java.lang.Boolean class methods
Last Updated :
19 Apr, 2022
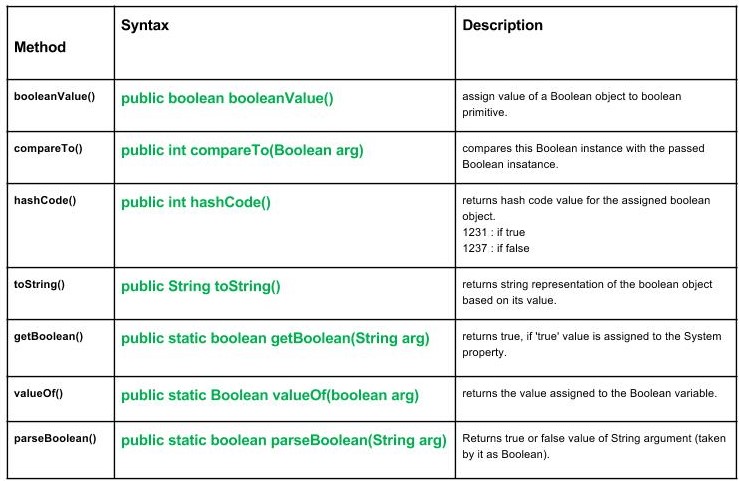 Boolean class methods.
Boolean class methods.
About :
java.lang.Boolean class wraps primitive type boolean value in an object.
Class Declaration
public final class Boolean
extends Object
implements Serializable, Comparable
Constructors :
Boolean(boolean val) : Assigning Boolean object representing the val argument.
Boolean(String str) : Assigning Boolean object representing the value true or false
according to the string.
Methods :
- booleanValue() : java.lang.Boolean.booleanValue() is used to assign value of a Boolean object to boolean primitive.
Syntax :
public boolean booleanValue()
Returns :
primitive boolean value of the boolean object.
- compareTo() : java.lang.Boolean.compareTo(Boolean arg) compares this Boolean instance with the passed Boolean instance.
Syntax :
public int compareTo(Boolean arg)
Parameter :
arg : boolean instance to be compared with this instance.
Returns :
0 : if this instance = argumented instance.
+ve value : if this instance > argumented instance.
-ve value : if this instance < argumented instance.
- hashCode() : java.lang.Boolean.hashCode() returns hash code value for the assigned boolean object.
Syntax :
public int hashCode()
Returns :
1231 : if the boolean value of object is true.
1237 : if the boolean value of object is false.
- toString() : java.lang.Boolean.toString() returns string representation of the boolean object based on its value.
Syntax :
public String toString()
Returns :
string value - 'true' if boolean object is true, else false.
Implementation:
Java
// Java program illustrating Boolean class methods
// booleanValue(), compareTo(), hashCode(), toString()
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a boolean object and assigning value to it.
Boolean bool1 = new Boolean(true);
Boolean bool2 = new Boolean(false);
System.out.println("Boolean object - bool1 : "+bool1);
System.out.println("Boolean object - bool2 : "+bool2);
// Creating a boolean primitive bool2
boolean bool3, bool4 ;
// Use of booleanValue()
// Assigning object value to primitive variable.
bool3 = bool1.booleanValue();
System.out.println("Primitive value of object i.e. bool3 : "+bool3);
bool4 = bool2.booleanValue();
System.out.println("Primitive value of object i.e. bool4 : "+bool4);
System.out.println("");
// Comparing two boolean instances bool1 and bool2
// Use of compareTo() method
int comp = bool1.compareTo(bool2);
if (comp > 0)
System.out.println("bool1 is greater than bool2 as comp = "+comp);
if (comp == 0)
System.out.println("bool1 is equal to bool2 as comp = "+comp);
if (comp < 0)
System.out.println("bool1 is less than bool2 as comp = "+comp);
System.out.println("");
// HashCode value of the boolean object.
// use of hashCode() method
int h1 = bool1.hashCode();
int h2 = bool2.hashCode();
System.out.println("Hash Code value of bool1 : " + h1);
System.out.println("Hash Code value of bool2 : " + h2);
System.out.println("");
// String representation of the boolean object
// Use of toString() method.
String s1, s2;
s1 = bool1.toString();
s2 = bool2.toString();
System.out.println("String value of bool1 : " + s1);
System.out.println("String value of bool2 : " + s2);
}
}
Output:
Boolean object - bool1 : true
Boolean object - bool2 : false
Primitive value of object i.e. bool3 : true
Primitive value of object i.e. bool4 : false
bool1 is greater than bool2 as comp = 1
Hash Code value of bool1 : 1231
Hash Code value of bool2 : 1237
String value of bool1 : true
String value of bool2 : false
- getBoolean() : java.lang.Boolean.getBoolean(String arg) returns true, if 'true' value is assigned to the System property.
To assign any value to the property, we are using setProperty() method of System class.
Syntax :
public static boolean getBoolean(String arg)
Parameters :
arg - name of the property
Returns :
true : if 'true' value is assigned to the System property.
false : if no such property exists or if exists then no value is assigned to it.
Implementation:
Java
// Java program illustrating getBoolean() method
import java.lang.*; // Using Boolean and System classes
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Use of getBoolean() to check whether
any value is assigned to Property - p1, p2 or not */
boolean b1 = Boolean.getBoolean("p1");
boolean b2 = Boolean.getBoolean("p2");
System.out.println("Bool Value of p1 : "+b1);
System.out.println("Bool Value of p2 : "+b2);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Since, no value assigned to p1, p2, Bool value is false");
System.out.println("Assign value to p1,p2 using java.lang.System.setProperty()");
System.out.println("");
System.setProperty("p1","true");
System.setProperty("p2","Cool");
boolean b3 = Boolean.getBoolean("p1");
boolean b4 = Boolean.getBoolean("p2");
System.out.println("Bool Value of p1 : " + b3);
System.out.println("Bool Value of p2 : " + b4);
}
}
Output:
Bool Value of p1 : false
Bool Value of p2 : false
Since, no value assigned to p1, p2, Bool value is false
Assign value to p1,p2 using java.lang.System.setProperty()
Bool Value of p1 : true
Bool Value of p2 : false
- valueOf() : java.java.lang.Boolean.valueOf(boolean arg) returns the value assigned to the Boolean variable.
If true value is assigned then true is returned else, false.
To assign any value to the property, we are using setProperty() method of System class.
Syntax :
public static Boolean valueOf(boolean arg)
Parameters :
arg - boolean variable
Returns :
True : if true value is assigned to the boolean variable, else false
- parseBoolean() : java.lang.Boolean.parseBoolean(String s) returns true or false value of String argument(taken by it as Boolean).
It is case insensitive method.
Syntax :
public static boolean parseBoolean(String arg)
Parameters :
arg - String argument taken as Boolean
Returns :
Boolean value of a String argument
Implementation:
Java
// Java program illustrating parseBoolean() and valueOf() method
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean b1 = false;
boolean b2 = true;
// Use of valueOf() method
boolean val1 = Boolean.valueOf(b1);
boolean val2 = Boolean.valueOf(b2);
System.out.println("Value of b1 : "+ val1);
System.out.println("Value of b2 : " +val2);
System.out.println("");
// Use of parseBoolean() method
String st1, st2, st3;
st1 = "True";
st2 = "yes";
st3 = "true"; // Case insensitive
boolean p1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(st1);
boolean p2 = Boolean.parseBoolean(st2);
boolean p3 = Boolean.parseBoolean(st3);
System.out.println("Value of String st1 as Boolean : "+p1);
System.out.println("Value of String st2 as Boolean : "+p2);
System.out.println("Value of String st3 as Boolean : "+p3);
}
}
Output:
Value of b1 : false
Value of b2 : true
Value of String st1 as Boolean : true
Value of String st2 as Boolean : false
Value of String st3 as Boolean : true
Similar Reads
Java.lang.Boolean Class in Java
Java provides a wrapper class Boolean in java.lang package. The Boolean class wraps a value of the primitive type boolean in an object. An object of type Boolean contains a single field, whose type is boolean. In addition, this class provides useful methods like to convert a boolean to a String and
7 min read
Booleans Class | Guava | Java
Booleans is a utility class for primitive type Boolean. It provides Static utility methods pertaining to boolean primitives, that are not already found in either Boolean or Arrays. Declaration : @GwtCompatible(emulated=true) public final class Booleans extends Object Below given are some methods pro
3 min read
Boolean toString() Method in Java
In Java, the toString() method of the Boolean class is a built-in method to return the Boolean value in string format. The Boolean class is a part of java.lang package. This method is useful when we want the output in the string format in places like text fields, console output, or simple text forma
2 min read
java.lang.MethodType Class in Java
MethodType is a Class that belongs to java.lang package. This class consists of various types of methods that help in most of cases to find the method type based on the input object, or parameters of the method. All the instances of methodType are immutable. This means the objects of the methodType
4 min read
java.math class and its methods | Set 1
Math class provides mathematical functions to perform basic numeric operations such as exponential, logarithm, square root, and trigonometric functions. cosh, sin, tan, abs, bitLength, multiply and many more. Implementations of the functions of Math class do not return bit-for-bit same results. Henc
4 min read
Array getBoolean() Method in Java
The java.lang.reflect.Array.getBoolean() returns the given index from the specified Array as a short. Syntax: Array.getBoolean(Object []array,int index) Parameters: array: The object array whose index is to be returned. index: The particular index of the given array. The element at 'index' in the gi
3 min read
Java.lang.Class class in Java | Set 1
Java provides a class with name Class in java.lang package. Instances of the class Class represent classes and interfaces in a running Java application. The primitive Java types (boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, and double), and the keyword void are also represented as Class objects. It
15+ min read
java.lang.reflect.Method Class in Java
java.lang.reflect.Method class provides necessary details about one method on a certain category or interface and provides access for the same. The reflected method could also be a category method or an instance method (including an abstract method). This class allows broadening of conversions to oc
3 min read
Java HashSet contains() Method
The contains() method of the HashSet class in Java is used to check if a specific element is present in the HashSet or not. So, mainly it is used to check if a set contains any particular element.Java// Java program to demonstrates the working of contains() import java.util.*; public class Geeks { p
1 min read
Boolean equals() method in Java with examples
The equals() method of Boolean class is a built in method of Java which is used check equality of two Boolean object. Syntax: BooleanObject.equals(Object ob) Parameter: It take a parameter ob of type Object as input which is the instance to be compared. Return Type: The return type is boolean. It re
2 min read