart:

Example:
C#
// Using Nested-if statement
using System;
class Geeks
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int i = 10;
if (i == 10) {
// nested - if statement
// will only be executed if statement
// above it is true
if (i < 12)
Console.WriteLine("i is smaller than 12 too");
else
Console.WriteLine("i is greater than 15");
}
}
}
Outputi is smaller than 12 too
5. Switch Statement
Switch statement is an alternative to long if-else-if ladders. The expression is checked for different cases and the one match is executed. break statement is used to move out of the switch. If the break is not used, the control will flow to all cases below it until break is found or switch comes to an end. There is default case (optional) at the end of switch, if none of the case matches then default case is executed.
Syntax:
switch (expression)
{
case value1: // statement sequence
break;
case value2: // statement sequence
break;
.
.
.
case valueN: // statement sequence
break;
default: // default statement sequence
}
Flowchart:
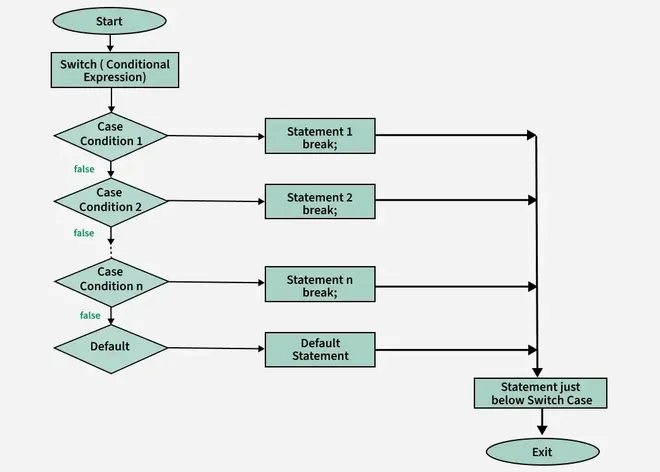
Example:
C#
// Using Switch case
using System;
public class Geeks
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int number = 30;
// Using Switch case
switch(number)
{
case 10:
Console.WriteLine("case 10");
break;
case 20:
Console.WriteLine("case 20");
break;
case 30:
Console.WriteLine("case 30");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("None matches");
break;
}
}
}
6. Nested Switch
Nested Switch case are allowed in C# . In this case, switch is present inside other switch case. Inner switch is present in one of the cases in parent switch.
Example:
C#
// Using nested switch case
using System;
public class Geeks
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int outter = 2;
int inner = 3;
// Using Nested Switch Case
switch(outter){
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Outter Case 1");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Outter Case 2");
switch(inner)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Inner Case 1");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Inner Case 2");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("Inner Case 3");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Default Inner Run");
break;
}
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Default Outter Run");
break;
}
}
}
OutputOutter Case 2
Inner Case 3
Similar Reads
Introduction
C# TutorialC# (pronounced "C-sharp") is a modern, versatile, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft in 2000 that runs on the .NET Framework. Whether you're creating Windows applications, diving into Unity game development, or working on enterprise solutions, C# is one of the top choices fo
4 min read
Introduction to .NET FrameworkThe .NET Framework is a software development framework developed by Microsoft that provides a runtime environment and a set of libraries and tools for building and running applications on Windows operating systems. The .NET framework is primarily used on Windows, while .NET Core (which evolved into
6 min read
C# .NET Framework (Basic Architecture and Component Stack)C# (C-Sharp) is a modern, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft in 2000. It is a part of the .NET ecosystem and is widely used for building desktop, web, mobile, cloud, and enterprise applications. This is originally tied to the .NET Framework, C# has evolved to be the primary
6 min read
C# Hello WorldThe Hello World Program is the most basic program when we dive into a new programming language. This simply prints "Hello World!" on the console. In C#, a basic program consists of the following:A Namespace DeclarationClass Declaration & DefinitionClass Members(like variables, methods, etc.)Main
4 min read
Common Language Runtime (CLR) in C#The Common Language Runtime (CLR) is a component of the Microsoft .NET Framework that manages the execution of .NET applications. It is responsible for loading and executing the code written in various .NET programming languages, including C#, VB.NET, F#, and others.When a C# program is compiled, th
4 min read
Fundamentals
C# IdentifiersIn programming languages, identifiers are used for identification purposes. Or in other words, identifiers are the user-defined name of the program components. In C#, an identifier can be a class name, method name, variable name, or label. Example: public class GFG { static public void Main () { int
2 min read
C# Data TypesData types specify the type of data that a valid C# variable can hold. C# is a strongly typed programming language because in C# each type of data (such as integer, character, float, and so forth) is predefined as part of the programming language and all constants or variables defined for a given pr
7 min read
C# VariablesIn C#, variables are containers used to store data values during program execution. So basically, a Variable is a placeholder of the information which can be changed at runtime. And variables allows to Retrieve and Manipulate the stored information. In Brief Defination: When a user enters a new valu
4 min read
C# LiteralsIn C#, a literal is a fixed value used in a program. These values are directly written into the code and can be used by variables. A literal can be an integer, floating-point number, string, character, boolean, or even null. Example:// Here 100 is a constant/literal.int x = 100; Types of Literals in
5 min read
C# OperatorsIn C#, Operators are special types of symbols which perform operations on variables or values. It is a fundamental part of language which plays an important role in performing different mathematical operations. It takes one or more operands and performs operations to produce a result.Types of Operat
7 min read
C# KeywordsKeywords or Reserved words are the words in a language that are used for some internal process or represent some predefined actions. These words are therefore not allowed to be used as variable names or objects. Doing this will result in a compile-time error.Example:C#// C# Program to illustrate the
5 min read
Control Statements
C# Decision Making (if, if-else, if-else-if ladder, nested if, switch, nested switch)Decision Making in programming is similar to decision making in real life. In programming too, a certain block of code needs to be executed when some condition is fulfilled. A programming language uses control statements to control the flow of execution of program based on certain conditions. These
5 min read
C# Switch StatementIn C#, Switch statement is a multiway branch statement. It provides an efficient way to transfer the execution to different parts of a code based on the value of the expression. The switch expression is of integer type such as int, char, byte, or short, or of an enumeration type, or of string type.
4 min read
C# LoopsLooping in a programming language is a way to execute a statement or a set of statements multiple times, depending on the result of the condition to be evaluated to execute statements. The result condition should be true to execute statements within loops.Types of Loops in C#Loops are mainly divided
4 min read
C# Jump Statements (Break, Continue, Goto, Return and Throw)In C#, Jump statements are used to transfer control from one point to another point in the program due to some specified code while executing the program. In, this article, we will learn to different jump statements available to work in C#.Types of Jump StatementsThere are mainly five keywords in th
4 min read
OOP Concepts
Methods
Arrays
C# ArraysAn array is a group of like-typed variables that are referred to by a common name. And each data item is called an element of the array. The data types of the elements may be any valid data type like char, int, float, etc. and the elements are stored in a contiguous location. Length of the array spe
8 min read
C# Jagged ArraysA jagged array is an array of arrays, where each element in the main array can have a different length. In simpler terms, a jagged array is an array whose elements are themselves arrays. These inner arrays can have different lengths. Can also be mixed with multidimensional arrays. The number of rows
4 min read
C# Array ClassArray class in C# is part of the System namespace and provides methods for creating, searching, and sorting arrays. The Array class is not part of the System.Collections namespace, but it is still considered as a collection because it is based on the IList interface. The Array class is the base clas
7 min read
How to Sort an Array in C# | Array.Sort() Method Set - 1Array.Sort Method in C# is used to sort elements in a one-dimensional array. There are 17 methods in the overload list of this method as follows:Sort<T>(T[]) MethodSort<T>(T[], IComparer<T>) MethodSort<T>(T[], Int32, Int32) MethodSort<T>(T[], Comparison<T>) Method
8 min read
How to find the rank of an array in C#Array.Rank Property is used to get the rank of the Array. Rank is the number of dimensions of an array. For example, 1-D array returns 1, a 2-D array returns 2, and so on. Syntax: public int Rank { get; } Property Value: It returns the rank (number of dimensions) of the Array of type System.Int32. B
2 min read
ArrayList
String
Tuple
Indexers