Epoxy Library using DataBinding in Android
Last Updated :
25 May, 2025
Epoxy is an Android library developed by Airbnb for building complex RecyclerViews with ease. It allows a flexible, easy to use approach to creating lists, improving the process of creating and managing complex, dynamic UI components. Epoxy enables the building of RecyclerView layouts in a declarative style, giving developers the ability to manage various data types and UI elements more efficiently. Instead of dealing with custom ViewHolders, adapters, and layouts manually, Epoxy abstracts the entire workflow and simplifies much of this work.
Epoxy leverages model-based UI development (where each view in the UI is treated as a model object) to allow developers to create efficient, reusable, and maintainable UI components. In this article, we will know about how to implement the Epoxy with DataBinding.
Refer to the previous to know more about EpoxyModels and EpoxyController: Epoxy RecyclerView Library in Android
Advantages of Epoxy
The Epoxy library has several advantages that makes it more preferable for production:
- Epoxy has a clean separation of concerns by using individual view models for each UI component.
- Epoxy creates an abstraction layer for much of the work related with RecyclerView Adapters and ViewHolder which decreases a lot of the boilerplate and repetitive code.
- Epoxy handles UI updated most efficiently making it easier to dynamically update lists without recycling views.
- With Epoxy, developers can define UI components declaratively, which leads to cleaner and more maintainable code.
What are Epoxy Groups?
Epoxy Groups are a feature that allows you to group related items within an EpoxyController. This concept allows developers to organize lists into sections or categories, making it easier to handle complex layouts. Groups are often used to display categorized data or distinct sections in a RecyclerView. For example, if you are building a list, you could group three textviews, with an ImageView. The groups allow you to visually separate data for a cleaner and more structured UI.
Step by Step Implementation
Step 1: Add dependency for Epoxy and DataBinding Support
Navigate to Gradle Scripts > build.gradle.kts and add the following code under the android{} scope for DataBinding support:
android {
...
buildFeatures {
dataBinding=true
}
}Add kapt plugin under the plugins() scope
plugins {
...
id("kotlin-kapt")
}Add the dependencies for Epoxy under the dependencies{} scope
dependencies {
...
implementation("com.airbnb.android:epoxy:5.1.4")
implementation("com.airbnb.android:epoxy-databinding:5.1.4")
implementation("com.airbnb.android:epoxy-annotations:5.1.4")
kapt("com.airbnb.android:epoxy-processor:5.1.4")
//Glide - optional (for image loading)
implementation("com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.16.0")
}Check for the updated version of the epoxy library from here.
Also, add the following code at the end of the file separately
kapt {
correctErrorTypes = true
}
Step 2: Create a model using data class
Navigate to app > kotlin+java > {package-name}, right click on the folder and select, New > Kotlin Class/File and name the file User.kt. This file will contain a data class that will be used to store user data as a reference. Now, add the below code to the file.
User.kt:
Kotlin
package org.geeksforgeeks.demo.model
data class User(
var imageUrl:String,
var name:String,
var email:String,
var phone:String
)
Step 3: Create Epoxy Model
Epoxy allows you to create "models" that define the views in your RecyclerView. You can use the @EpoxyModelClass annotation to define a model. Since we are using DataBinding, we will also use the @EpoxyAttribute annotation to bind data to the views.
Create a Kotlin file with the name EpoxyModel.kt and create two Epoxy models, each for a Text and Image as shown below.
EpoxyModel.kt:
Kotlin
package org.geeksforgeeks.demo.epoxy
import androidx.databinding.ViewDataBinding
import com.airbnb.epoxy.DataBindingEpoxyModel
import com.airbnb.epoxy.EpoxyAttribute
import com.airbnb.epoxy.EpoxyModelClass
import org.geeksforgeeks.demo.R
import org.geeksforgeeks.demo.BR
// Epoxy model for binding text data to a layout using DataBinding
@EpoxyModelClass
abstract class ItemTextModel : DataBindingEpoxyModel() {
// Attribute to be set in the Epoxy controller
@EpoxyAttribute
lateinit var textdata: String
// Specifies the layout resource to use
override fun getDefaultLayout(): Int {
return R.layout.user_info
}
// Binds the textdata to the variable 'element' in the layout
override fun setDataBindingVariables(binding: ViewDataBinding?) {
binding?.setVariable(BR.element, textdata)
}
}
// Epoxy model for binding image data (as String URL or resource name) to a layout
@EpoxyModelClass
abstract class ItemImageModel : DataBindingEpoxyModel() {
// Attribute to be set in the Epoxy controller
@EpoxyAttribute
var image: String = ""
// Specifies the layout resource to use
override fun getDefaultLayout(): Int {
return R.layout.user_essential
}
// Binds the image string to the variable 'elementImage' in the layout
override fun setDataBindingVariables(binding: ViewDataBinding?) {
binding?.setVariable(BR.elementImage, image)
}
}
Step 4: Setup layouts for each Epoxy Models
Now, let's create the layouts we have defined in the EpoxyModels. Navigate to app > res > layout, right click on the folder and select, New > Layout Resource File and name the files as user_essential.xml and user_info.xml. Add the following code to the files.
user_info.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable
name="element"
type="String" />
</data>
<LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{element}"
android:paddingHorizontal="8dp"
android:paddingVertical="4dp"
tools:text="Email: [email protected]"/>
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable
name="elementImage"
type="String" />
</data>
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/user_essential"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
imageUrl="@{elementImage}"
tools:src="@tools:sample/avatars"/>
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
Step 5: Create a Data Binding Adapter
Create a Kotlin file with the name EpoxyBinding.kt and add the following code to the file. This code defines a Data Binding Adapter that allows you to easily load images into an ImageView using the Glide image loading library directly from your layout XML files.
EpoxyBinding.kt:
Kotlin
package org.geeksforgeeks.demo.epoxy
import android.widget.ImageView
import androidx.databinding.BindingAdapter
import com.bumptech.glide.Glide
@BindingAdapter("imageUrl")
fun imageUrl(imageView: ImageView, imageUrl: String?) {
imageUrl?.let {
Glide.with(imageView.context)
.load(imageUrl)
.into(imageView)
}
}
Step 6: Create an EpoxyController
The EpoxyController is responsible for managing the data and controlling the Epoxy models. You can subclass EpoxyController and define how the items are displayed. In this controller:
- The variable data, holds a list of User objects.
- The buildModels() method is overridden to create the Epoxy models and bind them to the data.
- ItemImageModel_() is a DSL (domain-specific language) that creates the model and binds the data.
We have also introduced groups in this file, that groups views based upon your choice. Now, create a Koltin with the name EpoxyController.kt and add the following code to it.
EpoxyController.kt:
Kotlin
package org.geeksforgeeks.demo.epoxy
import com.airbnb.epoxy.TypedEpoxyController
import com.airbnb.epoxy.group
import org.geeksforgeeks.demo.R
import org.geeksforgeeks.demo.model.User
class EpoxyController : TypedEpoxyController<List<User>>() {
override fun buildModels(data: List<User>?) {
data?.forEach { user ->
group {
id("group_${user.phone}")
layout(R.layout.group_container)
add(
ItemImageModel_()
.id("image_${user.imageUrl}")
.image(user.imageUrl)
)
group {
id("nested_group_${user.phone}")
layout(R.layout.nested_container)
add(
ItemTextModel_()
.id("name_${user.name}")
.textdata(user.name)
)
add(
ItemTextModel_()
.id("email_${user.email}")
.textdata("Email: ${user.email}")
)
add(
ItemTextModel_()
.id("phone_${user.phone}")
.textdata("Phone Number: ${user.phone}")
)
}
}
}
}
}
Step 7: Setup layouts for displaying data through the EpoxyController
Now, let's create the layouts we have defined in the EpoxyController. Navigate to app > res > layout, right click on the folder and select, New > Layout Resource File and name the files as group_container.xml and nested_container.xml. Add the following code to the files.
group_container.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingVertical="8dp"
android:orientation="horizontal" />
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" />
Step 8: Working with MainActivity.kt
Navigate to the MainActivity.kt file and setup the EpoxyRecyclerView by populating it with data as shown below. Given below are the code for MainActivity.kt and corresponding layout file activity_main.xml.
MainActivity.kt
package org.geeksforgeeks.demo
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager
import org.geeksforgeeks.demo.epoxy.EpoxyController
import org.geeksforgeeks.demo.model.User
import org.geeksforgeeks.demo.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
private val epoxyController = EpoxyController()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// Inflate view binding
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
// Sample user data
val user = listOf(
User(
imageUrl = "https://picsum.photos/200",
name = "John Doe",
email = "[email protected]",
phone = "+1 234 567 890"
),
User(
imageUrl = "https://picsum.photos/201",
name = "Jane Smith",
email = "[email protected]",
phone = "+1 234 567 891")
)
// Setup RecyclerView and pass data to EpoxyController
setupRecyclerView()
epoxyController.setData(user)
}
// Configures RecyclerView with Epoxy controller
private fun setupRecyclerView() {
epoxyController.setFilterDuplicates(true)
binding.recyclerView.apply {
adapter = epoxyController.adapter
layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this@MainActivity)
setHasFixedSize(true)
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.airbnb.epoxy.EpoxyRecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:clipToPadding="false"
android:padding="8dp"
android:overScrollMode="never"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>
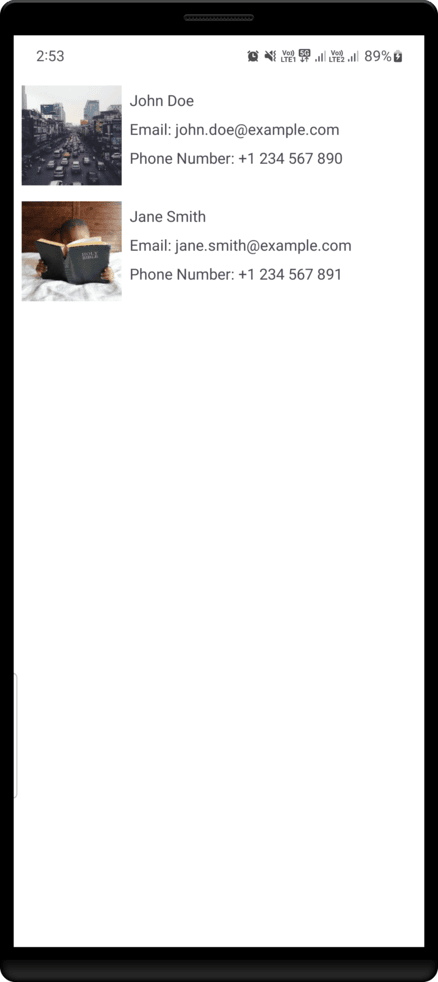
Output: