Cortisol is a steroid hormone that your adrenal glands (the glands on top of your kidneys) make. Cortisol affects several aspects of your health and helps regulate your body’s response to stress. High or low levels of cortisol can impact your health.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Advertisement
Advertisement
Cortisol is a hormone your adrenal glands make and release. It’s a glucocorticoid, a type of steroid hormone.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You may mainly think of cortisol when it comes to stress. But it’s an essential hormone that affects almost every organ and tissue in your body. It plays many other important roles, including:
Your body continuously monitors your cortisol levels to maintain steady levels (homeostasis). High or low cortisol levels can be harmful to your health.
Yes, cortisol plays a key role in managing your body’s stress response. Your body releases cortisol when you experience any of the following types of stress:
But cortisol has many other functions, too.
Cortisol affects nearly every organ system in your body. And it helps regulate several key functions.
During times of stress, your body can release cortisol after releasing its “fight or flight” hormones, like adrenaline. This happens so you continue to stay on high alert. Cortisol also triggers the release of glucose (sugar) from your liver. This provides fast energy during times of stress.
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes in your body that allow you to live and function. Thousands of metabolic processes happen at all times.
Advertisement
Cortisol affects your metabolism by helping regulate how your body uses glucose (sugar) for energy. The hormone does this in many ways. For example, cortisol triggers your pancreas to decrease insulin and increase glucagon. Insulin lowers blood glucose (sugar). Glucagon raises it.
Cortisol also acts on other bodily tissues to manage glucose use, including your:
In short spurts, cortisol can boost your immunity by limiting inflammation. But if you have consistently high levels of cortisol, your body can get used to it. This can lead to inflammation and a weakened immune system.
The exact way in which cortisol regulates blood pressure in humans is unclear. But elevated levels of cortisol can cause high blood pressure. And lower-than-normal levels of cortisol can cause low blood pressure.
Most people have lower cortisol levels in the evening when they go to sleep. And they have peak levels in the morning right before they wake up. This suggests that cortisol plays a key role in your circadian rhythm and how your body wakes up.
Your body has an elaborate system to regulate your cortisol levels. Your hypothalamus and pituitary gland control the cortisol production in your adrenal glands. The process goes like this:
To have healthy cortisol levels, your hypothalamus, pituitary gland and adrenal glands must all be functioning properly.
If you have high levels of cortisol (hypercortisolism) for a long time, it’s usually Cushing syndrome. Causes of high cortisol levels and Cushing syndrome include:
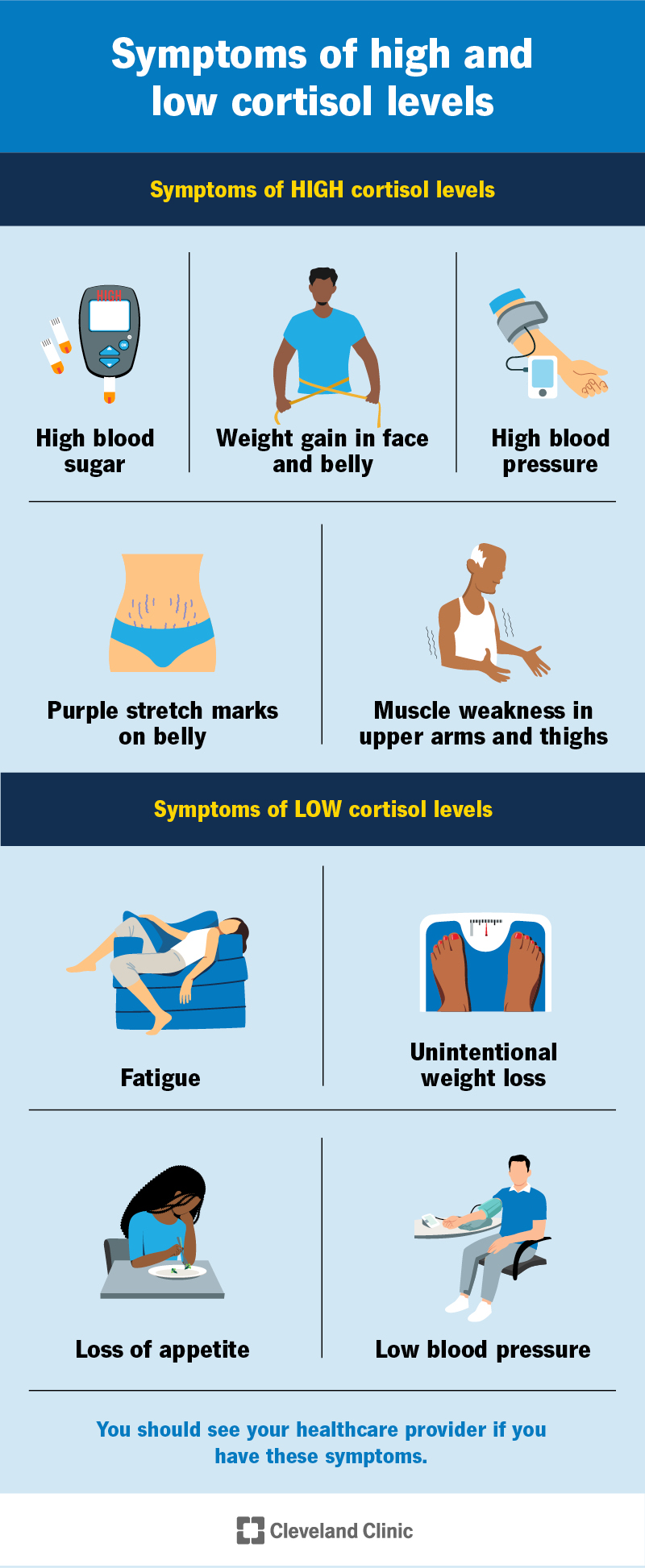
Symptoms of high cortisol levels, or Cushing syndrome, can include:
Healthcare providers call lower-than-normal cortisol levels (hypocortisolism) adrenal insufficiency. There are two types of adrenal insufficiency: primary and secondary.
Advertisement
Primary adrenal insufficiency most often happens when your immune system attacks your adrenal glands. It’s called Addison’s disease. An infection or blood loss to the tissue in your adrenal glands can also lead to a lack of cortisol.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency happens if you have an underactive pituitary gland (hypopituitarism) or a pituitary tumor. These conditions can limit ACTH production, which limits cortisol production. You can also develop low cortisol levels after suddenly stopping treatment with corticosteroids.
Symptoms of low cortisol levels, or adrenal insufficiency, can include:
If you have symptoms of Cushing syndrome or adrenal insufficiency, contact your healthcare provider.
If you’re concerned about your daily stress levels, talk to your provider about steps you can take to manage stress.
If you have Cushing syndrome, you’ll need medical treatment to lower your cortisol levels. Treatment usually involves medication and/or surgery.
In general, though, there are several ways to help lower your cortisol levels, including:
Advertisement
Cortisol often gets a bad rap. But it’s an essential hormone that impacts several aspects of your body. Many stress-relieving strategies can help manage your cortisol levels. But in some cases, having abnormally high or low levels of cortisol is out of your control. If you experience symptoms of high or low cortisol levels, it’s important to see your healthcare provider. They can run some simple tests to see if your adrenal glands or pituitary gland is responsible for your symptoms.
Advertisement
Last reviewed on 02/17/2025.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.